
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Most cited
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Most cited
From articles published in Diabetes & Metabolism Journal during the past two years (2022 ~ ).
Original Articles
- Drug/Regimen
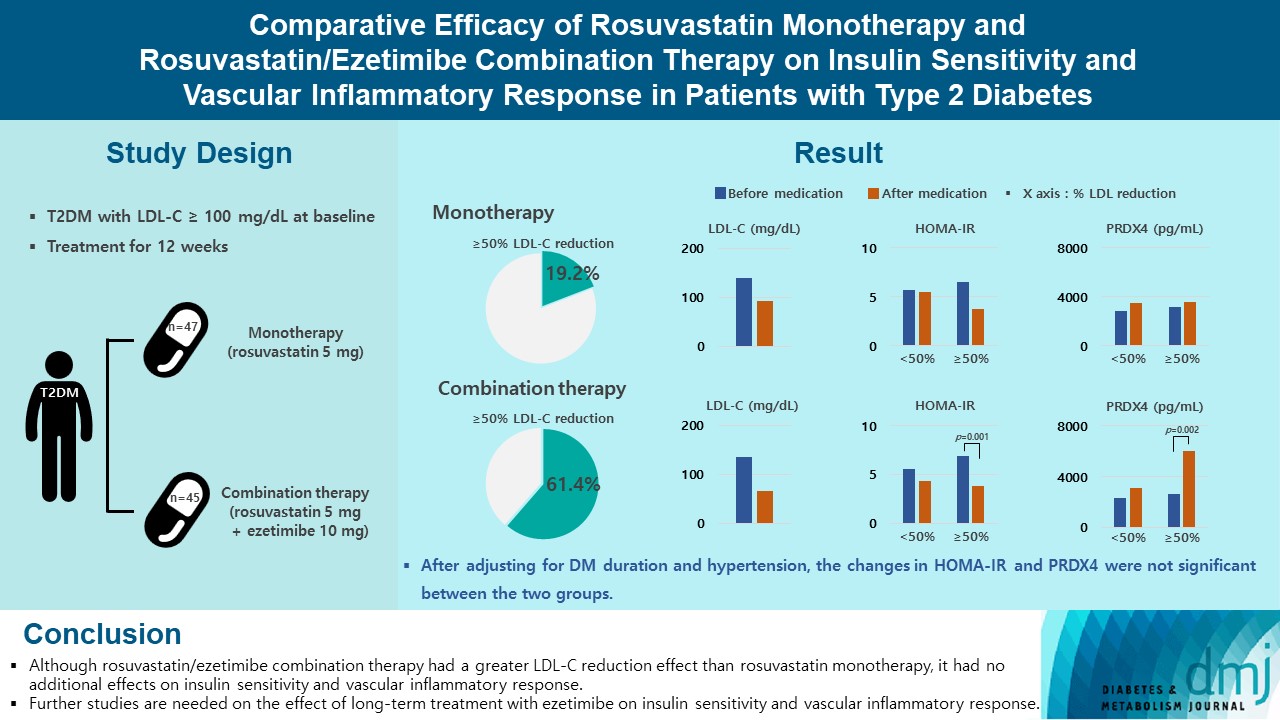
- Comparative Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy and Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammatory Response in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Hye Han, Kyong Hye Joung, Jun Choul Lee, Ok Soon Kim, Sorim Choung, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Hyun Jin Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):112-121. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0402
- 1,972 View
- 221 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) induces endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, which are the main factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The present study aimed to compare the effects of rosuvastatin monotherapy and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and vascular inflammatory response in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 101 patients with T2DM and dyslipidemia were randomized to either rosuvastatin monotherapy (5 mg/day, n=47) or rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy (5 mg/10 mg/day, n=45) and treated for 12 weeks. Serum lipids, glucose, insulin, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), and peroxiredoxin 4 (PRDX4) levels were determined before and after 12 weeks of treatment.
Results
The reduction in low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% from baseline after treatment was more in the combination therapy group. The serum sICAM-1 levels increased significantly in both groups, but there was no difference between the two groups. The significant changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and PRDX4 were confirmed only in the subgroup in which LDL-C was reduced by 50% or more in the combination therapy group. However, after adjusting for diabetes mellitus duration and hypertension, the changes in HOMA-IR and PRDX4 were not significant between the two groups.
Conclusion
Although rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy had a greater LDL-C reduction effect than rosuvastatin monotherapy, it had no additional effects on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. Further studies are needed on the effect of long-term treatment with ezetimibe on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 55. CrossRef
- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Basic Research
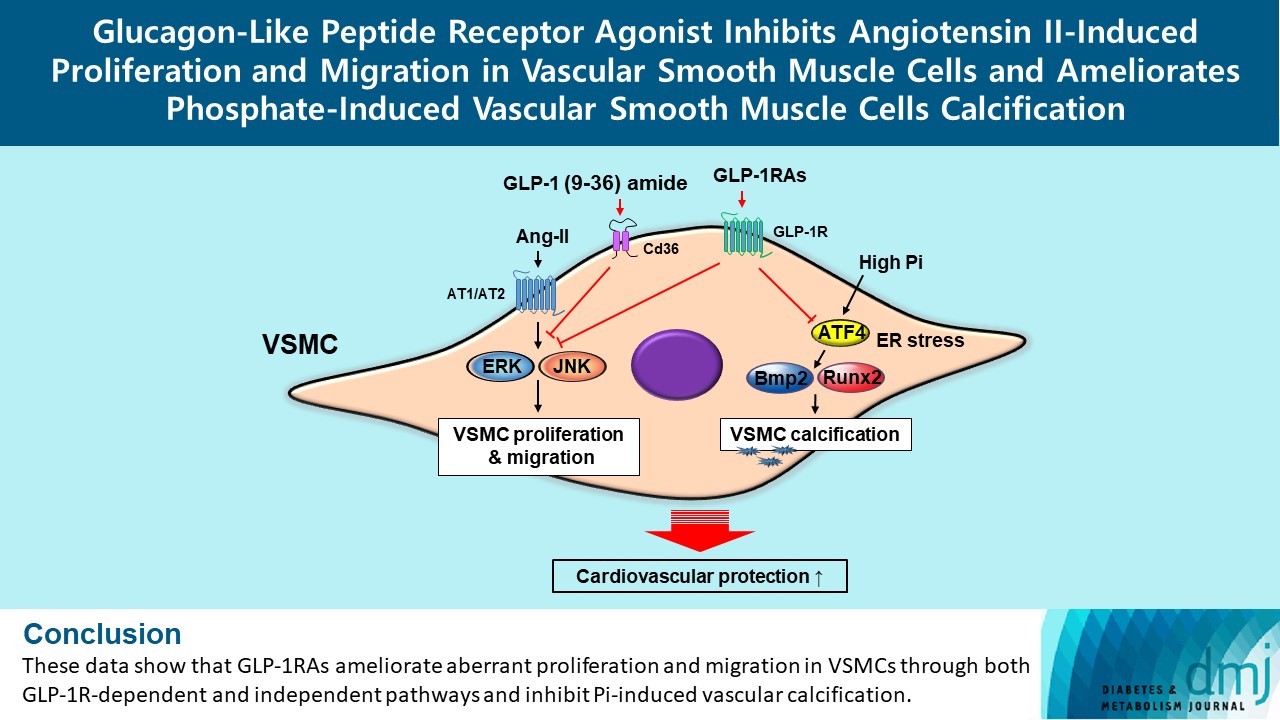
- Glucagon-Like Peptide Receptor Agonist Inhibits Angiotensin II-Induced Proliferation and Migration in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Ameliorates Phosphate-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Calcification
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):83-96. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0363
- 1,676 View
- 167 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), which is a therapeutic agent for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system.
