
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 37(4); 2013 > Article
-
Original ArticleComplications Diabetic Retinopathy and Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jae-Seung Yun1, Seung-Hyun Ko1, Ji-Hoon Kim2, Kun-Woong Moon2, Yong-Moon Park3,4, Ki-Dong Yoo2, Yu-Bae Ahn1
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2013;37(4):262-269.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.262
Published online: August 14, 2013
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
3Department of Preventive Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
4Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Arnold School of Public health, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA.
- Corresponding author: Yu-Bae Ahn. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, 93 Jungbu-daero, Paldal-gu, Suwon 442-723, Korea. ybahn@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2013 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- We investigated the relationship between endothelial dysfunction and diabetic retinopathy (DR) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Methods
- We used a cross-sectional design to examine 167 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. All patients underwent biochemical and ophthalmological examination. We assessed endothelial dysfunction by a flow-mediated vasodilation method of the brachial artery. Changes in vasodilation (flow-mediated vasodilatation, %FMD) were expressed as percent change over baseline values.
-
Results
- The mean±standard deviation of patient age was 54.1±8.6 years. The %FMD was significantly lower in patients with DR than without DR. The prevalence of retinopathy decreased across increasing tertiles of %FMD. After adjusting for patients' age, sex, diabetes duration, use of insulin, use of antihypertensive, antiplatelet, and lipid lowering medications, systolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and urinary albumin excretion, participants with a reduced %FMD were more likely to have DR (odds ratio, 11.819; 95% confidence interval, 2.201 to 63.461; P=0.004, comparing the lowest and highest tertiles of %FMD).
-
Conclusion
- Endothelial dysfunction was associated with DR, which was most apparent when the endothelial dysfunction was severe. Our study provides insights into the possible mechanism of the influence of endothelial dysfunction on the development of DR.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is becoming increasingly prevalent worldwide. Morbidity and mortality of T2DM are caused primarily by vascular complications: microangiopathy and macroangiopathy. Therefore, in addition to strict glycemic control, regular screenings and early detection of diabetic vascular complications are essential for reducing the morbidity and mortality of patients with type 2 diabetes.
- In addition to conventional cardiovascular risk factors, endothelial dysfunction is important in the early pathophysiology of vascular complications [1]. Beyond its role as simply a passive barrier for blood vessels, the endothelium has important physiological functions that are mediated by the release of vasoactive factors responsible for regulating vessel wall tone, cellular growth, homeostasis, and inflammation. Broadly speaking, the term endothelial dysfunction refers to an impairment of the ability of the endothelium to properly maintain vascular homeostasis, and it may be an important determinant of altered vascular reactivity [2]. Arguably, the most critical mediator of endothelium-derived molecules is nitric oxide (NO) [3], and the earliest and most important marker of endothelial dysfunction is represented by a reduction in NO bioactivity. The most widely-used technique for assessing systemic endothelial function is called "flow-mediated vasodilatation" (FMD). This noninvasive method is based on the principle that physiological increases in blood flow and endothelial shear stress induce vasodilatation, which are mainly mediated by an increased endothelial NO release. FMD is known to be endothelium-dependent and gives a reliable measure of endothelial function in peripheral arteries [4].
- Endothelial dysfunction is considered the first step in the progression of accelerated atherosclerosis [5]. In addition to the relationship with macrovascular complications [6-9], endothelial dysfunction also has been associated with the development of microalbuminuria [10], which itself is strongly connected with retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes [11]. This finding suggests that endothelial dysfunction might affect the development of diabetic microvascular complications. However, relatively few studies have examined the relationship between endothelial function and diabetic retinopathy (DR), and varying conclusions between studies have made the relationship even more ambiguous [12-14].
- The purpose of this study was to investigate and clarify the association between the presence of DR and endothelial dysfunction as measured by FMD in type 2 diabetic patients.
INTRODUCTION
- Participants
- In the current study, 214 subjects with type 2 diabetes aged 25 to 75 years were recruited between March 2010 and March 2011 from the university-affiliated diabetes center at St. Vincent's Hospital in South Korea. A detailed questionnaire was used to obtain participant information, including medical history, current cigarette smoking status and the use of antihypertensive, antiplatelet, and lipid-lowering medications. The patients' height and weight were measured to determine their body mass index (BMI). Participants were excluded if they had a history of coronary artery or cerebrovascular disease, acute infections, chronic liver disease, heart failure, malignancy, uncontrolled diabetes (glycated hemoglobin [HbA1c] >10%), uncontrolled hypertension (systolic blood pressure >160 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure >100 mm Hg), or had used steroid agents or thiazolidinedione within the preceding 3 months. All other treatments (insulin, antihypertensive, antiplatelet, and lipid-lowering medications) had been maintained for at least 3 months. The study protocol was approved by the ethics committees of the participating centers. All patients signed informed consent statements.
