
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Original Article
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):201-210. Published online February 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0375
- 3,183 View
- 212 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
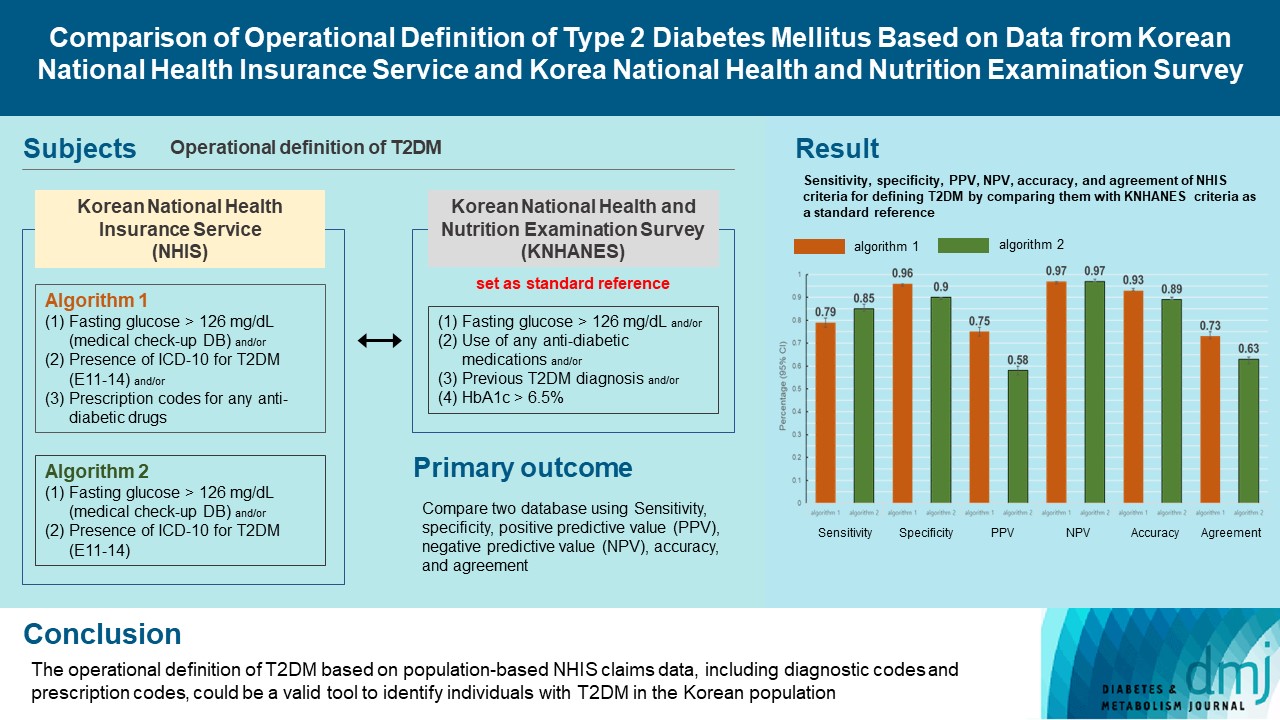
We evaluated the validity and reliability of the operational definition of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database.
Methods
Adult subjects (≥40 years old) included in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) from 2008 to 2017 were merged with those from the NHIS health check-up database, producing a cross-sectional dataset. We evaluated the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and agreement of the NHIS criteria for defining T2DM by comparing them with the KNHANES criteria as a standard reference.
Results
In the study population (n=13,006), two algorithms were devised to determine from the NHIS dataset whether the diagnostic claim codes for T2DM were accompanied by prescription codes for anti-diabetic drugs (algorithm 1) or not (algorithm 2). Using these algorithms, the prevalence of T2DM was 14.9% (n=1,942; algorithm 1) and 20.8% (n=2,707; algorithm 2). Good reliability in defining T2DM was observed for both algorithms (Kappa index, 0.73 [algorithm 1], 0.63 [algorithm 2]). However, the accuracy (0.93 vs. 0.89) and specificity (0.96 vs. 0.90) tended to be higher for algorithm 1 than for algorithm 2. The validity (accuracy, ranging from 0.91 to 0.95) and reliability (Kappa index, ranging from 0.68 to 0.78) of defining T2DM by NHIS criteria were independent of age, sex, socioeconomic status, and accompanied hypertension or dyslipidemia.
Conclusion
The operational definition of T2DM based on population-based NHIS claims data, including diagnostic codes and prescription codes, could be a valid tool to identify individuals with T2DM in the Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in young Korean adults
Junchul Ha, Oak-Kee Hong, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; : 111584. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in young Korean adults
Review
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Implications across the Life Span
- Brandy Wicklow, Ravi Retnakaran
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):333-344. Published online February 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0348

- 5,060 View
- 396 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) has historically been perceived as a medical complication of pregnancy that also serves as a harbinger of maternal risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the future. In recent decades, a growing body of evidence has detailed additional lifelong implications that extend beyond T2DM, including an elevated risk of ultimately developing cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, the risk factors that mediate this lifetime cardiovascular risk are evident not only after delivery but are present even before the pregnancy in which GDM is first diagnosed. The concept thus emerging from these data is that the diagnosis of GDM enables the identification of women who are already on an enhanced track of cardiometabolic risk that starts early in life. Studies of the offspring of pregnancies complicated by diabetes now suggest that the earliest underpinnings of this cardiometabolic risk profile may be determined in utero and may first manifest clinically in childhood. Accordingly, from this perspective, GDM is now seen as a chronic metabolic disorder that holds implications across the life span of both mother and child.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ATP5me alleviates high glucose-induced myocardial cell injury
Qingsha Hou, Fang Yan, Xiuling Li, Huanling Liu, Xiang Yang, Xudong Dong
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 129: 111626. CrossRef - Prevalence and Predictors of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Overt Diabetes in Pregnancy: A Secondary Analysis of Nationwide Data from India
Saurav Basu, Vansh Maheshwari, Rutul Gokalani, Chandrakant Lahariya