Methods
To examine the protective effects of GLP-1RAs on proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), A-10 cells exposed to angiotensin II (Ang II) were treated with either exendin-4, liraglutide, or dulaglutide. To examine the effects of GLP-1RAs on vascular calcification, cells exposed to high concentration of inorganic phosphate (Pi) were treated with exendin-4, liraglutide, or dulaglutide.
Results
Ang II increased proliferation and migration of VSMCs, gene expression levels of Ang II receptors AT1 and AT2, proliferation marker of proliferation Ki-67 (Mki-67), proliferating cell nuclear antigen (Pcna), and cyclin D1 (Ccnd1), and the protein expression levels of phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-Erk), phospho-c-JUN N-terminal kinase (p-JNK), and phospho-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (p-Pi3k). Exendin-4, liraglutide, and dulaglutide significantly decreased the proliferation and migration of VSMCs, the gene expression levels of Pcna, and the protein expression levels of p-Erk and p-JNK in the Ang II-treated VSMCs. Erk inhibitor PD98059 and JNK inhibitor SP600125 decreased the protein expression levels of Pcna and Ccnd1 and proliferation of VSMCs. Inhibition of GLP-1R by siRNA reversed the reduction of the protein expression levels of p-Erk and p-JNK by exendin-4, liraglutide, and dulaglutide in the Ang II-treated VSMCs. Moreover, GLP-1 (9-36) amide also decreased the proliferation and migration of the Ang II-treated VSMCs. In addition, these GLP-1RAs decreased calcium deposition by inhibiting activating transcription factor 4 (Atf4) in Pi-treated VSMCs.
Conclusion
These data show that GLP-1RAs ameliorate aberrant proliferation and migration in VSMCs through both GLP-1Rdependent and independent pathways and inhibit Pi-induced vascular calcification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incretin Hormone Secretion in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Roles of Obesity, Insulin Sensitivity and Treatment with Metformin and GLP-1s
Andrea Etrusco, Mislav Mikuš, Antonio D’Amato, Fabio Barra, Petar Planinić, Trpimir Goluža, Giovanni Buzzaccarini, Jelena Marušić, Mara Tešanović, Antonio Simone Laganà
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 653. CrossRef
- Incretin Hormone Secretion in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Roles of Obesity, Insulin Sensitivity and Treatment with Metformin and GLP-1s
Review
- Lifestyle
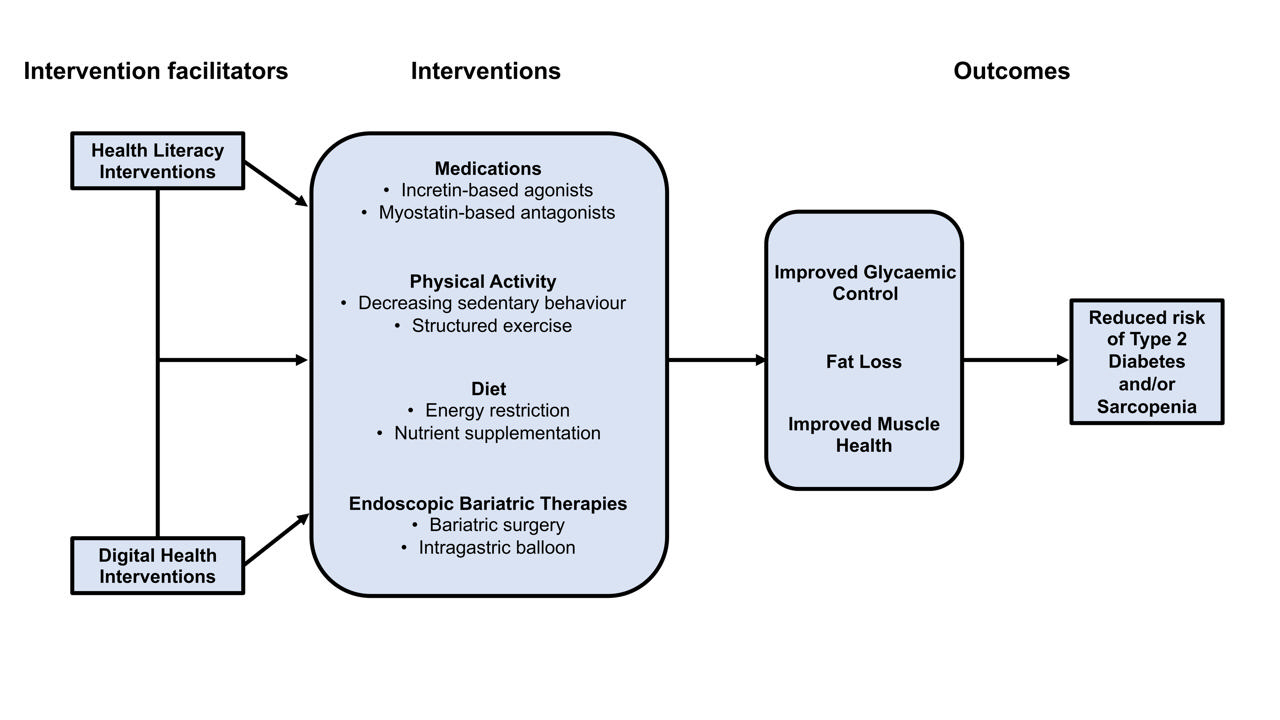
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Sarcopenia as Comorbid Chronic Diseases in Older Adults: Established and Emerging Treatments and Therapies
- Jakub Mesinovic, Jackson J. Fyfe, Jason Talevski, Michael J. Wheeler, Gloria K.W. Leung, Elena S. George, Melkamu T. Hunegnaw, Costas Glavas, Paul Jansons, Robin M. Daly, David Scott
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):719-742. Published online September 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0112
- 4,511 View
- 436 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and sarcopenia (low skeletal muscle mass and function) share a bidirectional relationship. The prevalence of these diseases increases with age and they share common risk factors. Skeletal muscle fat infiltration, commonly referred to as myosteatosis, may be a major contributor to both T2DM and sarcopenia in older adults via independent effects on insulin resistance and muscle health. Many strategies to manage T2DM result in energy restriction and subsequent weight loss, and this can lead to significant declines in muscle mass in the absence of resistance exercise, which is also a first-line treatment for sarcopenia. In this review, we highlight recent evidence on established treatments and emerging therapies targeting weight loss and muscle mass and function improvements in older adults with, or at risk of, T2DM and/or sarcopenia. This includes dietary, physical activity and exercise interventions, new generation incretin-based agonists and myostatin-based antagonists, and endoscopic bariatric therapies. We also highlight how digital health technologies and health literacy interventions can increase uptake of, and adherence to, established and emerging treatments and therapies in older adults with T2DM and/or sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fucoidan ameliorates diabetic skeletal muscle atrophy through PI3K/Akt pathway