- Laboratory examination
- Blood samples were collected from all subjects after they had fasted for 12 hours, and standard lipid parameters (total cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein-cholesterol), blood glucose and HbA1c were measured. Fasting and 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose levels were measured using an automated enzymatic method and HbA1c levels were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography with a reference range of 4.4% to 6.4%. The urinary albumin excretion rate was measured by enzyme immunoassay using immunoturbidimetry (Eiken, Tokyo, Japan).
- Assessment of DR
- For detection of DR, participants had a standardized clinical examination and retinal photography. DR was graded from the digital retinal photographs at the retinal vascular imaging center by graders masked to the participants' clinical details. A DR severity score was assigned to each eye according to the modified Airlie House Classification system [15]. The patients were assigned to one of two groups: no evidence of DR or presence of DR at any stage.
- Measurement of endothelial function
- The FMD of the brachial artery was measured by ultrasound according to the guidelines described by Corretti et al. [16]. After the patients fasted for 12 hours (including caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol) vascular measurement was performed. A GE Vivid 7 Dimensions ultrasound system (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) equipped with a 12-MHz ultrasound probe was used to measure the internal diameter of the brachial artery by one examiner at a position several centimeters from the elbow, where the artery could be easily located. After the patient rested for 15 minutes, the mean diameter (D0) was measured. A pneumatic tourniquet on the right forearm was inflated to apply at least 50 mm Hg above the systolic blood pressure for 4 to 5 minutes. A second mean diameter (D1) scan was performed after the cuff was deflated. A nitroglycerin (NTG) tablet (0.3 mg) was then administered sublingually, and an image was recorded 3.5 to 5 minutes later. Measurements of each vessel's diameter were taken from the anterior to the posterior intima at the end of diastole as measured by the R wave on a continuously recorded electrocardiogram. The diameter of the brachial artery was calculated as the average diameter of triplicate measurements. The percent FMD (%FMD) of the brachial artery was expressed as the percent increase in the maximal vessel diameter after cuff deflation within 120 seconds relative to that of the baseline diameter. The percent NTG-mediated vasodilation (%NMD) was expressed as the percent increase in the diameter three minutes after administration of NTG compared to that of the baseline diameter. In our laboratory, the intraobserver variability for repeated measurements of resting brachial diameters was 0.04±0.05 mm [17].
- Statistical analysis
- Data are presented either as mean±standard deviation or, in the case of a skewed distribution, as median (interquartile range). In addition, categorical data are expressed as number (%). The baseline clinical parameters were compared by t-test and Mann-Whitney U test for continuous variables, and by chi-square test for categorical variables. The change in %FMD was categorized into tertiles. A test for trends in the demographic and biochemical characteristics across tertiles was performed using linear or logistic regression analyses. The association of FMD with the presence of DR was examined by multiple logistic regression analysis adjusted for age and sex (model 1), as well as for variables that had a significant difference between patients with and without DR (model 2), and then further adjusted for %NMD. The statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). P values of less than 0.05 were considered significant.
METHODS
- The main clinical characteristics and laboratory data of the groups are presented in Table 1. Total 167 patients (90 men and 77 women) were enrolled in this study. Their mean age was 54.1±8.6 years, and their mean HbA1c level and mean diabetic duration were 7.5%±1.0% and 7.3±6.0 years, respectively (Table 1).
- Twenty-nine patients (17.4%) had DR. There were three patients who had proliferative DR, and we did not make a separate DR group, because of the small number (1.8%) of patients for this analysis. As shown in Table 1, those with DR had a significantly longer diabetic duration. Moreover, the use of antihypertensive and antiplatelet medications, as well as insulin treatments was greater in patients with DR than in those without. Furthermore, patients who developed DR had significantly higher fasting and 2-hour plasma glucose, HbA1c level, and urinary albumin excretion rates.
- The mean value of %FMD in the study population was 3.85%. We also analyzed endothelial response according to other variances. %FMD showed a significant difference between the sexes (3.29%±5.36% for men vs. 6.02%±7.17% for women, P=0.01), but age showed only a weak correlation with FMD response, and was not statistically significant (r=-0.140, P=0.071). There were no differences in other variables, such as medications, diabetic duration, BMI, blood pressure, and lipid profiles between male and female groups, except insulin use (4.4% vs. 16.9%, P=0.008). There were also no significant differences of %FMD in endothelial dysfunction between people who did and did not take medications, such as insulin (4.67%±6.51% vs. 3.40%±5.27%, P=0.436), angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEI), angiotensin-II receptor blocker (ARB) (4.91%±6.34% vs. 3.45%±6.48%, P=0.205), antiplatelet agent (5.10%±6.34% vs. 4.16%±6.43%, P=0.353), and lipid lowering agent (4.99%±6.30% vs. 3.45%±6.54%, P=0.159), all of which can affect endothelial function. The %FMD was significantly lower in patients with DR than without DR (P<0.001). However, there was no significant difference in NTG-induced dilation between the two groups (Table 1).