Preventive Medicine: Research & Reviews.2024; 1(1): 52. CrossRef - Serum betaine and dimethylglycine in mid-pregnancy and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a case-control study
Ziqing Zhou, Yao Yao, Yanan Sun, Xin Wang, Shang Huang, Jianli Hou, Lijun Wang, Fengxiang Wei
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality assessment of videos on social media platforms related to gestational diabetes mellitus in China: A cross-section study
Qin-Yu Cai, Jing Tang, Si-Zhe Meng, Yi Sun, Xia Lan, Tai-Hang Liu
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e29020. CrossRef - Inflammation and decreased cardiovagal modulation are linked to stress and depression at 36th week of pregnancy in gestational diabetes mellitus
Manoharan Renugasundari, Gopal Krushna Pal, Latha Chaturvedula, Nivedita Nanda, K. T. Harichandrakumar, Thiyagarajan Durgadevi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Women with gestational diabetes mellitus, controlled for plasma glucose level, exhibit maternal and fetal dyslipidaemia that may warrant treatment
Barbara J. Meyer, Colin Cortie, Marloes Dekker-Nitert, Helen L. Barrett, Dilys J. Freeman
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 204: 110929. CrossRef - Pregnancy diet to prevent gestational diabetes: study design and dietary assessments
Sylvia H. Ley
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2023; 118(5): 847. CrossRef
- ATP5me alleviates high glucose-induced myocardial cell injury
Original Article
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
- Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):211-219. Published online February 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0346
- 3,472 View
- 258 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
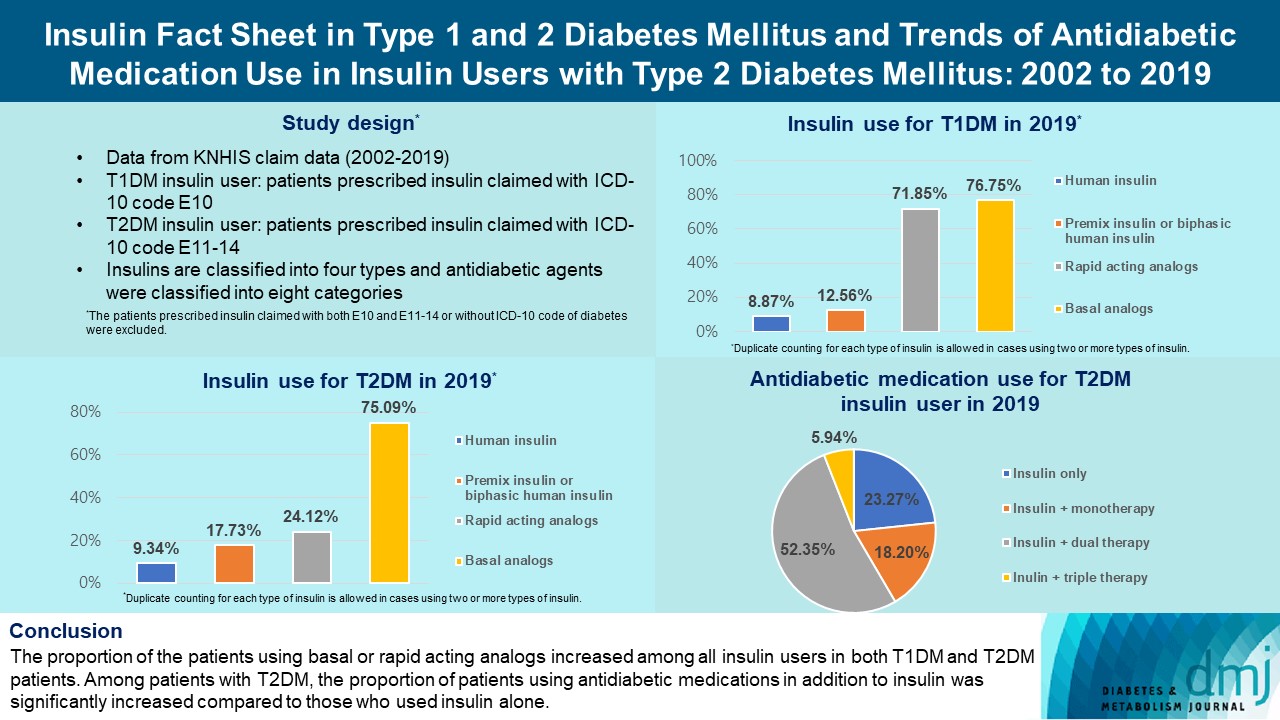
This study investigated the trends of insulin use among Korean patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Changes in prescription of antidiabetic medications in T2DM patients taking insulin therapy were evaluated.
Methods
We analyzed data from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea to evaluate the prevalence of insulin users and trends of insulin use in T1DM and T2DM patients from January 2002 to December 2019. We also investigated numbers and types of antidiabetic medications in insulin users with T2DM.
Results
The overall total number of insulin users increased from 2002 to 2019, reaching 348,254 for T2DM and 20,287 for T1DM in 2019 compared with 109,974 for T2DM and 34,972 for T1DM in 2002. The proportion of patients using basal analogs and short acting analogs have increased and those using human insulin, premixed insulin, or biphasic human insulin have decreased (rapid acting analogs: 71.85% and 24.12% in T1DM and T2DM, respectively, in 2019; basal analogs: 76.75% and 75.09% in T1DM and T2DM, respectively, in 2019). The use of other antidiabetic medication in addition to insulin increased for T2DM, especially in dual therapy, reaching up to 52.35% in 2019 compared with 16.72% in 2002.
Conclusion
The proportion of the patients using basal or rapid acting analogs increased among all insulin users in both T1DM and T2DM patients. Among patients with T2DM, the proportion of patients using antidiabetic medications in addition to insulin was significantly increased compared to those who used insulin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
Heeyoung Kim, Choon Ok Kim, Hyeonsoo Park, Min Soo Park, Dasohm Kim, Taegon Hong, Yesong Shin, Byung Hak Jin
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 31(1): 59. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Response
- Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:767-80)
- Daniel Nyarko Hukportie, Fu-Rong Li, Rui Zhou, Jia-Zhen Zheng, Xiao-Xiang Wu, Xian-Bo Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):150-151. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0007
- 1,334 View
- 92 Download
Letter
- Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:767-80)
- Yun Kyung Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):147-149. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0002
- 1,271 View
- 93 Download
Editorial
- Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level for Primary Prevention in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Yoon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):42-44. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0454
- 1,646 View
- 133 Download
Review
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
- Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Society of Heart Failure
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):10-26. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0420
- 4,267 View
- 406 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
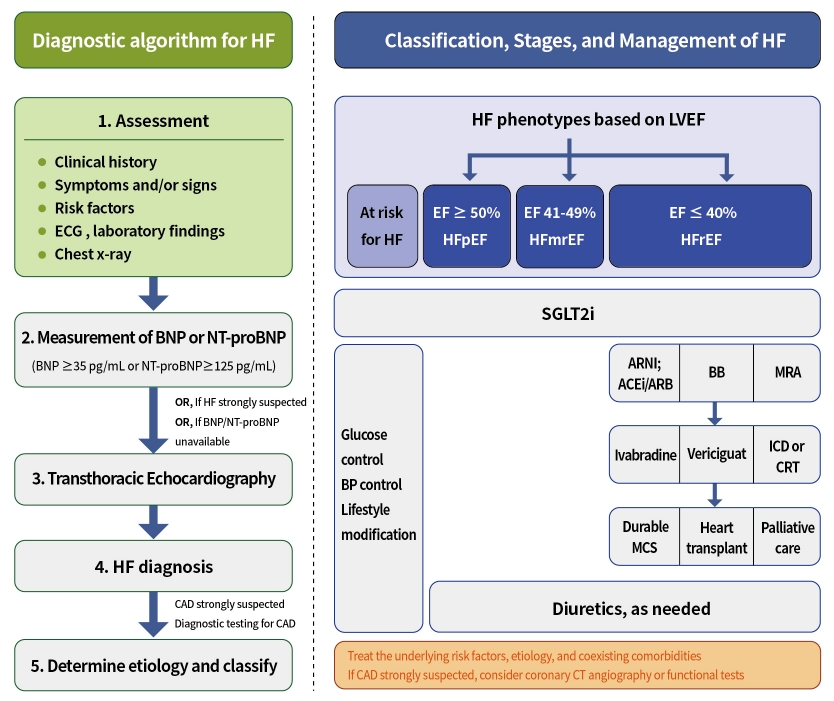
ePub - Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for the development of heart failure. Furthermore, the prognosis of heart failure is worse in patients with diabetes mellitus than in those without it. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper management of heart failure in patients with diabetes mellitus are important. This review discusses the current criteria for diagnosis and screening tools for heart failure and the currently recommended pharmacological therapies for heart failure. We also highlight the effects of anti-diabetic medications on heart failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Hae Jin Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kyu Yeon Hur, In-Kyung Jeong, Mark Yorek
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin versus glimepiride on cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin: The gemi‐heart study
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Jun Hwa Hong, In‐Chang Hwang, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2181. CrossRef - Optimization of guideline-directed medical treatment for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction
Minjung Bak, Jin-Oh Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(5): 595. CrossRef
- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography
- Hwi Seung Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, In Young Bae, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):104-117. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0081
- 3,173 View
- 175 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
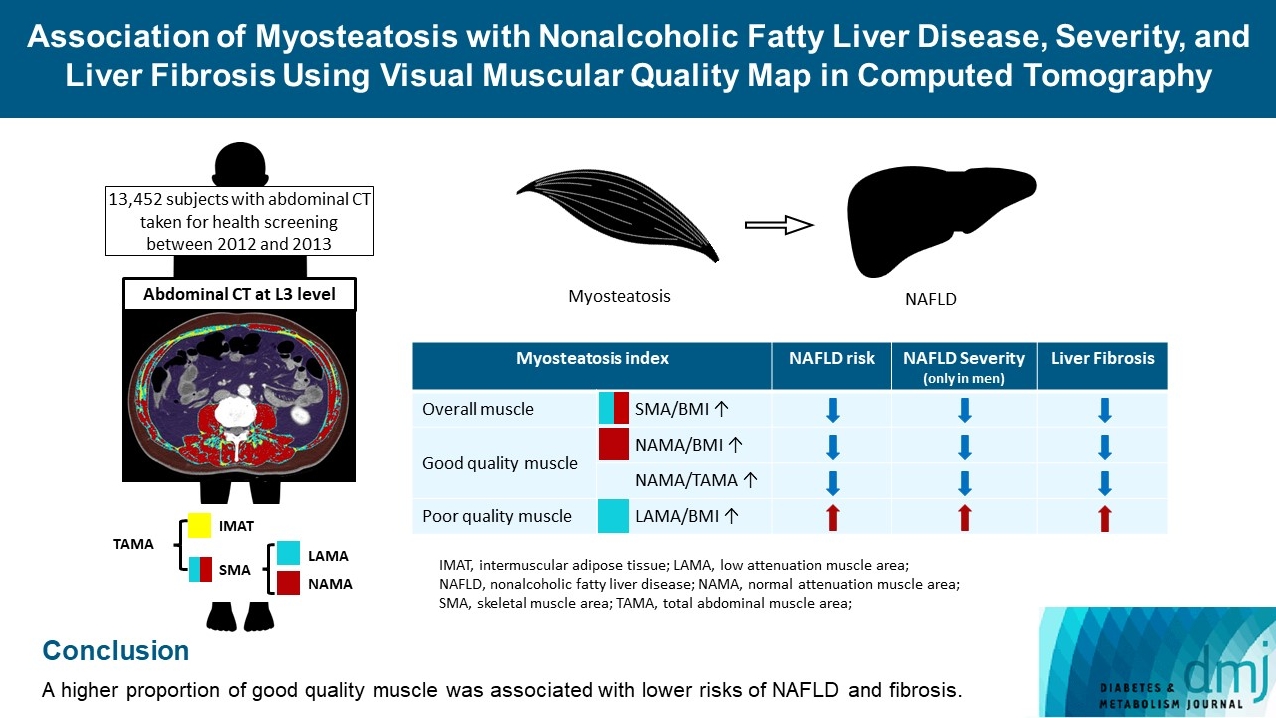
The association of myosteatosis measured using visual muscular quality map in computed tomography (CT) with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), its severity, and fibrosis was analyzed in a large population.
Methods
Subjects (n=13,452) with abdominal CT between 2012 and 2013 were measured total abdominal muscle area (TAMA) at L3 level. TAMA was segmented into intramuscular adipose tissue and skeletal muscle area (SMA), which was further classified into normal attenuation muscle area (NAMA) and low attenuation muscle area (LAMA). The following variables were adopted as indicators of myosteatosis: SMA/body mass index (BMI), NAMA/BMI, NAMA/TAMA, and LAMA/BMI. NAFLD and its severity were assessed by ultrasonography, and liver fibrosis was measured by calculating the NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) and fibrosis-4 index (FIB-4) scores.
Results
According to multiple logistic regression analyses, as quartiles of SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA increased, the odds ratios (ORs) for NAFLD decreased in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all). The ORs of moderate/severe NAFLD were significantly higher in the Q1 group than in the Q4 group for SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA in men. The ORs of intermediate/high liver fibrosis scores assessed by NFS and FIB-4 scores increased linearly with decreasing quartiles for SMA/BMI, NAMA/BMI, and NAMA/TAMA in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all). Conversely, the risk for NAFLD and fibrosis were positively associated with LAMA/BMI quartiles in each sex (P for trend <0.001 for all).
Conclusion
A higher proportion of good quality muscle was associated with lower risks of NAFLD and fibrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
Hwi Seung Kim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 304. CrossRef - Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 301. CrossRef - Sarcopenia, a condition shared by various diseases: can we alleviate or delay the progression?