Caixia Li, Yaping Liu, Mingzhi Yang, Haoyue Huang, Lulu Tang, Yufan Miao, Wenjie Li, Xing Li
Journal of Functional Foods.2024; 114: 106076. CrossRef
- Fucoidan ameliorates diabetic skeletal muscle atrophy through PI3K/Akt pathway
Original Articles
- Basic Research
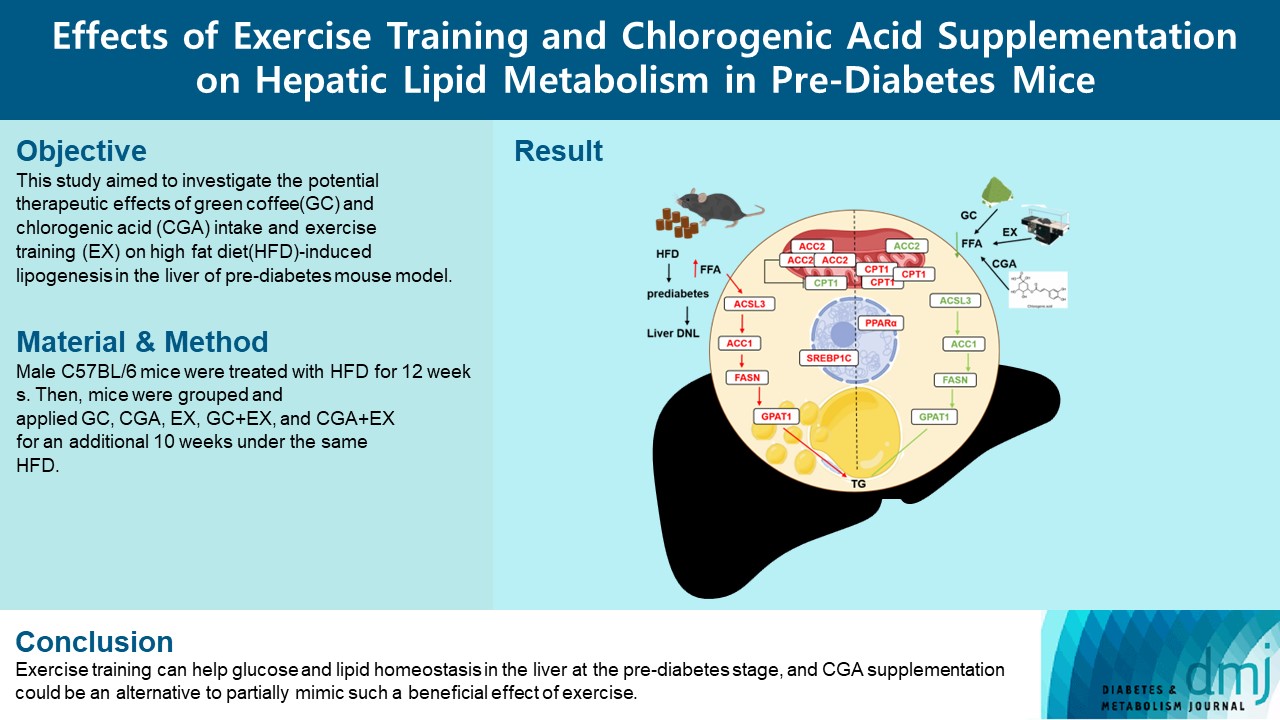
- Effects Of Exercise Training And Chlorogenic Acid Supplementation On Hepatic Lipid Metabolism In Prediabetes Mice
- Samaneh Shirkhani, Sayyed Mohammad Marandi, Mohammad Hossein Nasr-Esfahani, Seung Kyum Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):771-783. Published online September 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0265
- 2,242 View
- 167 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Since prediabetes is a risk factor for metabolic syndromes, it is important to promote a healthy lifestyle to prevent prediabetes. This study aimed to determine the effects of green coffee (GC), chlorogenic acid (CGA) intake, and exercise training (EX) on hepatic lipid metabolism in prediabetes male C57BL/6 mice.
Methods
Forty-nine mice were randomly divided into two groups feeding with a normal diet (n=7) or a high-fat diet (HFD, n=42) for 12 weeks. Then, HFD mice were further divided into six groups (n=7/group): control (pre-D), GC, CGA, EX, GC+EX, and CGA+EX. After additional 10 weeks under the same diet, plasma, and liver samples were obtained.
Results
HFD-induced prediabetes conditions with increases in body weight, glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipid profiles were alleviated in all treatment groups. Acsl3, a candidate gene identified through an in silico approach, was lowered in the pre-D group, while treatments partly restored it. HFD induced adverse alterations of de novo lipogenesis- and β oxidation-associated molecules in the liver. However, GC and CGA supplementation and EX reversed or ameliorated these changes. In most cases, GC or CGA supplementation combined with EX has no synergistic effect and the GC group had similar results to the CGA group.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that regular exercise is an effective non-therapeutic approach for prediabetes, and CGA supplementation could be an alternative to partially mimic the beneficial effects of exercise on prediabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research progress on the pharmacological activity and mechanism of chlorogenic acid in alleviating acute kidney injury in sepsis patients
Perioperative Precision Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research progress on the pharmacological activity and mechanism of chlorogenic acid in alleviating acute kidney injury in sepsis patients
- Technology/Device
- Clinical and Lifestyle Determinants of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Da Young Lee, Namho Kim, Inha Jung, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Jihee Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sung-Min Park, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):826-836. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0273

- 1,773 View
- 191 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
There was limited evidence to evaluate the association between lifestyle habits and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) metrics. Thus, we aimed to depict the behavioral and metabolic determinants of CGM metrics in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This is a prospective observational study. We analyzed data from 122 insulin-treated patients with T2DM. Participants wore Dexcom G6 and Fitbit, and diet information was identified for 10 days. Multivariate-adjusted logistic regression analysis was performed for the simultaneous achievement of CGM-based targets, defined by the percentage of time in terms of hyper, hypoglycemia and glycemic variability (GV). Intake of macronutrients and fiber, step counts, sleep, postprandial C-peptide-to-glucose ratio (PCGR), information about glucose lowering medications and metabolic factors were added to the analyses. Additionally, we evaluated the impact of the distribution of energy and macronutrient during a day, and snack consumption on CGM metrics.