- We analyzed the patients' clinical characteristics according to the %FMD tertiles. The patients were grouped into three tertiles (first tertile, lower response; second tertile, intermediate response; third tertile, higher response). The prevalence of retinopathy decreased with increasing %FMD tertile (Table 2). However, there were no significant differences in medication use, such as insulin, antihypertensive agent, lipid-lowering agent, or antiplatelet agents among the tertile groups. In addition, there were no differences in smoking, diabetic duration, blood pressure, fasting, and 2-hour plasma glucose, HbA1c, lipid profiles, or urinary albumin excretion by %FMD tertile.
- To examine the independent associations between key risk factors and the incidence of DR, a multiple logistic regression analysis was performed. Due to the skewed distribution of the %FMD, tertiles were applied for this variable with the lowest tertile being the reference category. We found that the duration of diabetes, HbA1c value, and urinary albumin excretion rate remained significantly associated with DR incidence (Table 3). The lowest %FMD tertile showed an increased risk of DR compared to the highest %FMD tertile, although the relationship between the intermediate and highest %FMD groups was not statistically significant. This association persisted after further adjustment for %NMD (data not shown).
RESULTS
- In this study, we investigated the association of DR and endothelial dysfunction in T2DM patients. We identified endothelial dysfunction as an independent predictor of an increased DR prevalence in patients with T2DM. As predicted, the %FMD was lower in DR patients than in T2DM subjects without DR. After taking many other variables into account using a multiple logistic analysis, severe endothelial dysfunction remained an independent risk factor for DR.
- There are several factors that can affect endothelial function. Caballero et al. [18] suggested that %FMD was significantly higher in female patients. In addition, there are many studies on drugs that can affect endothelial function, such as insulin, ACEI, ARB, and statin [19-21], and the recent studies argue that fenofibrate can also improve endothelial function of type 2 diabetic patients [22]. In our study, female patients showed a tendency for increased FMD response, but the age of the patients and the use of medications had no influence on endothelial function.
- We observed that diabetic patients with retinopathy showed more severely impaired FMD than diabetic patients without retinopathy. However, we found that patients who had DR demonstrated longer durations of diabetes, poorer glucose control, and an increased use of medications. Taking all of these considerations into account, we adjusted for sex, age, diabetic duration, medications, fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, and urinary albumin excretion; as a result, endothelial dysfunction was associated with DR. In addition, we found that the group with a low response to %FMD was 10 times more likely to have DR than those with a high response to %FMD, but the intermediate-response %FMD group did not demonstrate statistical significance. This means that endothelial dysfunction could affect the development of DR, specifically in patients with severe endothelial dysfunction. However, this study was cross-sectional; therefore, these findings cannot prove the association between early endothelial dysfunction and DR. In contrast with previous studies [13,23], in our study, the %FMD (endothelial-dependent vasodilation) was unaffected by adjusting for %NMD (endothelial-independent vasodilation). This result may suggest that pure endothelial dysfunction can contribute to DR pathogenesis.
- In diabetes mellitus, development of microvascular complications and impaired vascular responses to reactive hyperemia have several underlying pathogenetic mechanisms in common. Many biochemical pathways associated with hyperglycemia can increase the production of free radicals by reducing the amount of biologically active NO [24]. The activation of protein kinase C, nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate depletion, and the formation of advanced glycation end products in diabetes causes a decrease of NO and vascular dysfunction. These events could lead to retinal vascular endothelial dysfunction, and result in increased retinal blood flow and retinal vasodilation [25]. Indeed, an abnormal retinal vascular response to hyperoxia is associated with the development of DR [26].
- Various methods have been used to study endothelial function. FMD of the brachial artery by ultrasound is the most widely-used vascular test to assess endothelial-dependent vasodilation and the most reproducible test when appropriate methodologies are applied [27]. FMD reflects endothelial function in relatively large conduit vessels by measuring brachial artery diameter changes induced by increased shear stress. In respect to DR, the mechanisms for reactive hyperemia in the microvasculature of the brachial artery are different from those in microvasculature of the retina. In the latter, a neurohormonal mechanism plays an important role [28]. However, when the systemic nature of endothelial dysfunction is considered, a macrovascular endothelial defect may extend to the microvasculature, as a few studies have been performed to examine the relationship between FMD and endothelial dysfunction in other microvascular arterial beds. One recent study shows a weak correlation between FMD and flicker-induced retinal vasodilation, which may reflect endothelial function of the retinal circulation [29]. In coronary heart disease, endothelial dysfunction has not only been confined to the coronary arteries, but was found in conduit arteries of the peripheral circulatory system as well [30-32]. However, other studies claimed that there is no relationship between changes in conduit function and in other microcirculation [33,34]. Possible explanations for the discrepancy between studies include differences in the stimulation methods, and in the risk factor profile (or underlying disease) for the patient groups. In light of the result of our study, further studies are needed to correlate FMD with other vascular function tests, including retinal vasodilation response.
- Previous studies reported the association between DR and FMD in patients with type 2 diabetes [13,14,35]. However, these studies did not adjust for the factors that could affect the DR and endothelial function. Also, as discussed earlier, these studies could not exclude the effect of endothelial independent vasodilation. We used the statistical method of logistic regression to clarify the relationship between DR and endothelial dysfunction more clearly after adjusting for various factors.