Giovanni Tarantino, Gaia Sinatti, Vincenzo Citro, Silvano Santini, Clara Balsano
Internal and Emergency Medicine.2023; 18(7): 1887. CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Current view of the surgical anatomy of the anterolateral abdominal wall muscles and their aponeuroses
A.V. Pavlov, A.S. Baranova, A.V. Fedoseyev, A.I. Vvedensky, G.S. Lazutina, N.V. Ovchinnikova, I.V. Bakharev
Operativnaya khirurgiya i klinicheskaya anatomiya (Pirogovskii nauchnyi zhurnal).2023; 7(3): 44. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef
- Association of Myosteatosis with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Severity, and Liver Fibrosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map in Computed Tomography (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:104-17)
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Cardiovascular Outcomes according to Comorbidities and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Practice Guideline of Korean Lipid and Atheroscelerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):45-58. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0344
- 2,895 View
- 257 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
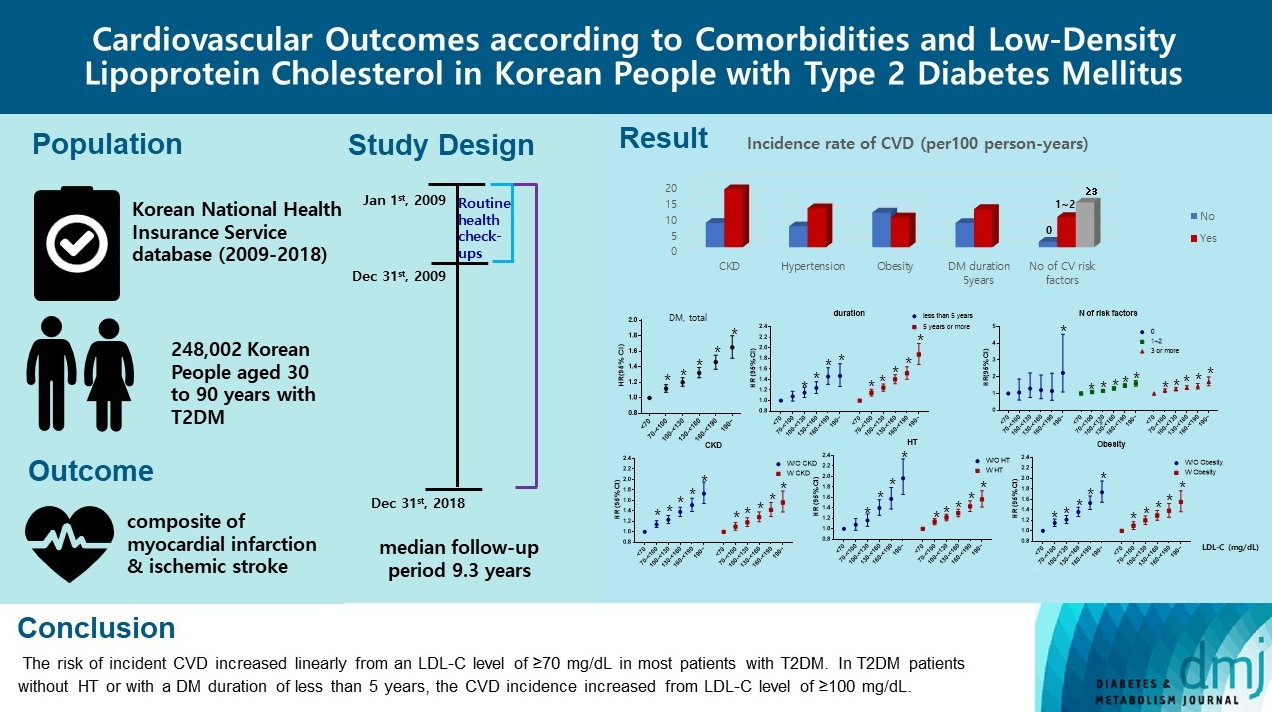
There are no clear data to support the cardiovascular (CV) risk categories and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) treatment goals in Korean people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We evaluated the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) according to comorbidities and suggested LDL-C treatment goals in Korean people with T2DM in nationwide cohort data.
Methods
Using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database, 248,002 people aged 30 to 90 years with T2DM who underwent routine health check-ups during 2009 were included. Subjects with previous CVD were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was incident CVD, defined as a composite of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke during the follow-up period from 2009 to 2018.
Results
The mean age of the study participants was 59.6±10.9 years, and median follow-up period was 9.3 years. CVD incidence increased in the order of DM duration of 5 years or more (12.04/1,000 person-years), hypertension (HT) (12.27/1,000 personyears), three or more CV risk factors (14.10/1,000 person-years), and chronic kidney disease (18.28/1,000 person-years). The risk of incident CVD increased linearly from an LDL-C level of ≥70 mg/dL in most patients with T2DM. In T2DM patients without HT or with a DM duration of less than 5 years, the CVD incidence increased from LDL-C level of ≥100 mg/dL.
Conclusion
For primary prevention of CVD in Korean adults with T2DM, it can be helpful to lower LDL-C targets when there are chronic kidney disease, HT, a long duration of diabetes mellitus, or three or more CV risk factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level for Primary Prevention in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Yoon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 42. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Significant Gap Between Guidelines and Practice in the Management of LDL Cholesterol: Insight From the Survey of the Korean Society of Myocardial Infarction
Sang Yeub Lee, Kyung Hoon Cho, Jang Hoon Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jin yong Hwang, Myung Ho Jeong, Weon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Junghyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Practice Guideline of Korean Lipid and Atheroscelerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):59-71. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0320
- 2,654 View
- 222 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
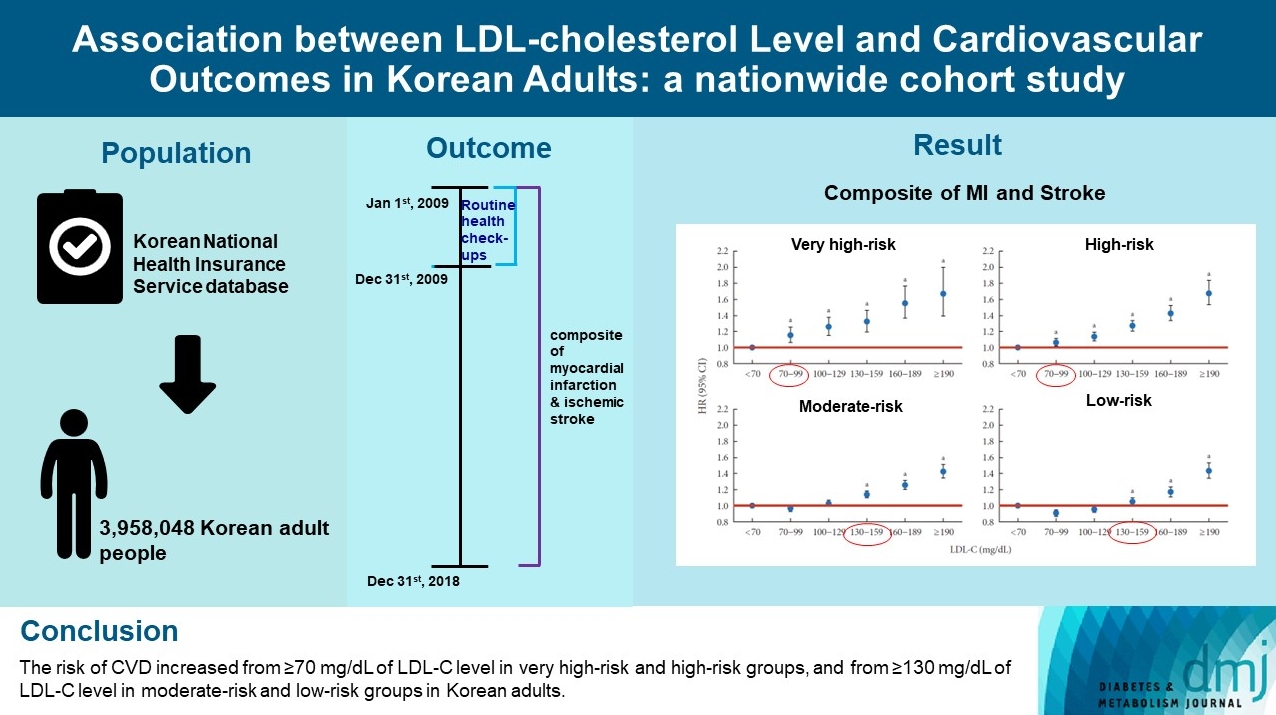
To validate the treatment target of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level according to the cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk which was recommended by Korean dyslipidemia guideline.