Results
Logistic regression analysis revealed that female, participants with high PCGR, low glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and daytime step count had a higher probability of achieving all targets based on CGM (odds ratios [95% confidence intervals] which were 0.24 [0.09 to 0.65], 1.34 [1.03 to 1.25], 0.95 [0.9 to 0.99], and 1.15 [1.03 to 1.29], respectively). And participants who ate snacks showed a shorter period of hyperglycemia and less GV compared to those without.
Conclusion
We confirmed that residual insulin secretion, daytime step count, HbA1c, and women were the most relevant determinants of adequate glycemic control in insulin-treated patients with T2DM. In addition, individuals with snack consumption were exposed to lower times of hyperglycemia and GV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Lotte Bogaert, Iris Willems, Patrick Calders, Eveline Dirinck, Manon Kinaupenne, Marga Decraene, Bruno Lapauw, Boyd Strumane, Margot Van Daele, Vera Verbestel, Marieke De Craemer
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(4): 102995. CrossRef
- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Review
- Complications
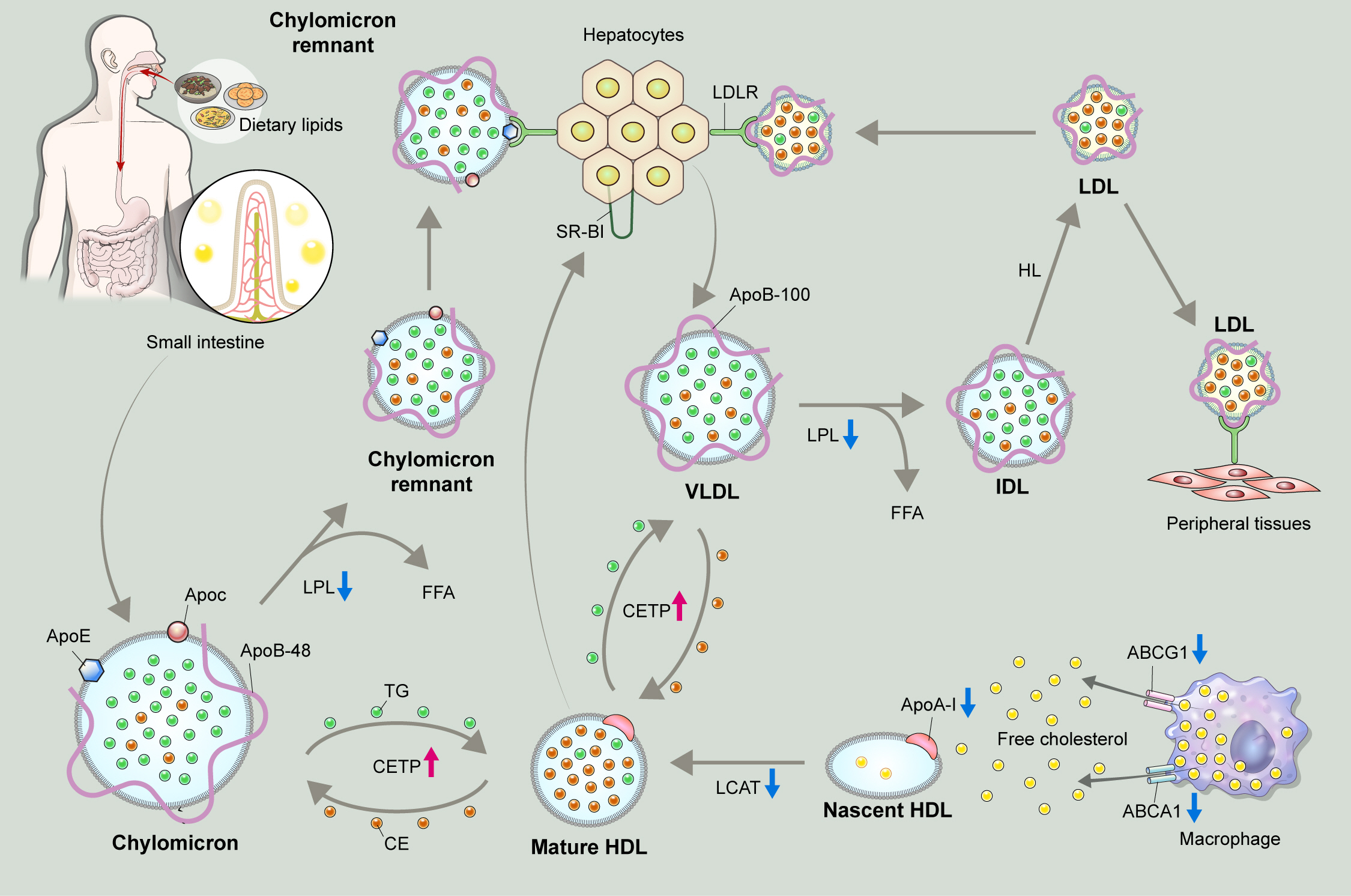
- Dyslipidemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Updated Overview
- Sang Heon Suh, Soo Wan Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):612-629. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0067
- 3,035 View
- 408 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Dyslipidemia is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor. Whereas the recommendations for the treatment target of dyslipidemia in the general population are being more and more rigorous, the 2013 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes clinical practice guideline for lipid management in chronic kidney disease (CKD) presented a relatively conservative approach with respect to the indication of lipid lowering therapy and therapeutic monitoring among the patients with CKD. This may be largely attributed to the lack of high-quality evidence derived from CKD population, among whom the overall feature of dyslipidemia is considerably distinctive to that of general population. In this review article, we cover the characteristic features of dyslipidemia and impact of dyslipidemia on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD. We also review the current evidence on lipid lowering therapy to modify the risk of cardiovascular events in this population. We finally discuss the association between dyslipidemia and CKD progression and the potential strategy to delay the progression of CKD in relation to lipid lowering therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
Jafar Karami, Bahman Razi, Danyal Imani, Saeed Aslani, Mahdi Pakjoo, Mahdieh Fasihi, Keyhan Mohammadi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(5): 362. CrossRef
- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
Original Article
- Lifestyle
- Clinical Effects of a Home Care Pilot Program for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Sejeong Lee, KyungYi Kim, Ji Eun Kim, Yura Hyun, Minyoung Lee, Myung-Il Hahm, Sang Gyu Lee, Eun Seok Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):693-702. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0170

- 1,891 View
- 138 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Given the importance of continuous self-care for people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM), the Ministry of Health and Welfare of Korea launched a pilot program for chronic disease management. Herein, we applied a home care pilot program to people with T1DM to investigate its effects.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study was conducted at a single tertiary hospital (January 2019 to October 2021). A multidisciplinary team comprising doctors, nurses, and clinical nutritionists provided specialized education and periodically assessed patients’ health status through phone calls or text messages. A linear mixed model adjusting for age, sex, and body mass index was used to analyze the glycemic control changes before and after implementing the program between the intervention and control groups.