- Some limitations were noted in this study. First, the size of the patient population was small compared with that of large studies of T2DM. Second, this study was a cross-sectional study and further longitudinal studies are needed to evaluate the association between early endothelial dysfunction and the development of DR. Third, we included patients who used insulin therapy and we did not assess their insulin resistance, which could affect endothelial dysfunction [36] and DR [37]. However, patients maintained stable insulin doses during the 3 months, and there were no differences in medication use among the tertiles. With the use of multiple logistic regression, DR was not significantly associated with the use of insulin and we concluded that insulin treatment had no influence on the development of DR.
- In summary, we showed that endothelial dysfunction is an independent predictor of DR, which is most visible when the endothelial dysfunction is most severe. Although more studies are needed to confirm these findings and to elucidate the mechanisms for these associations, our study provides a possible mechanism for endothelial dysfunction's role in the development of DR.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported by a grant (Y.B.A., 2009) from the Korean Diabetes Association.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- 1. Verma S, Anderson TJ. Fundamentals of endothelial function for the clinical cardiologist. Circulation 2002;105:546-549. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Tooke JE. Microvascular function in human diabetes. A physiological perspective. Diabetes 1995;44:721-726. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 1991;43:109-142. PubMed
- 4. Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM, Spiegelhalter DJ, Miller OI, Sullivan ID, Lloyd JK, Deanfield JE. Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet 1992;340:1111-1115. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Davignon J, Ganz P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004;109(23 Suppl 1):III27-III32. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Creager MA, Cooke JP, Mendelsohn ME, Gallagher SJ, Coleman SM, Loscalzo J, Dzau VJ. Impaired vasodilation of forearm resistance vessels in hypercholesterolemic humans. J Clin Invest 1990;86:228-234. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Panza JA, Quyyumi AA, Brush JE Jr, Epstein SE. Abnormal endothelium-dependent vascular relaxation in patients with essential hypertension. N Engl J Med 1990;323:22-27. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Williams SB, Cusco JA, Roddy MA, Johnstone MT, Creager MA. Impaired nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996;27:567-574. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Henry RM, Ferreira I, Kostense PJ, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Heine RJ, Kamp O, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD. Type 2 diabetes is associated with impaired endothelium-dependent, flow-mediated dilation, but impaired glucose metabolism is not: the Hoorn Study. Atherosclerosis 2004;174:49-56. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Stehouwer CD, Gall MA, Twisk JW, Knudsen E, Emeis JJ, Parving HH. Increased urinary albumin excretion, endothelial dysfunction, and chronic low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes: progressive, interrelated, and independently associated with risk of death. Diabetes 2002;51:1157-1165. PubMed
- 11. Wirta O, Pasternack A, Mustonen J, Laippala P, Lahde Y. Retinopathy is independently related to microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Nephrol 1999;51:329-334. PubMed