Methods
We used the Korean National Health Insurance Service database which included 3,958,048 people aged 20 to 89 years who underwent regular health screening. The primary outcome was incident CVD, defined as a composite of myocardial infarction and stroke during the follow-up period from 2009 to 2018.
Results
The risk of CVD increased from LDL-C level of 70 mg/dL in very high-risk and high-risk groups and from 130 mg/dL in moderate-risk and low-risk groups. Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) of LDL-C ranges 70–99, 100–129, 130–159, 160–189, and ≥190 mg/dL were 1.20 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08–1.33), 1.27 (1.15–1.42), 1.39 (1.23–1.56), 1.69 (1.45–1.96), and 1.84 (1.49– 2.27) in very high-risk group, and 1.07 (1.02–1.13), 1.16 (1.10–1.21), 1.29 (1.22–1.36), 1.45 (1.36–1.55), and 1.73 (1.58–1.90) in high-risk group. Adjusted HRs (95% CI) of LDL-C ranges 130–159, 160–189, and ≥190 mg/dL were 1.15 (1.11–1.20), 1.28 (1.22– 1.34), and 1.45 (1.36–1.54) in moderate-risk group and 1.07 (1.02–1.13), 1.20 (1.13–1.26), and 1.47 (1.37–1.57) in low-risk group.
Conclusion
We confirmed the incidence of CVD was increased in higher LDL-C range. The risk of CVD increased from ≥70 mg/dL of LDL-C in very high-risk and high-risk groups, and from ≥130 mg/dL of LDL-C in moderate-risk and low-risk groups in Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Triple Combination of Olmesartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin in Hypertensive Patients with Low-to-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Control, Phase IV Clinical Trial
Byung Jin Kim, Kwang Soo Cha, Wook Hyun Cho, Eung Ju Kim, Seung-Hyuk Choi, Moo Hyun Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Jun-Bean Park, Seong-Mi Park, Il Suk Sohn, Kyu Hyung Ryu, In-Ho Chae
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Triple Combination of Olmesartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin in Hypertensive Patients with Low-to-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Control, Phase IV Clinical Trial
Review
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
- Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon, on Behalf of Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Clinical Practice Guideline Committee, Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. Published online January 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0448
- 3,513 View
- 375 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
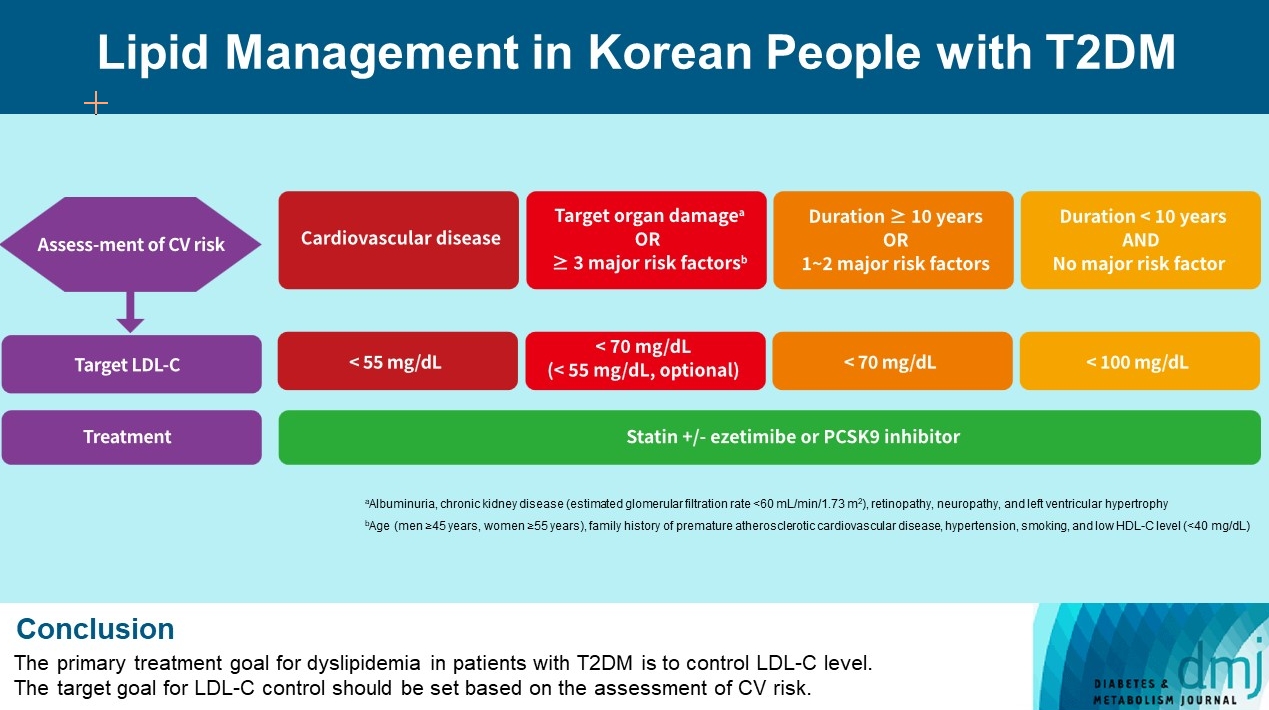