Results
Among 408 people with T1DM, 196 were enrolled in the intervention group and 212 in the control group. The reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) after the program was significantly greater in the intervention group than in the control group (estimated marginal mean, –0.57% vs. –0.23%, P=0.008); the same trend was confirmed for glycoalbumin (GA) (–3.2% vs. –0.39%, P<0.001). More patients achieved the target values of HbA1c (<7.0%) and GA (<20%) in the intervention group than in the control group at the 9-month follow-up (34.5% vs. 19.6% and 46.7% vs. 28.0%, respectively).
Conclusion
The home care program for T1DM was clinically effective in improving glycemic control and may provide an efficient care option for people with T1DM, and positive outcomes are expected to expand the program to include more patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glycemic outcomes and patient satisfaction and self-management improves in transition from standard to virtual multidisciplinary care
Noga Minsky, Liat Arnon Klug, Tatyana Kolobov, Elizabeth Tarshish, Yuval Shalev Many, Aviva Lipsitz, Amna Jabarin, Nicole Morozov, Dania Halperin, Moshe Shalom, Rachel Nissanholtz-Gannot, Genya Aharon-Hananel, Amir Tirosh, Orly Tamir
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111587. CrossRef
- Glycemic outcomes and patient satisfaction and self-management improves in transition from standard to virtual multidisciplinary care
Review
- Basic Research
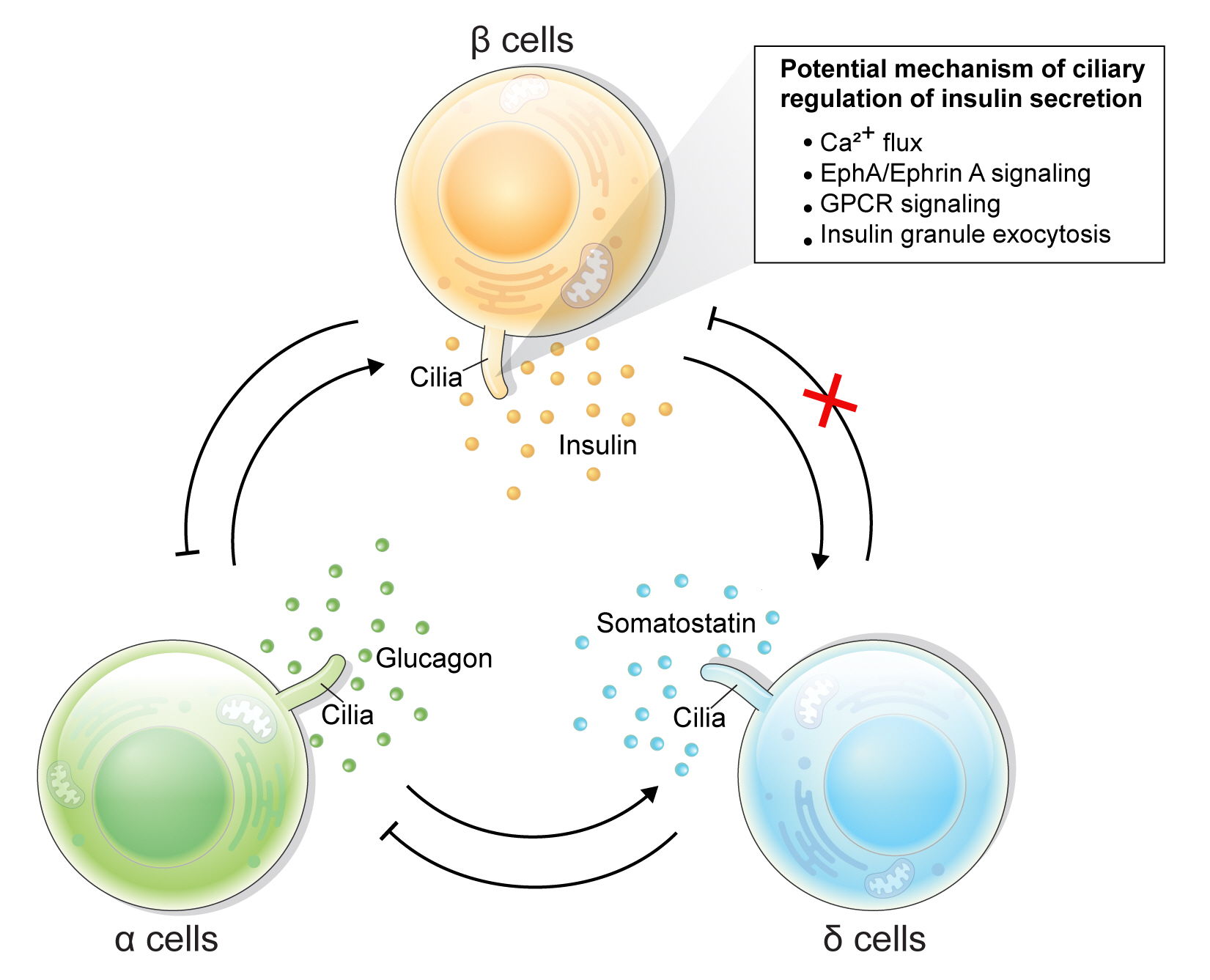
- Rediscovering Primary Cilia in Pancreatic Islets
- Eun Young Lee, Jing W. Hughes
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):454-469. Published online April 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0442
- 2,563 View
- 240 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Primary cilia are microtubule-based sensory and signaling organelles on the surfaces of most eukaryotic cells. Despite their early description by microscopy studies, islet cilia had not been examined in the functional context until recent decades. In pancreatic islets as in other tissues, primary cilia facilitate crucial developmental and signaling pathways in response to extracellular stimuli. Many human developmental and genetic disorders are associated with ciliary dysfunction, some manifesting as obesity and diabetes. Understanding the basis for metabolic diseases in human ciliopathies has been aided by close examination of cilia action in pancreatic islets at cellular and molecular levels. In this article, we review the evidence for ciliary expression on islet cells, known roles of cilia in pancreas development and islet hormone secretion, and summarize metabolic manifestations of human ciliopathy syndromes. We discuss emerging data on primary cilia regulation of islet cell signaling and the structural basis of cilia-mediated cell crosstalk, and offer our interpretation on the role of cilia in glucose homeostasis and human diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beta cell primary cilia mediate somatostatin responsiveness via SSTR3
Samantha E. Adamson, Zipeng A. Li, Jing W. Hughes
Islets.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Beta cell primary cilia mediate somatostatin responsiveness via SSTR3
Response
- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
- Hwi Seung Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):304-305. Published online March 15, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0058
- 1,599 View
- 119 Download
- 1 Crossref
Original Articles
- Basic Research
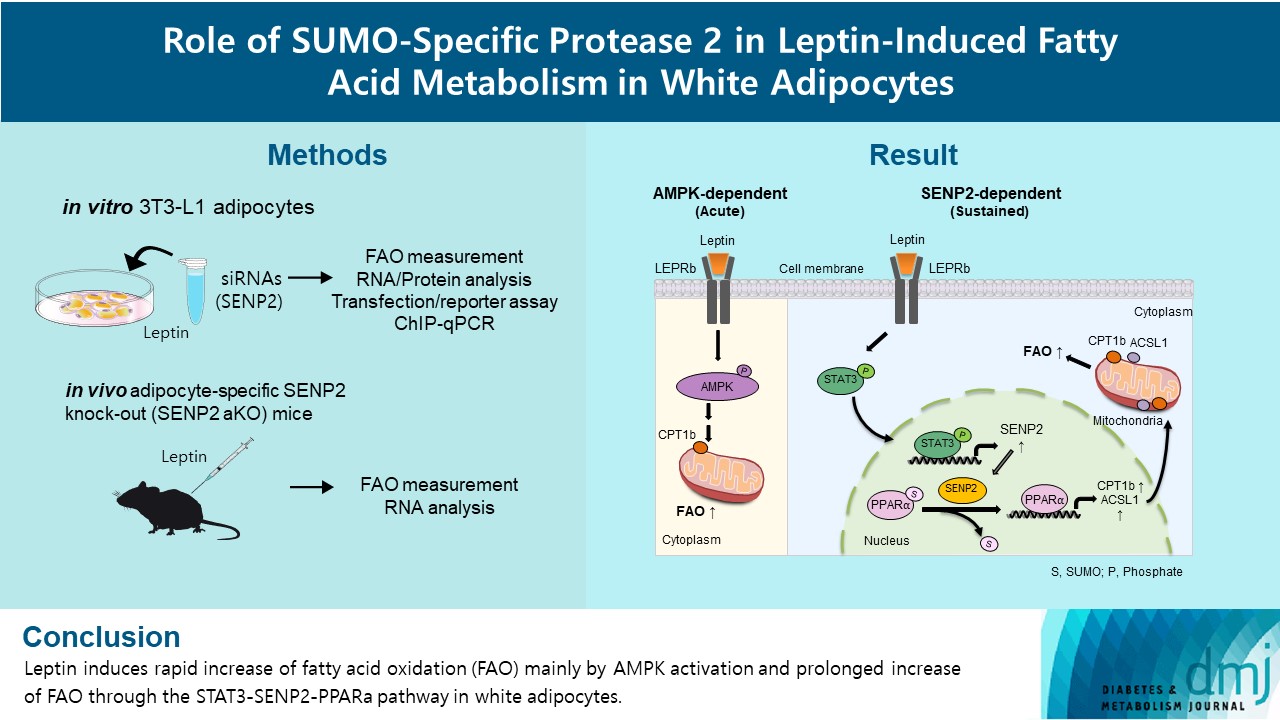
- Role of SUMO-Specific Protease 2 in Leptin-Induced Fatty Acid Metabolism in White Adipocytes