- 12. van Hecke MV, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Stolk RP, Henry RM, Heine RJ, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD, Polak BC. Are retinal microvascular abnormalities associated with large artery endothelial dysfunction and intima-media thickness? The Hoorn Study. Clin Sci (Lond) 2006;110:597-604. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Suetsugu M, Takebayashi K, Aso Y. Association between diabetic microangiopathy and vascular endothelial function evaluated by flow-mediated vasodilatation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract 2007;61:920-926. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Malecki MT, Osmenda G, Walus-Miarka M, Skupien J, Cyganek K, Mirkiewicz-Sieradzka B, damek-Guzik TA, Guzik TJ, Sieradzki J. Retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with increased intima-media thickness and endothelial dysfunction. Eur J Clin Invest 2008;38:925-930. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Wong TY, Klein R, Islam FM, Cotch MF, Folsom AR, Klein BE, Sharrett AR, Shea S. Diabetic retinopathy in a multi-ethnic cohort in the United States. Am J Ophthalmol 2006;141:446-455. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Corretti MC, Anderson TJ, Benjamin EJ, Celermajer D, Charbonneau F, Creager MA, Deanfield J, Drexler H, Gerhard-Herman M, Herrington D, Vallance P, Vita J, Vogel R. International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force. Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: a report of the International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;39:257-265. PubMed
- 17. Herrington DM, Fan L, Drum M, Riley WA, Pusser BE, Crouse JR, Burke GL, McBurnie MA, Morgan TM, Espeland MA. Brachial flow-mediated vasodilator responses in population-based research: methods, reproducibility and effects of age, gender and baseline diameter. J Cardiovasc Risk 2001;8:319-328. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Caballero AE, Arora S, Saouaf R, Lim SC, Smakowski P, Park JY, King GL, LoGerfo FW, Horton ES, Veves A. Microvascular and macrovascular reactivity is reduced in subjects at risk for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 1999;48:1856-1862. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Akalin A, Temiz G, Akcar N, Sensoy B. Short term effects of atorvastatin on endothelial functions and oxidized LDL levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr J 2008;55:861-866. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Potenza MA, Gagliardi S, Nacci C, Carratu MR, Montagnani M. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes: from mechanisms to therapeutic targets. Curr Med Chem 2009;16:94-112. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Shahin Y, Khan JA, Samuel N, Chetter I. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors effect on endothelial dysfunction: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Atherosclerosis 2011;216:7-16. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Hamilton SJ, Chew GT, Davis TM, Watts GF. Fenofibrate improves endothelial function in the brachial artery and forearm resistance arterioles of statin-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Clin Sci (Lond) 2010;118:607-615. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Nguyen TT, Shaw JE, Robinson C, Kawasaki R, Wang JJ, Kreis AJ, Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy is related to both endothelium-dependent and -independent responses of skin microvascular flow. Diabetes Care 2011;34:1389-1393. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Tabit CE, Chung WB, Hamburg NM, Vita JA. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2010;11:61-74. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 25. Ciulla TA, Amador AG, Zinman B. Diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema: pathophysiology, screening, and novel therapies. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2653-2664. PubMed