ePub - Dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes is an important treatment target as a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Although the primary treatment goal for dyslipidemia is to control low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), achieving this goal remains suboptimal according to recent studies. It is important to set the target goal for LDL-C control based on an accurate risk assessment for CVD. Here, we summarize the latest evidence on lipid management in patients with diabetes and present a consensus of the Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis on the treatment goals of LDL-C according to the duration of diabetes, presence of CVD, target organ damage, or major cardiovascular risk factors. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and CVD, an LDL-C goal of <55 mg/dL and a reduction in LDL-C level by 50% or more from the baseline is recommended. For the primary prevention of CVD in patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes ≥10 years, major cardiovascular risk factors, or target organ damage, an LDL-C goal of <70 mg/dL is recommended. In patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes <10 years and no major cardiovascular risk factors, an LDL-C goal of <100 mg/dL is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Statin Discontinuation in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2024; 13(1): 41. CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 632. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(3): 237. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Original Articles
- Complications
- Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):242-254. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0001
- 2,861 View
- 164 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
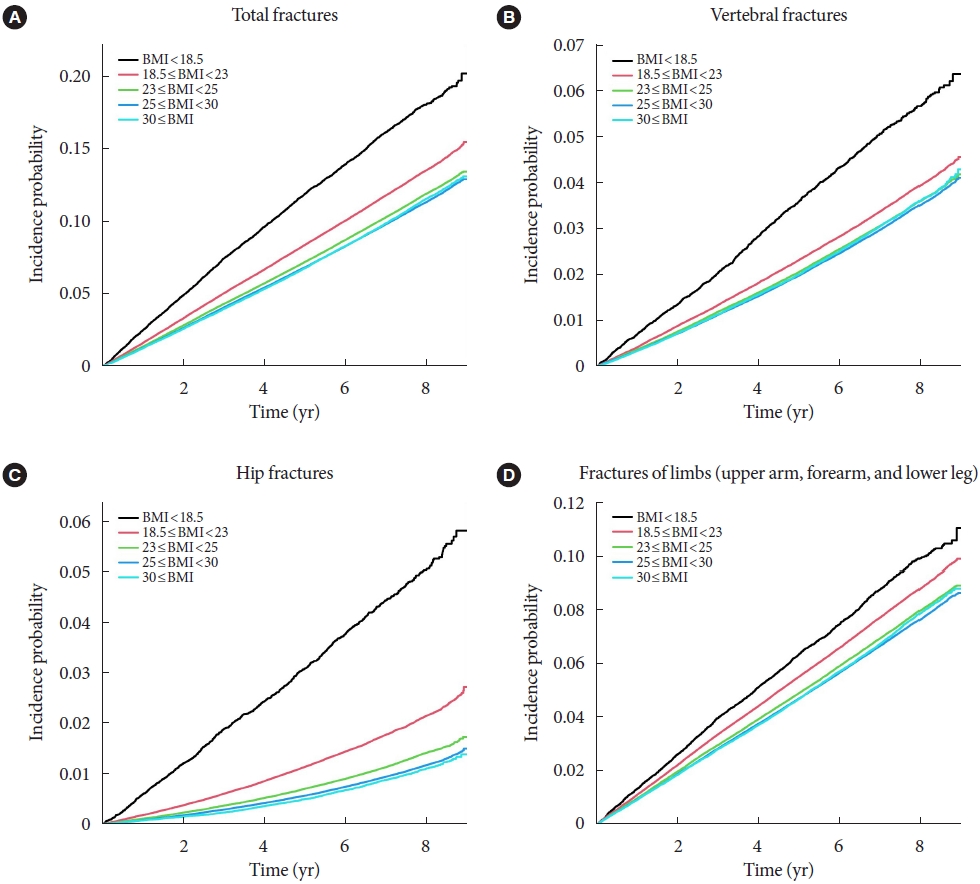
Body mass index (BMI) is a risk factor for the type 2 diabetes (T2DM), and T2DM accompanies various complications, such as fractures. We investigated the effects of BMI and T2DM on fracture risk and analyzed whether the association varied with fracture locations.
Methods
This study is a nationwide population-based cohort study that included all people with T2DM (n=2,746,078) who received the National Screening Program during 2009–2012. According to the anatomical location of the fracture, the incidence rate and hazard ratio (HR) were analyzed by dividing it into four categories: vertebra, hip, limbs, and total fracture.
Results
The total fracture had higher HR in the underweight group (HR, 1.268; 95% CI, 1.228 to 1.309) and lower HR in the obese group (HR, 0.891; 95% CI, 0.882 to 0.901) and the morbidly obese group (HR, 0.873; 95% CI, 0.857 to 0.89), compared to reference (normal BMI group). Similar trends were observed for HR of vertebra fracture. The risk of hip fracture was most prominent, the risk of hip fracture increased in the underweight group (HR, 1.896; 95% CI, 1.178 to 2.021) and decreased in the obesity (HR, 0.643; 95% CI, 0.624 to 0.663) and morbidly obesity group (HR, 0.627; 95% CI, 0.591 to 0.665). Lastly, fracture risk was least affected by BMI for limbs.
Conclusion
In T2DM patients, underweight tends to increase fracture risk, and overweight tends to lower fracture risk, but association between BMI and fracture risk varied depending on the affected bone lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dysuricemia—A New Concept Encompassing Hyperuricemia and Hypouricemia
Naoyuki Otani, Motoshi Ouchi, Einosuke Mizuta, Asuka Morita, Tomoe Fujita, Naohiko Anzai, Ichiro Hisatome
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1255. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:242-54)
Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 439. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:242-54)
So Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 437. CrossRef - Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on fractures, BMD, and bone metabolism markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xin Wang, Fengyi Zhang, Yufeng Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, Yingli Sheng, Wenbo Wang, Yujie Li
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(12): 2013. CrossRef
- Dysuricemia—A New Concept Encompassing Hyperuricemia and Hypouricemia
- Genetics
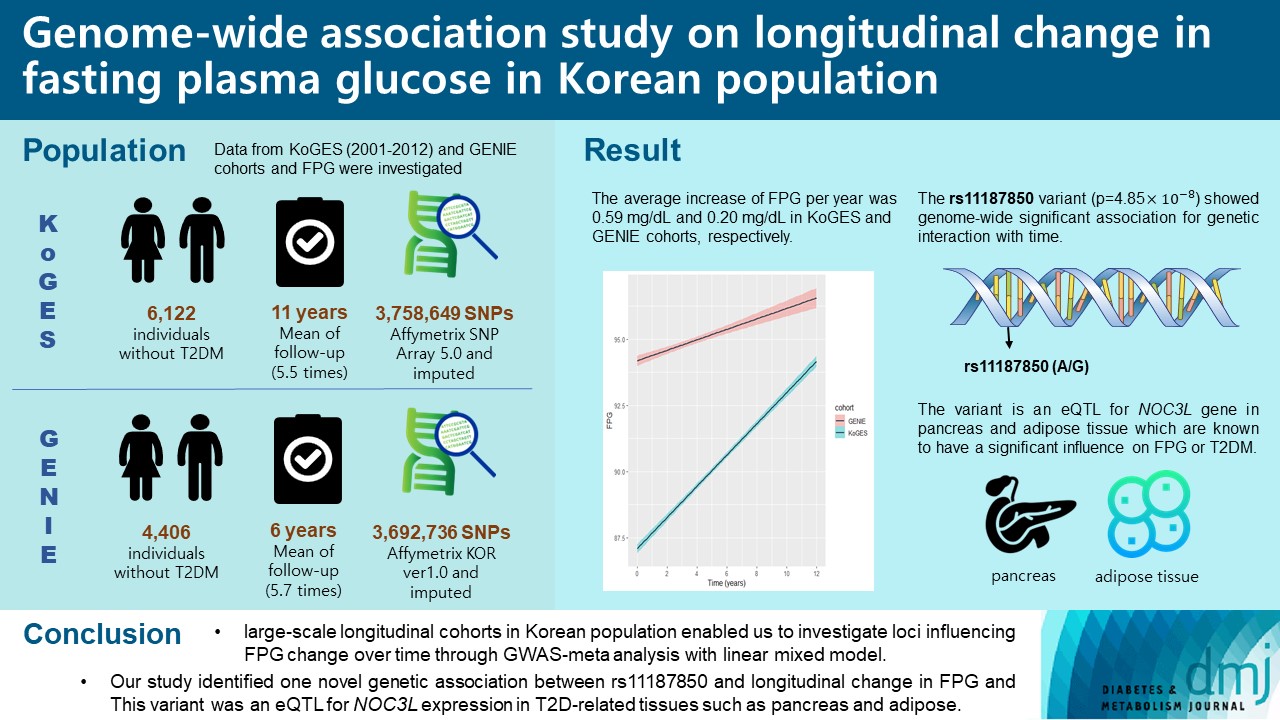
- Genome-Wide Association Study on Longitudinal Change in Fasting Plasma Glucose in Korean Population
- Heejin Jin, Soo Heon Kwak, Ji Won Yoon, Sanghun Lee, Kyong Soo Park, Sungho Won, Nam H. Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):255-266. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0375
- 2,591 View
- 165 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) on type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have identified more than 400 distinct genetic loci associated with diabetes and nearly 120 loci for fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and fasting insulin level to date. However, genetic risk factors for the longitudinal deterioration of FPG have not been thoroughly evaluated. We aimed to identify genetic variants associated with longitudinal change of FPG over time.
Methods
We used two prospective cohorts in Korean population, which included a total of 10,528 individuals without T2DM. GWAS of repeated measure of FPG using linear mixed model was performed to investigate the interaction of genetic variants and time, and meta-analysis was conducted. Genome-wide complex trait analysis was used for heritability calculation. In addition, expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) analysis was performed using the Genotype-Tissue Expression project.
Results
A small portion (4%) of the genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) interaction with time explained the total phenotypic variance of longitudinal change in FPG. A total of four known genetic variants of FPG were associated with repeated measure of FPG levels. One SNP (rs11187850) showed a genome-wide significant association for genetic interaction with time. The variant is an eQTL for NOC3 like DNA replication regulator (NOC3L) gene in pancreas and adipose tissue. Furthermore, NOC3L is also differentially expressed in pancreatic β-cells between subjects with or without T2DM. However, this variant was not associated with increased risk of T2DM nor elevated FPG level.
Conclusion
We identified rs11187850, which is an eQTL of NOC3L, to be associated with longitudinal change of FPG in Korean population.
- Complications
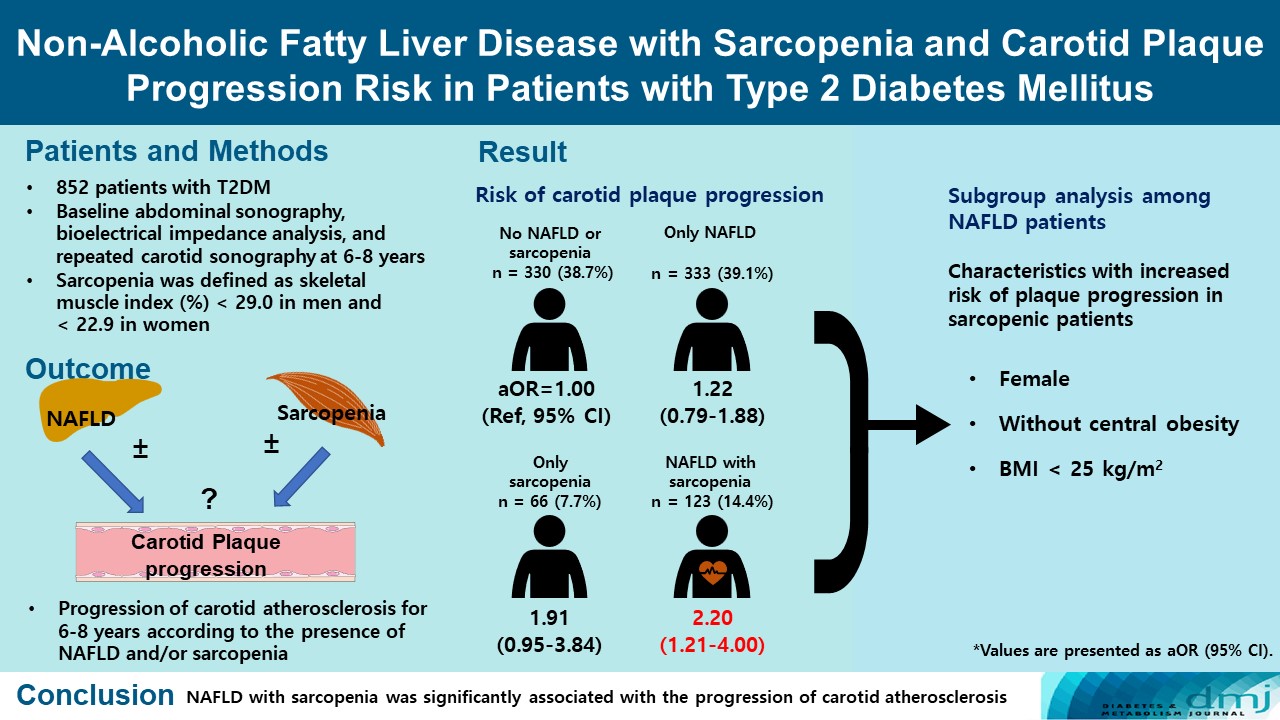
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Yong-ho Lee, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):232-241. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0355
- 3,517 View
- 221 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate whether non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without sarcopenia is associated with progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We investigated 852 T2DM patients who underwent abdominal ultrasonography, bioelectrical impedance analysis, and carotid artery ultrasonography at baseline and repeated carotid ultrasonography after 6 to 8 years. NAFLD was confirmed by abdominal ultrasonography, and sarcopenia was defined as a sex-specific skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) value <2 standard deviations below the mean for healthy young adults. SMI was calculated by dividing the sum of appendicular skeletal mass by body weight. We investigated the association between NAFLD with or without sarcopenia and the progression of carotid atherosclerosis.
Results
Of the 852 patients, 333 (39.1%) were classified as NAFLD without sarcopenia, 66 (7.7%) were classified as sarcopenia without NAFLD, and 123 (14.4%) had NAFLD with sarcopenia at baseline. After 6 to 8 years, patients with both NAFLD and sarcopenia had a higher risk of atherosclerosis progression (adjusted odds ratio, 2.20; P<0.009) than controls without NAFLD and sarcopenia. When a subgroup analysis was performed on only patients with NAFLD, female sex, absence of central obesity, and non-obesity were significant factors related to increased risk of plaque progression risk in sarcopenic patients.
Conclusion
NAFLD with sarcopenia was significantly associated with the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
Aditya Viswanath, Sherouk Fouda, Cornelius James Fernandez, Joseph M Pappachan
World Journal of Hepatology.2024; 16(2): 152. CrossRef - Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and carotid media‐intima thickness: A systematic review and a meta‐analysis
Manouchehr Khoshbaten, Sepideh H. Maleki, Sara Hadad, Amrit Baral, Ana V. Rocha, Laxmi Poudel, Alireza Abdshah
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes and sarcopenia
Yu. G. Samoilova, M. V. Matveeva, E. A. Khoroshunova, D. V. Podchinenova, L. L. Maksimova, G. G. Gorbach, A. B. Trivozhenko, V. A. Avkhimenko
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2023; 23(1): 3655. CrossRef
- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
- Basic Research
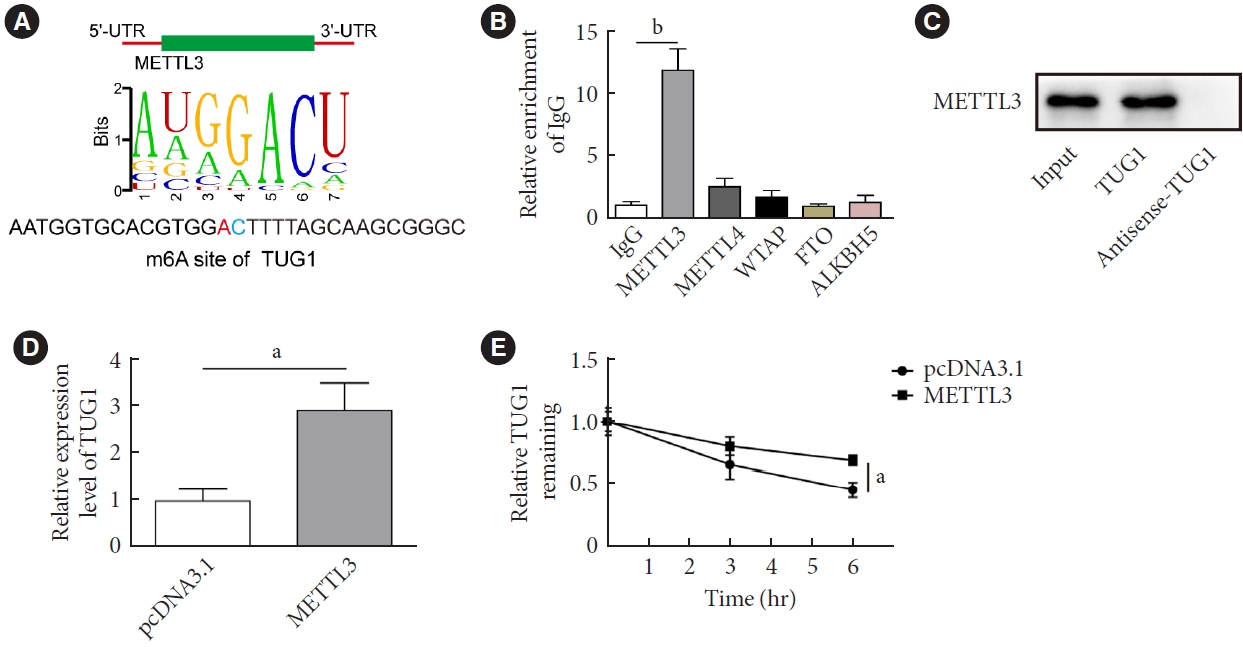
- N6-Methyladenosine Methyltransferase METTL3 Alleviates Diabetes-Induced Testicular Damage through Modulating TUG1/Clusterin Axis
- Yuan Tian, Yue-Hai Xiao, Chao Sun, Bei Liu, Fa Sun
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):287-300. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0306
- 2,152 View
- 153 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The present study investigated the regulatory effects of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methyltransferase like-3 (METTL3) in diabetes-induced testicular damage.
Methods
In vivo diabetic mice and high glucose (HG) treated GC-1 spg cells were established. The mRNA and protein expressions were determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry staining. Levels of testosterone, blood glucose, cell viability, and apoptosis were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, MTT, and flow cytometry, respectively. Molecular interactions were verified by RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA pull-down assay. Histopathological staining was performed to evaluate testicular injury.
Results
METTL3 and long non-coding RNA taurine up-regulated 1 (lncRNA TUG1) were downregulated in testicular tissues of diabetic mice and HG-treated GC-1 spg cells. METTL3 overexpression could reduce the blood glucose level, oxidative stress and testicular damage but enhance testosterone secretion in diabetic mouse model and HG-stimulated GC-1 spg cells. Mechanically, METTL3-mediated m6A methylation enhanced the stability of TUG1, then stabilizing the clusterin mRNA via recruiting serine and arginine rich splicing factor 1. Moreover, inhibition of TUG1/clusterin signaling markedly reversed the protective impacts of METTL3 overexpression on HG-stimulated GC-1 spg cells.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that METTL3 ameliorated diabetes-induced testicular damage by upregulating the TUG1/clusterin signaling. These data further elucidate the potential regulatory mechanisms of m6A modification on diabetes-induced testicular injury. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Negative Regulation of LINC01013 by METTL3 and YTHDF2 Enhances the Osteogenic Differentiation of Senescent Pre‐Osteoblast Cells Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide
Jiaxin Song, Yuejun Wang, Zhao Zhu, Wanqing Wang, Haoqing Yang, Zhaochen Shan
Advanced Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and diabetic associative diseases: An overview of epigenetic regulations of TUG1
Mohammed Ageeli Hakami
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2024; 31(5): 103976. CrossRef
- Negative Regulation of LINC01013 by METTL3 and YTHDF2 Enhances the Osteogenic Differentiation of Senescent Pre‐Osteoblast Cells Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