- Praise Chanmee Kim, Ji Seon Lee, Sung Soo Chung, Kyong Soo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):382-393. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0156
- 3,172 View
- 158 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Leptin is a 16-kDa fat-derived hormone with a primary role in controlling adipose tissue levels. Leptin increases fatty acid oxidation (FAO) acutely through adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and on delay through the SUMO-specific protease 2 (SENP2)–peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ/γ (PPARδ/γ) pathway in skeletal muscle. Leptin also directly increases FAO and decreases lipogenesis in adipocytes; however, the mechanism behind these effects remains unknown. Here, we investigated the role of SENP2 in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism by leptin in adipocytes and white adipose tissues.
Methods
The effects of leptin mediated by SENP2 on fatty acid metabolism were tested by siRNA-mediated knockdown in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The role of SENP2 was confirmed in vivo using adipocyte-specific Senp2 knockout (Senp2-aKO) mice. We revealed the molecular mechanism involved in the leptin-induced transcriptional regulation of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1b (Cpt1b) and long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase 1 (Acsl1) using transfection/reporter assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation.
Results
SENP2 mediated the increased expression of FAO-associated enzymes, CPT1b and ACSL1, which peaked 24 hours after leptin treatment in adipocytes. In contrast, leptin stimulated FAO through AMPK during the initial several hours after treatment. In white adipose tissues, FAO and mRNA levels of Cpt1b and Acsl1 were increased by 2-fold 24 hours after leptin injection in control mice but not in Senp2-aKO mice. Leptin increased PPARα binding to the Cpt1b and Acsl1 promoters in adipocytes through SENP2.
Conclusion
These results suggest that the SENP2-PPARα pathway plays an important role in leptin-induced FAO in white adipocytes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermittent cold stimulation affects energy metabolism and improves stress resistance in broiler heart
Tingting Li, Haidong Wei, Shijie Zhang, Xiaotao Liu, Lu Xing, Yuanyuan Liu, Rixin Gong, Jianhong Li
Poultry Science.2024; 103(1): 103190. CrossRef
- Intermittent cold stimulation affects energy metabolism and improves stress resistance in broiler heart
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
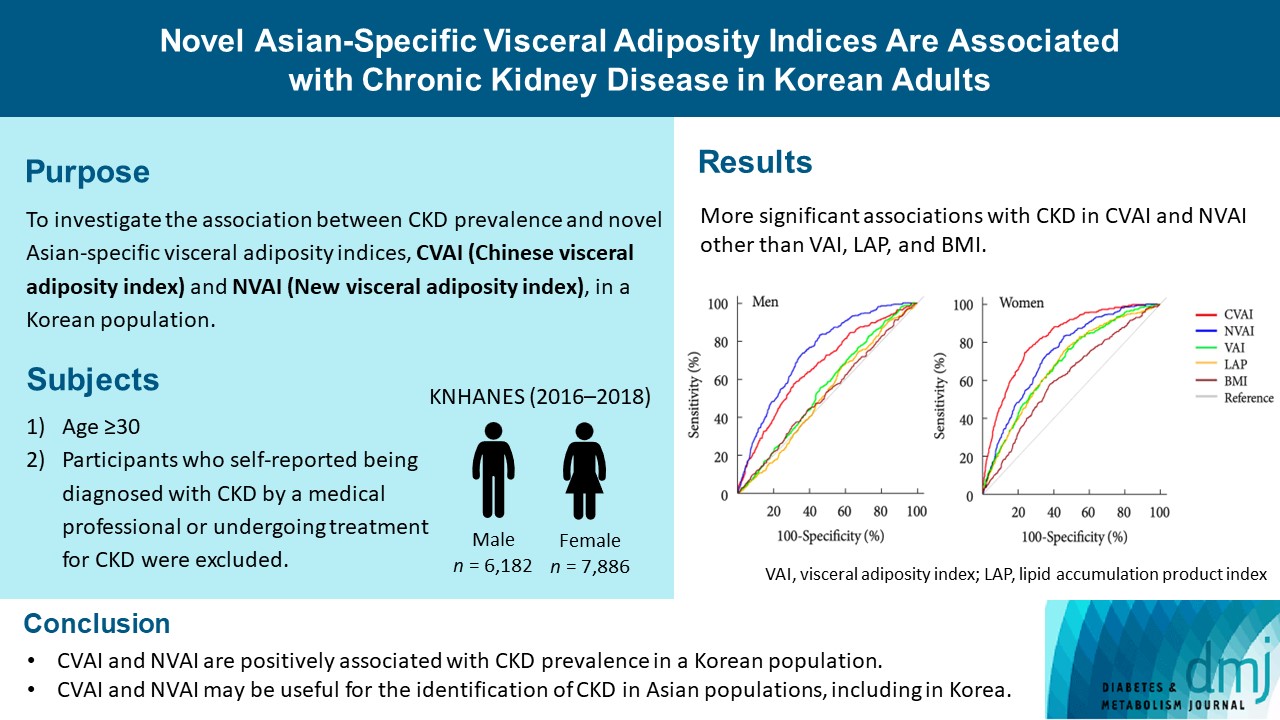
- Novel Asian-Specific Visceral Adiposity Indices Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Korean Adults
- Jonghwa Jin, Hyein Woo, Youngeun Jang, Won-Ki Lee, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):426-436. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0099
- 2,452 View
- 128 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The Chinese visceral adiposity index (CVAI) and new visceral adiposity index (NVAI) are novel indices of visceral adiposity used to predict metabolic and cardiovascular diseases in Asian populations. However, the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have not been investigated. We aimed to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with the prevalence of CKD in Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 14,068 participants in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (6,182 men and 7,886 women) were included. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were employed to compare the associations between indices of adiposity and CKD, and a logistic regression model was used to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with CKD prevalence.
Results
The areas under the ROC curves for CVAI and NVAI were significantly larger than for the other indices, including the visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product, in both men and women (all P<0.001). In addition, high CVAI or NVAI was significantly associated with a high CKD prevalence in both men (odds ratio [OR], 2.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31 to 3.48 in CVAI and OR, 6.47; 95% CI, 2.91 to 14.38 in NVAI, P<0.05) and women (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 1.85 to 12.79 in CVAI and OR, 3.03; 95% CI, 1.35 to 6.82 in NVAI, P<0.05); this association remained significant after adjustment for multiple confounding factors in men and women.
Conclusion
CVAI and NVAI are positively associated with CKD prevalence in a Korean population. CVAI and NVAI may be useful for the identification of CKD in Asian populations, including in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
Zenglei Zhang, Lin Zhao, Yiting Lu, Xu Meng, Xianliang Zhou
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
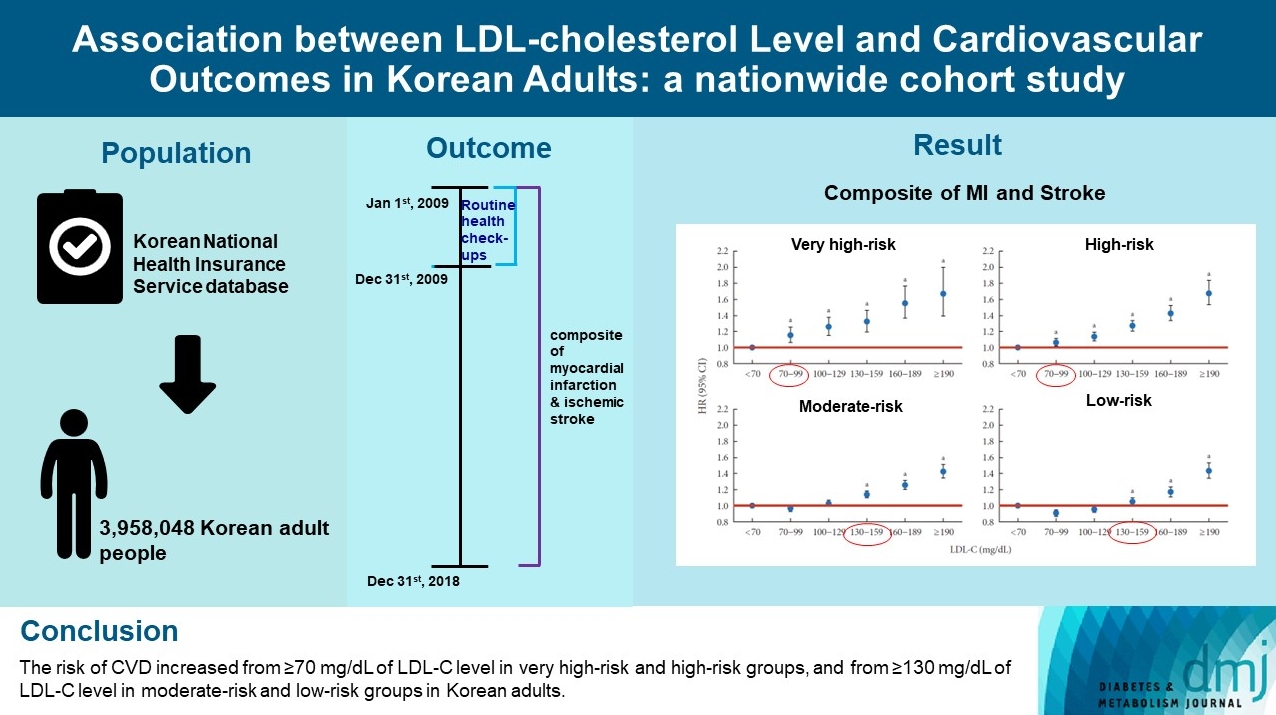
- Association between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Junghyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Practice Guideline of Korean Lipid and Atheroscelerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):59-71. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0320
- 2,702 View
- 224 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To validate the treatment target of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level according to the cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk which was recommended by Korean dyslipidemia guideline.
Methods
We used the Korean National Health Insurance Service database which included 3,958,048 people aged 20 to 89 years who underwent regular health screening. The primary outcome was incident CVD, defined as a composite of myocardial infarction and stroke during the follow-up period from 2009 to 2018.
Results
The risk of CVD increased from LDL-C level of 70 mg/dL in very high-risk and high-risk groups and from 130 mg/dL in moderate-risk and low-risk groups. Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) of LDL-C ranges 70–99, 100–129, 130–159, 160–189, and ≥190 mg/dL were 1.20 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08–1.33), 1.27 (1.15–1.42), 1.39 (1.23–1.56), 1.69 (1.45–1.96), and 1.84 (1.49– 2.27) in very high-risk group, and 1.07 (1.02–1.13), 1.16 (1.10–1.21), 1.29 (1.22–1.36), 1.45 (1.36–1.55), and 1.73 (1.58–1.90) in high-risk group. Adjusted HRs (95% CI) of LDL-C ranges 130–159, 160–189, and ≥190 mg/dL were 1.15 (1.11–1.20), 1.28 (1.22– 1.34), and 1.45 (1.36–1.54) in moderate-risk group and 1.07 (1.02–1.13), 1.20 (1.13–1.26), and 1.47 (1.37–1.57) in low-risk group.
Conclusion
We confirmed the incidence of CVD was increased in higher LDL-C range. The risk of CVD increased from ≥70 mg/dL of LDL-C in very high-risk and high-risk groups, and from ≥130 mg/dL of LDL-C in moderate-risk and low-risk groups in Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Triple Combination of Olmesartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin in Hypertensive Patients with Low-to-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Control, Phase IV Clinical Trial
Byung Jin Kim, Kwang Soo Cha, Wook Hyun Cho, Eung Ju Kim, Seung-Hyuk Choi, Moo Hyun Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Jun-Bean Park, Seong-Mi Park, Il Suk Sohn, Kyu Hyung Ryu, In-Ho Chae
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Triple Combination of Olmesartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin in Hypertensive Patients with Low-to-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Control, Phase IV Clinical Trial
Review
- Basic Research
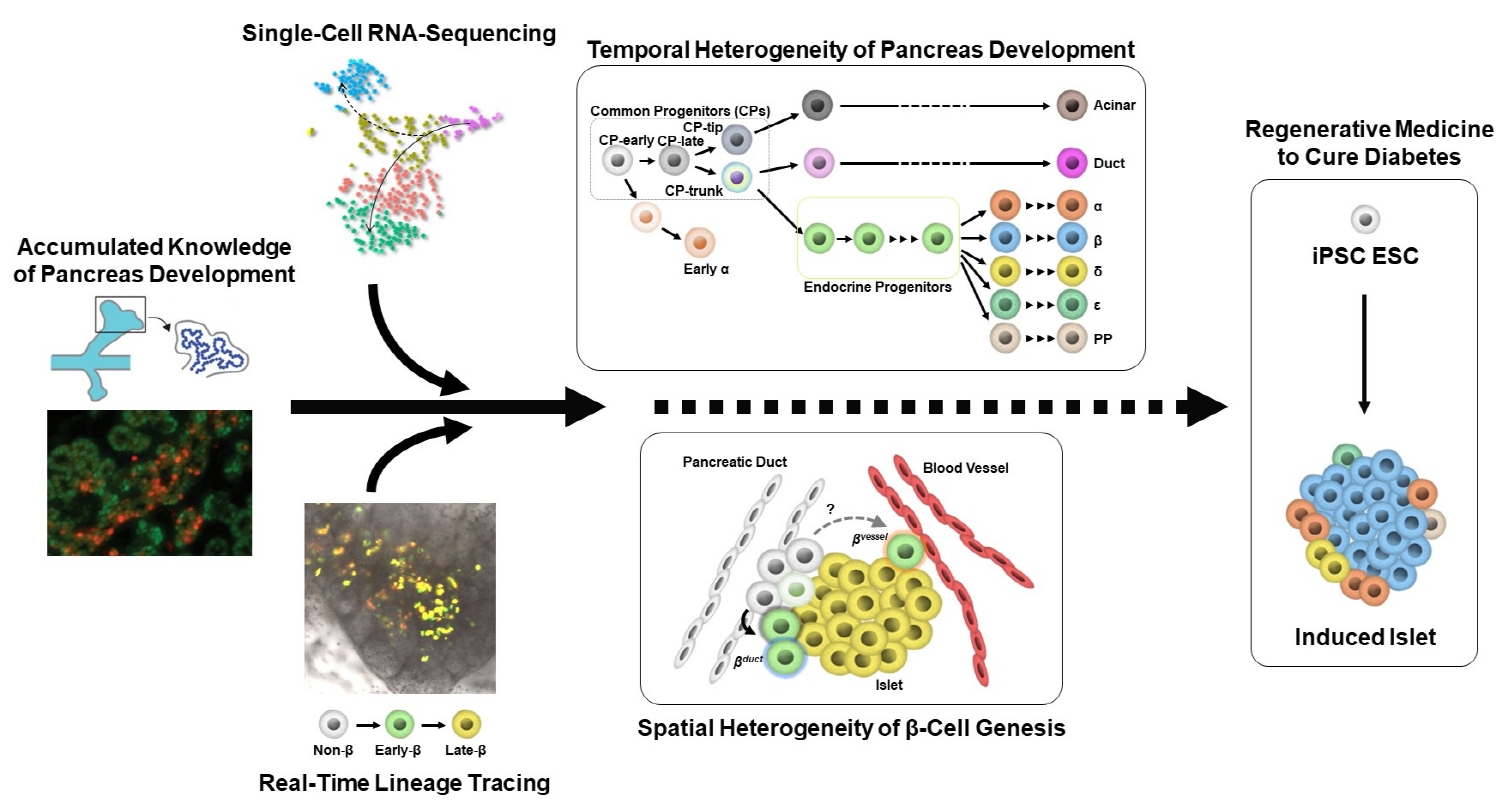
- Heterogeneity of Islet Cells during Embryogenesis and Differentiation
- Shugo Sasaki, Takeshi Miyatsuka
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):173-184. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0324
- 3,715 View
- 248 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes is caused by insufficient insulin secretion due to β-cell dysfunction and/or β-cell loss. Therefore, the restoration of functional β-cells by the induction of β-cell differentiation from embryonic stem (ES) and induced-pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, or from somatic non-β-cells, may be a promising curative therapy. To establish an efficient and feasible method for generating functional insulin-producing cells, comprehensive knowledge of pancreas development and β-cell differentiation, including the mechanisms driving cell fate decisions and endocrine cell maturation is crucial. Recent advances in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technologies have opened a new era in pancreas development and diabetes research, leading to clarification of the detailed transcriptomes of individual insulin-producing cells. Such extensive high-resolution data enables the inference of developmental trajectories during cell transitions and gene regulatory networks. Additionally, advancements in stem cell research have not only enabled their immediate clinical application, but also has made it possible to observe the genetic dynamics of human cell development and maturation in a dish. In this review, we provide an overview of the heterogeneity of islet cells during embryogenesis and differentiation as demonstrated by scRNA-seq studies on the developing and adult pancreata, with implications for the future application of regenerative medicine for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Newly discovered knowledge pertaining to glucagon and its clinical applications
Dan Kawamori, Shugo Sasaki
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(7): 829. CrossRef
- Newly discovered knowledge pertaining to glucagon and its clinical applications
Response
- Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
- Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):815-816. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0296
- [Original]
- 2,464 View
- 118 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Insights on the Use of Insulin and the Potential Use of Insulin Mimetics in Targeting Insulin Signalling in Alzheimer’s Disease
Amy Woodfield, Tatiana Gonzales, Erik Helmerhorst, Simon Laws, Philip Newsholme, Tenielle Porter, Giuseppe Verdile
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15811. CrossRef
- Current Insights on the Use of Insulin and the Potential Use of Insulin Mimetics in Targeting Insulin Signalling in Alzheimer’s Disease
Corrigendum
- New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
- Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):817-818. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0295
- Corrects: Diabetes Metab J 2022;46(4):517
- 2,047 View
- 144 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