- 26. Curtis TM, Gardiner TA, Stitt AW. Microvascular lesions of diabetic retinopathy: clues towards understanding pathogenesis? Eye (Lond) 2009;23:1496-1508. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Ghiadoni L, Versari D, Giannarelli C, Faita F, Taddei S. Non-invasive diagnostic tools for investigating endothelial dysfunction. Curr Pharm Des 2008;14:3715-3722. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Bloomgarden ZT. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2008;31:1080-1083. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 29. Pemp B, Weigert G, Karl K, Petzl U, Wolzt M, Schmetterer L, Garhofer G. Correlation of flicker-induced and flow-mediated vasodilatation in patients with endothelial dysfunction and healthy volunteers. Diabetes Care 2009;32:1536-1541. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Anderson TJ, Uehata A, Gerhard MD, Meredith IT, Knab S, Delagrange D, Lieberman EH, Ganz P, Creager MA, Yeung AC, Selwyn AP. Close relation of endothelial function in the human coronary and peripheral circulations. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;26:1235-1241. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Neunteufl T, Katzenschlager R, Hassan A, Klaar U, Schwarzacher S, Glogar D, Bauer P, Weidinger F. Systemic endothelial dysfunction is related to the extent and severity of coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 1997;129:111-118. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Teragawa H, Ueda K, Matsuda K, Kimura M, Higashi Y, Oshima T, Yoshizumi M, Chayama K. Relationship between endothelial function in the coronary and brachial arteries. Clin Cardiol 2005;28:460-466. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Hansell J, Henareh L, Agewall S, Norman M. Non-invasive assessment of endothelial function: relation between vasodilatory responses in skin microcirculation and brachial artery. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2004;24:317-322. ArticlePubMed
- 34. Shamim-Uzzaman QA, Pfenninger D, Kehrer C, Chakrabarti A, Kacirotti N, Rubenfire M, Brook R, Rajagopalan S. Altered cutaneous microvascular responses to reactive hyperaemia in coronary artery disease: a comparative study with conduit vessel responses. Clin Sci (Lond) 2002;103:267-273. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 35. Sogawa K, Nagaoka T, Tanano I, Tani T, Omae T, Nakabayashi S, Ishibazawa A, Takahashi A, Yoshida A. Association between diabetic retinopathy and flow-mediated vasodilation in type 2 DM. Curr Eye Res 2012;37:446-451. ArticlePubMed
- 36. Suzuki M, Takamisawa I, Yoshimasa Y, Harano Y. Association between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes and the effects of pioglitazone. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007;76:12-17. ArticlePubMed
- 37. Anan F, Takayuki M, Takahashi N, Nakagawa M, Eshima N, Saikawa T, Yoshimatsu H. Diabetic retinopathy is associated with insulin resistance and cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients. Hypertens Res 2009;32:299-305. ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
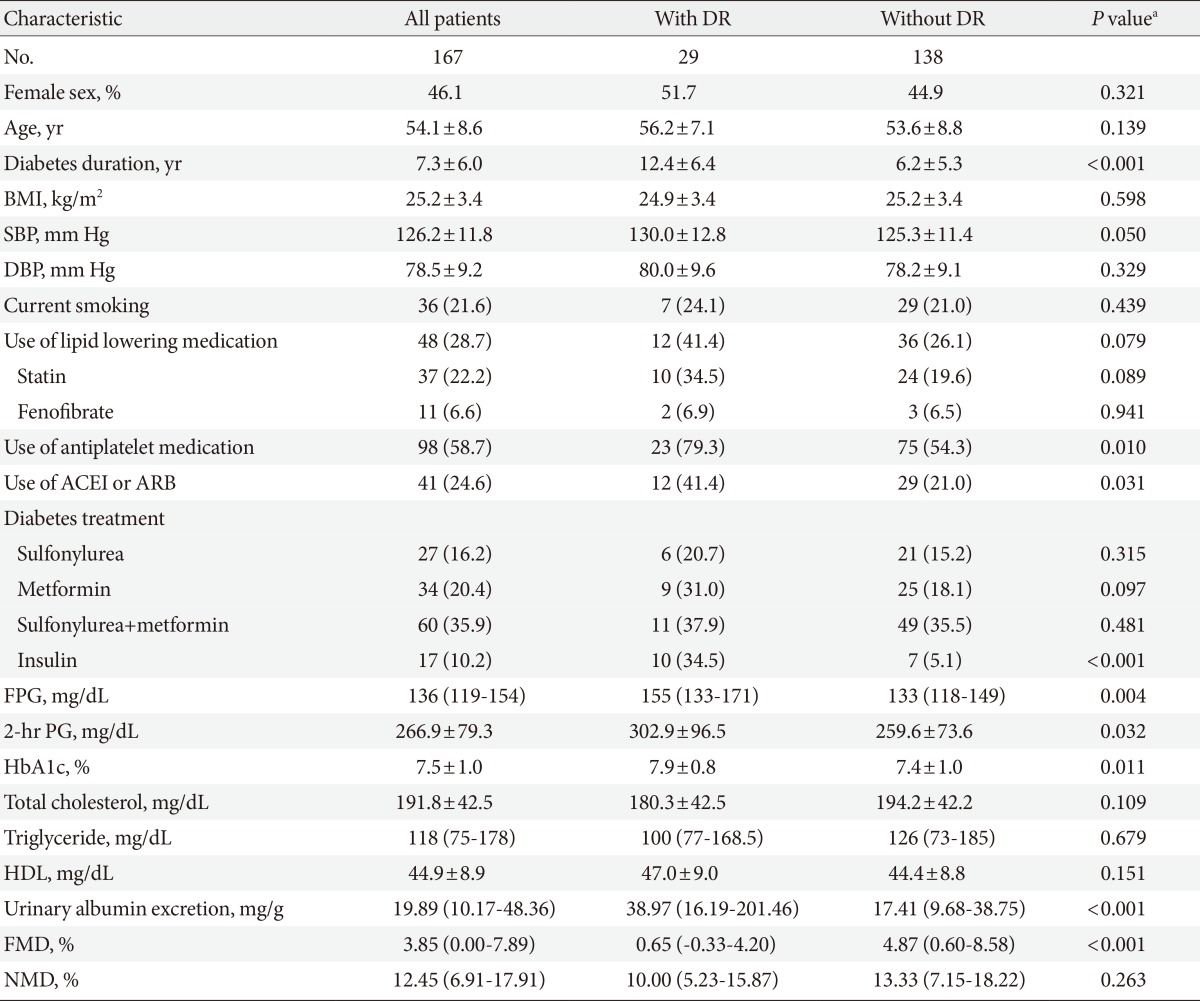
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range). P<0.05 was considered significant.
DR, diabetic retinopathy; BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin-II receptor blocker; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; 2-hr PG, 2-hour plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; HDL, high density lipoprotein; FMD, flow-mediated vasodilation; NMD, nitroglycerin-mediated vasodilation.
aComparing diabetic patients with and without diabetic retinopathy.
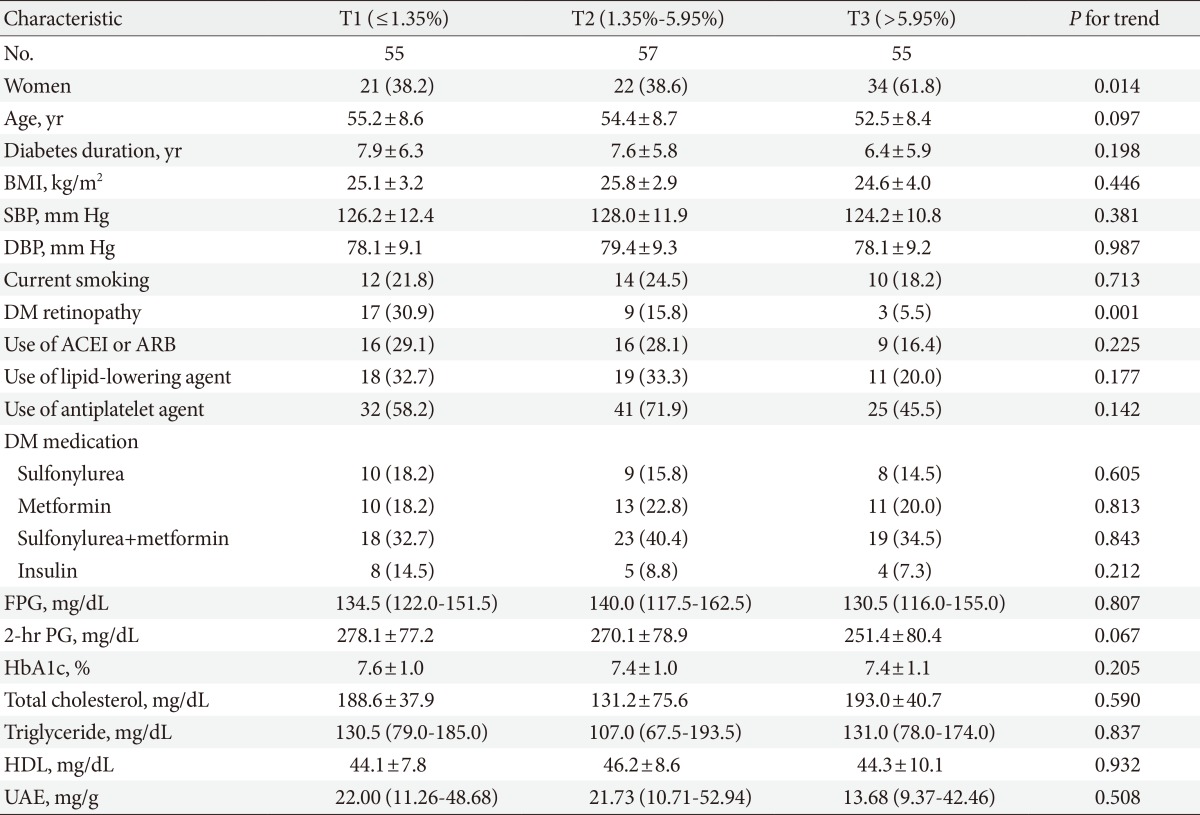
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range). P<0.05 was considered significant.
BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; DM, diabetes mellitus; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin-II receptor blocker; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; 2-hr PG, 2-hour plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; HDL, high density lipoprotein; UAE, urinary albumin excretion.
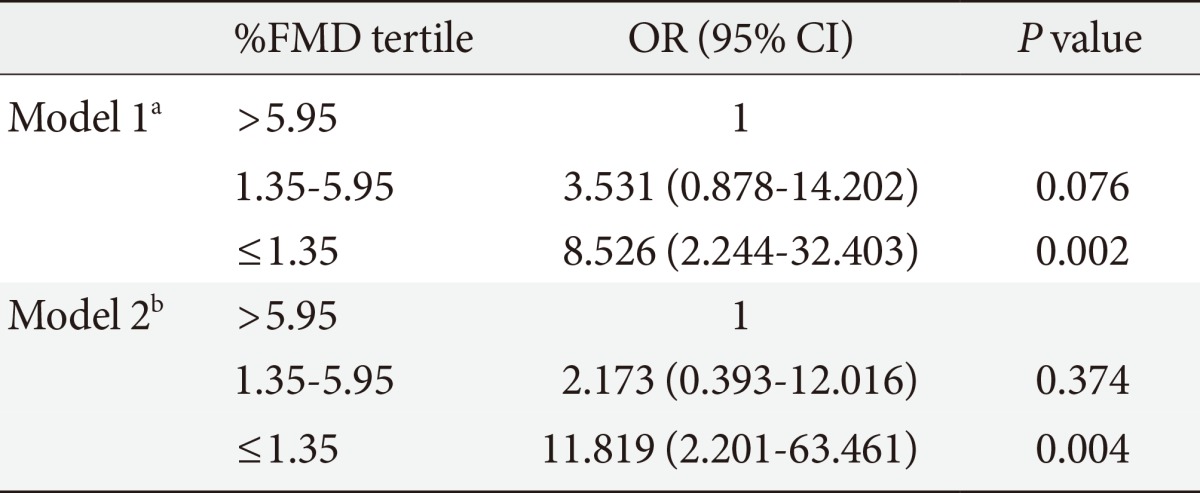
FMD, flow mediated vasodilation; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
aModel 1, adjusted for age and sex, bModel 2, adjusted for covariates in model 1 plus diabetes duration, use of insulin, use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin-II receptor blocker, antiplatelet and lipid-lowering medications, systolic blood pressure, fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and urinary albumin excretion.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Effects of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Polymorphisms on Retinal Tissue Perfusion in Mild Diabetic Retinopathy Patients Receiving the Medical Food, Ocufolin®
Hong Jiang, Zhiping Liu, Justin H Townsend, Jianhua Wang
Clinical Ophthalmology.2023; Volume 17: 1121. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic risk factors, peripheral arterial tonometry and metformin in adults with type 1 diabetes participating in the REducing with MetfOrmin Vascular Adverse Lesions trial
David Chen, Alicia J Jenkins, Nicola Greenlaw, Katie Dudman, Tamsin Fernandes, David M Carty, Alun D Hughes, Andrzej S Januszewski, Coen DA Stehouwer, John R Petrie
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro (mi) RNA and Diabetic Retinopathy
Sadashiv, Praveen Sharma, Shailendra Dwivedi, Sunita Tiwari, Pankaj Kumar Singh, Amit Pal, Sandeep Kumar
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.2022; 37(3): 267. CrossRef - Ethnomedicinal Value of Antidiabetic Plants in Bangladesh: A Comprehensive Review
Md. Masudur Rahman, Md. Josim Uddin, A. S. M. Ali Reza, Abu Montakim Tareq, Talha Bin Emran, Jesus Simal-Gandara
Plants.2021; 10(4): 729. CrossRef - Relating Retinal Vascular Oxygen Saturation and Microvasculature Morphology at Progressive Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Selin L. Auvazian, Jennifer Cano, Sophie Leahy, Preny Karamian, Amir Kashani, Andrew Moshfeghi, Hossein Ameri, Norman P. Blair, Mahnaz Shahidi
Translational Vision Science & Technology.2021; 10(6): 4. CrossRef - Renalase gene Glu37Asp polymorphism affects susceptibility to diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Monika Buraczynska, Karolina Gwiazda-Tyndel, Bartłomiej Drop, Wojciech Zaluska
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(12): 1595. CrossRef - Endothelium as a Therapeutic Target in Diabetes Mellitus: From Basic Mechanisms to Clinical Practice
Anastasios Tentolouris, Ioanna Eleftheriadou, Evangelia Tzeravini, Dimitrios Tsilingiris, Stavroula A. Paschou, Gerasimos Siasos, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2020; 27(7): 1089. CrossRef - miR‐181a/b‐5p regulates human umbilical vein endothelial cell angiogenesis by targeting PDGFRA
Tingting Sun, Linan Yin, Hongyu Kuang
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2020; 38(2): 222. CrossRef - The role of microRNAs in the healing of diabetic ulcers
Golnaz Goodarzi, Mahmood Maniati, Durdi Qujeq
International Wound Journal.2019; 16(3): 621. CrossRef - Role of altered coagulation-fibrinolytic system in the pathophysiology of diabetic retinopathy
Tapan Behl, Thirumurthy Velpandian, Anita Kotwani
Vascular Pharmacology.2017; 92: 1. CrossRef - Macular oedema as manifestation of diabetic retinopathy
Mukharram M. Bikbov, Rinat R. Fayzrakhmanov, Rinat M. Zaynullin, Artur F. Zaynetdinov, Timur R. Gilmanshin, Marat R. Kalanov
Diabetes mellitus.2017; 20(4): 263. CrossRef - Shedding light on miR-26a: Another key regulator of angiogenesis in diabetic wound healing
Carlos Zgheib, Kenneth W. Liechty
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology.2016; 92: 203. CrossRef - Lipoprotein(a) predicts the development of diabetic retinopathy in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Jin A. Choi, Jinwoo Kwon, Donghyun Jee, Yang Kyung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2016; 10(2): 426. CrossRef - Clinical Course and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Jin A Choi, Jinwoo Kwon, Donghyun Jee, Yang Kyung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 482. CrossRef - Relationship of systemic endothelial function and peripheral arterial stiffness with diabetic retinopathy
Laurence S Lim, Lieng H Ling, Chui Ming Gemmy Cheung, Peng Guan Ong, Lingli Gong, E Shyong Tai, Ranjana Mathur, Doric Wong, Wallace Foulds, Tien Yin Wong
British Journal of Ophthalmology.2015; 99(6): 837. CrossRef - Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Loss Is Associated with Urinary Albumin Excretion in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jin A. Choi, Sun-Hee Ko, Yi Ryeung Park, Dong-Hyun Jee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Chan Kee Park
Ophthalmology.2015; 122(5): 976. CrossRef - Flow Mediated Dilatation Is Reduced with the Progressive Stages of Glomerular Filtration Rate and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetic Patients without Coronary Heart Disease
Hiroyuki Ito, Mina Nakashima, Kentaro Meguro, Haruki Furukawa, Hitomi Yamashita, Akifusa Takaki, Chizuko Yukawa, Takashi Omoto, Masahiro Shinozaki, Shinya Nishio, Mariko Abe, Shinichi Antoku, Mizuo Mifune, Michiko Togane
Journal of Diabetes Research.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - The Role of MicroRNAs in Diabetic Complications—Special Emphasis on Wound Healing
João Moura, Elisabet Børsheim, Eugenia Carvalho
Genes.2014; 5(4): 926. CrossRef - Role of AMP‐Activated Protein Kinase in Cancer Therapy
Gauhar Rehman, Adeeb Shehzad, Abdul Latif Khan, Muhammad Hamayun
Archiv der Pharmazie.2014; 347(7): 457. CrossRef - Urinary albumin excretion rate: a risk factor for retinal hard exudates in macular region in type 2 diabetic patients
Shaocheng Wang, Siyong Lin, Xi Cao, Yuezhong Zheng, Jinyang Wang, Na Lu, Jinkui Yang
Chinese Medical Journal.2014; 127(12): 2293. CrossRef - Letter: Diabetic Retinopathy and Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J2013;37:262-9)
Seok Man Son
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(5): 391. CrossRef
- Related articles
-
- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Clinical and Lifestyle Determinants of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Comparison of on-Statin Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels for the Prediction of First Cardiovascular Event in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- The Role of Echocardiography in Evaluating Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Glycemic Control and Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from KNOW-CKD

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite



