
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Review
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Review
Reviews
- Pathophysiology
- Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors-Induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: From Its Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Practice
- Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):757-766. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0072
- 2,721 View
- 324 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
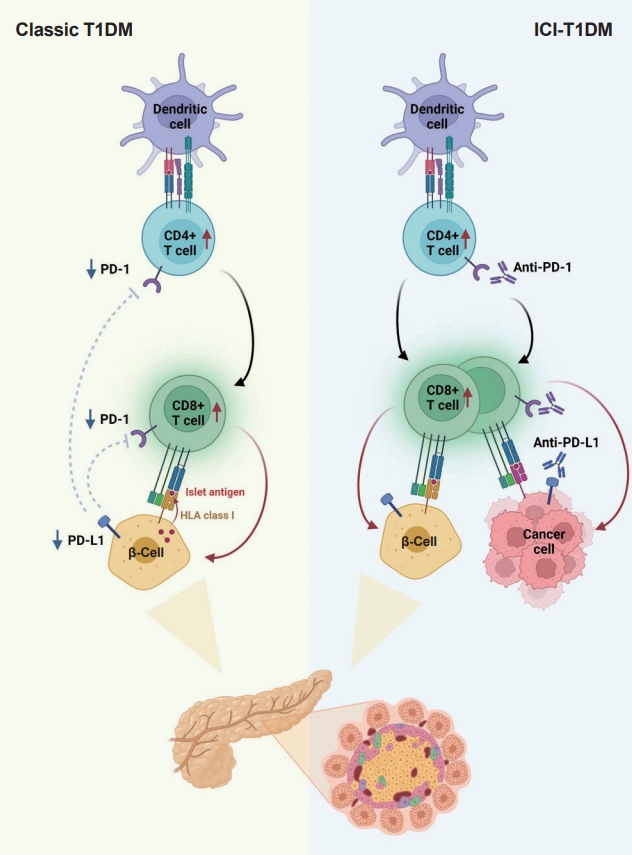
ePub - With the increasing use of immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1), for the treatment of malignancies, cases of ICI-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (ICI-T1DM) have been reported globally. This review focuses on the features and pathogenesis of this disease. T1DM is an immune-related adverse event that occurs following the administration of anti-PD-1 or anti-programmed death ligand-1 (PDL1) alone or in combination with anti-CTLA-4. More than half of the reported cases presented as abrupt-onset diabetic ketoacidosis. The primary mechanism of ICI-T1DM is T-cell stimulation, which results from the loss of interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 in pancreatic islet. The similarities and differences between ICI-T1DM and classical T1DM may provide insights into this disease entity. ICI-T1DM is a rare but often life-threatening medical emergency that healthcare professionals and patients need to be aware of. Early detection of and screening for this disease is imperative. At present, the only known treatment for ICI-T1DM is insulin injection. Further research into the mechanisms and risk factors associated with ICI-T1DM development may contribute to a better understanding of this disease entity and the identification of possible preventive strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Advances of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Related Endocrine Adverse Events
晶晶 王
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(02): 2706. CrossRef - Immune checkpoint inhibitor‑associated diabetes mellitus in patients with HCC: Report of three cases and literature review
Gaocheng Wang, Jingjing Wang, Shuilin Dong, Zhanguo Zhang, Wanguang Zhang, Jianping Zhao
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Advances of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Related Endocrine Adverse Events
- Complications
- Dyslipidemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Updated Overview
- Sang Heon Suh, Soo Wan Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):612-629. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0067
- 2,993 View
- 407 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
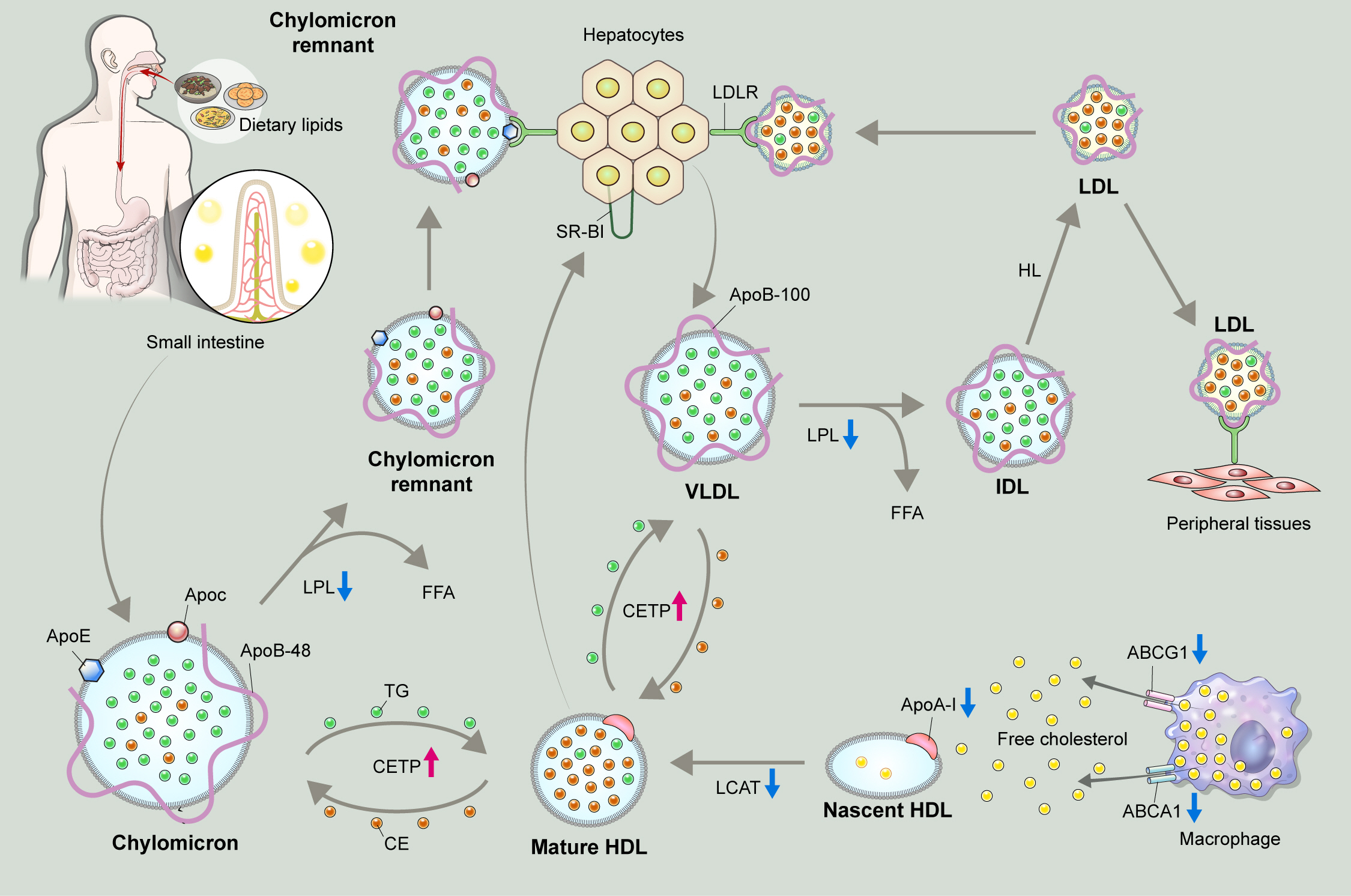
ePub - Dyslipidemia is a potentially modifiable cardiovascular risk factor. Whereas the recommendations for the treatment target of dyslipidemia in the general population are being more and more rigorous, the 2013 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes clinical practice guideline for lipid management in chronic kidney disease (CKD) presented a relatively conservative approach with respect to the indication of lipid lowering therapy and therapeutic monitoring among the patients with CKD. This may be largely attributed to the lack of high-quality evidence derived from CKD population, among whom the overall feature of dyslipidemia is considerably distinctive to that of general population. In this review article, we cover the characteristic features of dyslipidemia and impact of dyslipidemia on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD. We also review the current evidence on lipid lowering therapy to modify the risk of cardiovascular events in this population. We finally discuss the association between dyslipidemia and CKD progression and the potential strategy to delay the progression of CKD in relation to lipid lowering therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
Jafar Karami, Bahman Razi, Danyal Imani, Saeed Aslani, Mahdi Pakjoo, Mahdieh Fasihi, Keyhan Mohammadi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(5): 362. CrossRef
- Statin Therapy and Lipid Indices in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials
- Basic Research
- Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Health
- Sung-Min An, Seung-Hee Cho, John C. Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):595-611. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0011

- 3,754 View
- 435 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - In this review, we provide a brief synopsis of the connections between adipose tissue and metabolic health and highlight some recent developments in understanding and exploiting adipocyte biology. Adipose tissue plays critical roles in the regulation of systemic glucose and lipid metabolism and secretes bioactive molecules possessing endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine functions. Dysfunctional adipose tissue has a detrimental impact on metabolic health and is intimately involved in key aspects of metabolic diseases such as insulin resistance, lipid overload, inflammation, and organelle stress. Differences in the distribution of fat depots and adipose characteristics relate to divergent degrees of metabolic dysfunction found in metabolically healthy and unhealthy obese individuals. Thermogenic adipocytes increase energy expenditure via mitochondrial uncoupling or adenosine triphosphate-consuming futile substrate cycles, while functioning as a metabolic sink and participating in crosstalk with other metabolic organs. Manipulation of adipose tissue provides a wealth of opportunities to intervene and combat the progression of associated metabolic diseases. We discuss current treatment modalities for obesity including incretin hormone analogs and touch upon emerging strategies with therapeutic potential including exosome-based therapy, pharmacological activation of brown and beige adipocyte thermogenesis, and administration or inhibition of adipocyte-derived factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads
Srinivasa Reddy Bonam, Dylan Mastrippolito, Philippe Georgel, Sylviane Muller
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2024; 45(1): 81. CrossRef - Senescent adipocytes and type 2 diabetes – current knowledge and perspective concepts
Weronika Kruczkowska, Julia Gałęziewska, Mateusz Kciuk, Adrianna Gielecińska, Elżbieta Płuciennik, Zbigniew Pasieka, Lin-Yong Zhao, Yi-Jin Yu, Damian Kołat, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat
Biomolecular Concepts.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral Adipose Tissue: The Hidden Culprit for Type 2 Diabetes
Sneha Dhokte, Krzysztof Czaja
Nutrients.2024; 16(7): 1015. CrossRef - Beyond the Cold: Activating Brown Adipose Tissue as an Approach to Combat Obesity
Cristina Elena Negroiu, Iulia Tudorașcu, Cristina Maria Bezna, Sanziana Godeanu, Marina Diaconu, Raluca Danoiu, Suzana Danoiu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(7): 1973. CrossRef
- Pharmacological targets at the lysosomal autophagy–NLRP3 inflammasome crossroads
- Basic Research
- Rediscovering Primary Cilia in Pancreatic Islets
- Eun Young Lee, Jing W. Hughes
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):454-469. Published online April 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0442
- 2,556 View
- 240 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
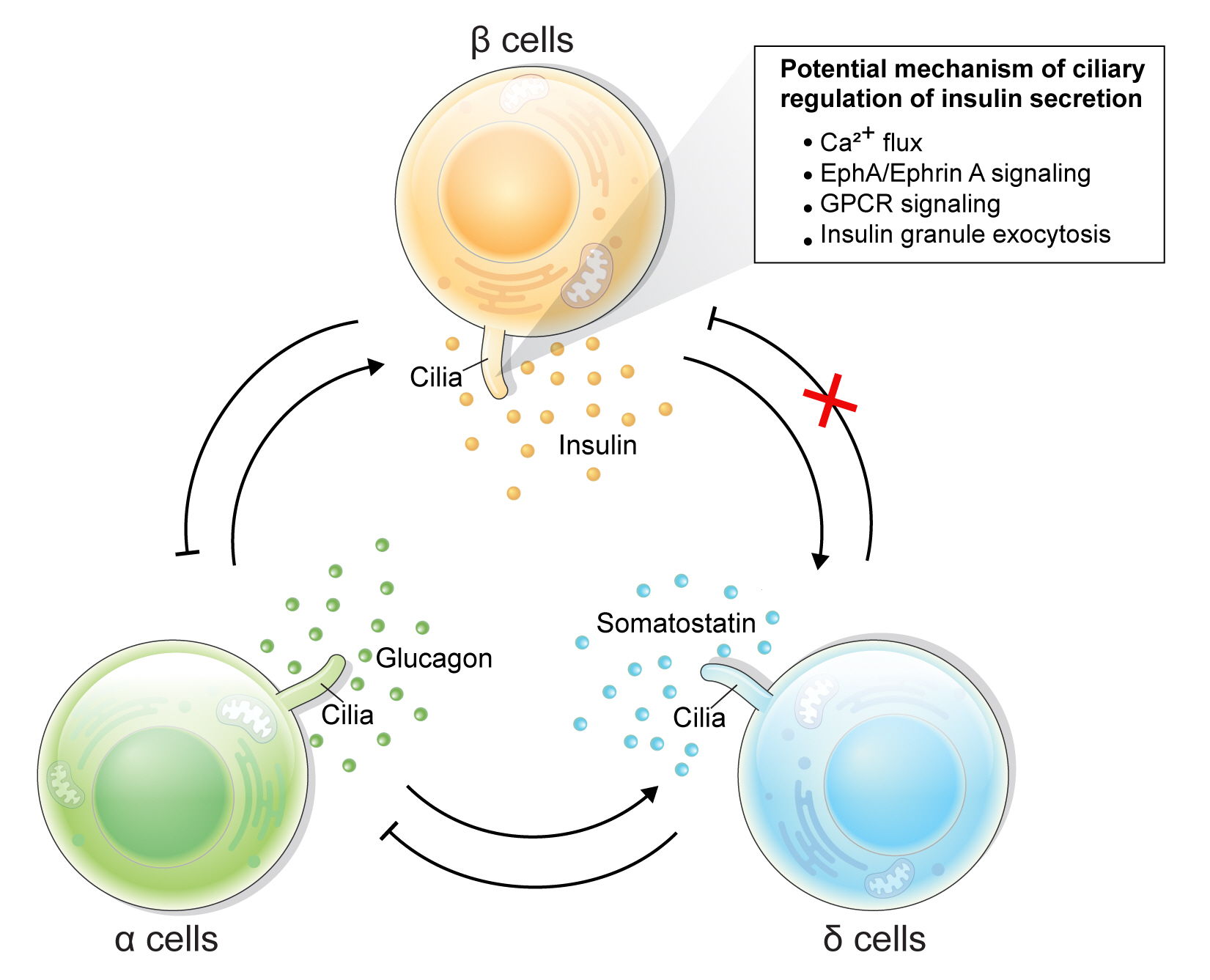
ePub - Primary cilia are microtubule-based sensory and signaling organelles on the surfaces of most eukaryotic cells. Despite their early description by microscopy studies, islet cilia had not been examined in the functional context until recent decades. In pancreatic islets as in other tissues, primary cilia facilitate crucial developmental and signaling pathways in response to extracellular stimuli. Many human developmental and genetic disorders are associated with ciliary dysfunction, some manifesting as obesity and diabetes. Understanding the basis for metabolic diseases in human ciliopathies has been aided by close examination of cilia action in pancreatic islets at cellular and molecular levels. In this article, we review the evidence for ciliary expression on islet cells, known roles of cilia in pancreas development and islet hormone secretion, and summarize metabolic manifestations of human ciliopathy syndromes. We discuss emerging data on primary cilia regulation of islet cell signaling and the structural basis of cilia-mediated cell crosstalk, and offer our interpretation on the role of cilia in glucose homeostasis and human diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beta cell primary cilia mediate somatostatin responsiveness via SSTR3
Samantha E. Adamson, Zipeng A. Li, Jing W. Hughes
Islets.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Beta cell primary cilia mediate somatostatin responsiveness via SSTR3
- Basic Research
- Regulation of Cellular Senescence in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: From Mechanisms to Clinical Applications
- Kanako Iwasaki, Cristian Abarca, Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):441-453. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0416

- 4,639 View
- 415 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Cellular senescence is accelerated by hyperglycemia through multiple pathways. Therefore, senescence is an important cellular mechanism to consider in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and an additional therapeutic target. The use of drugs that remove senescent cells has led to improvements in blood glucose levels and diabetic complications in animal studies. Although the removal of senescent cells is a promising approach for the treatment of T2DM, two main challenges limit its clinical application: the molecular basis of cellular senescence in each organ is yet to be understood, and the specific effect of removing senescent cells in each organ has to be determined. This review aims to discuss future applications of targeting senescence as a therapeutic option in T2DM and elucidate the characteristics of cellular senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype in the tissues important for regulating glucose levels: pancreas, liver, adipocytes, and skeletal muscle.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Amide Alkaloids as Privileged Sources of Senomodulators for Therapeutic Purposes in Age-Related Diseases
Mazzarine Dotou, Aurore L’honoré, Roba Moumné, Chahrazade El Amri
Journal of Natural Products.2024; 87(3): 617. CrossRef - Study on the Pathogenesis of Cell Senescence in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver
丽媛 黄
Medical Diagnosis.2024; 14(01): 76. CrossRef - Senescent adipocytes and type 2 diabetes – current knowledge and perspective concepts
Weronika Kruczkowska, Julia Gałęziewska, Mateusz Kciuk, Adrianna Gielecińska, Elżbieta Płuciennik, Zbigniew Pasieka, Lin-Yong Zhao, Yi-Jin Yu, Damian Kołat, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat
Biomolecular Concepts.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Long-Term Passage on Porcine SMCs’ Function and the Improvement of TGF-β1 on Porcine SMCs’ Secretory Function in Late Passage
Yan-Yan Zheng, Ze-Nan Hu, Zheng Liu, Yi-Chen Jiang, Ren-Peng Guo, Shi-Jie Ding, Guang-Hong Zhou
Foods.2023; 12(14): 2682. CrossRef - Exploring the Relationship between Cellular Senescence Markers and Aging-Related Diseases
怡 罗
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(08): 12298. CrossRef
- Amide Alkaloids as Privileged Sources of Senomodulators for Therapeutic Purposes in Age-Related Diseases
- Basic Research
- Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c, Diabetes, and Aging-Related Diseases
- Byung Soo Kong, Changhan Lee, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):315-324. Published online February 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0333
- 5,641 View
- 284 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
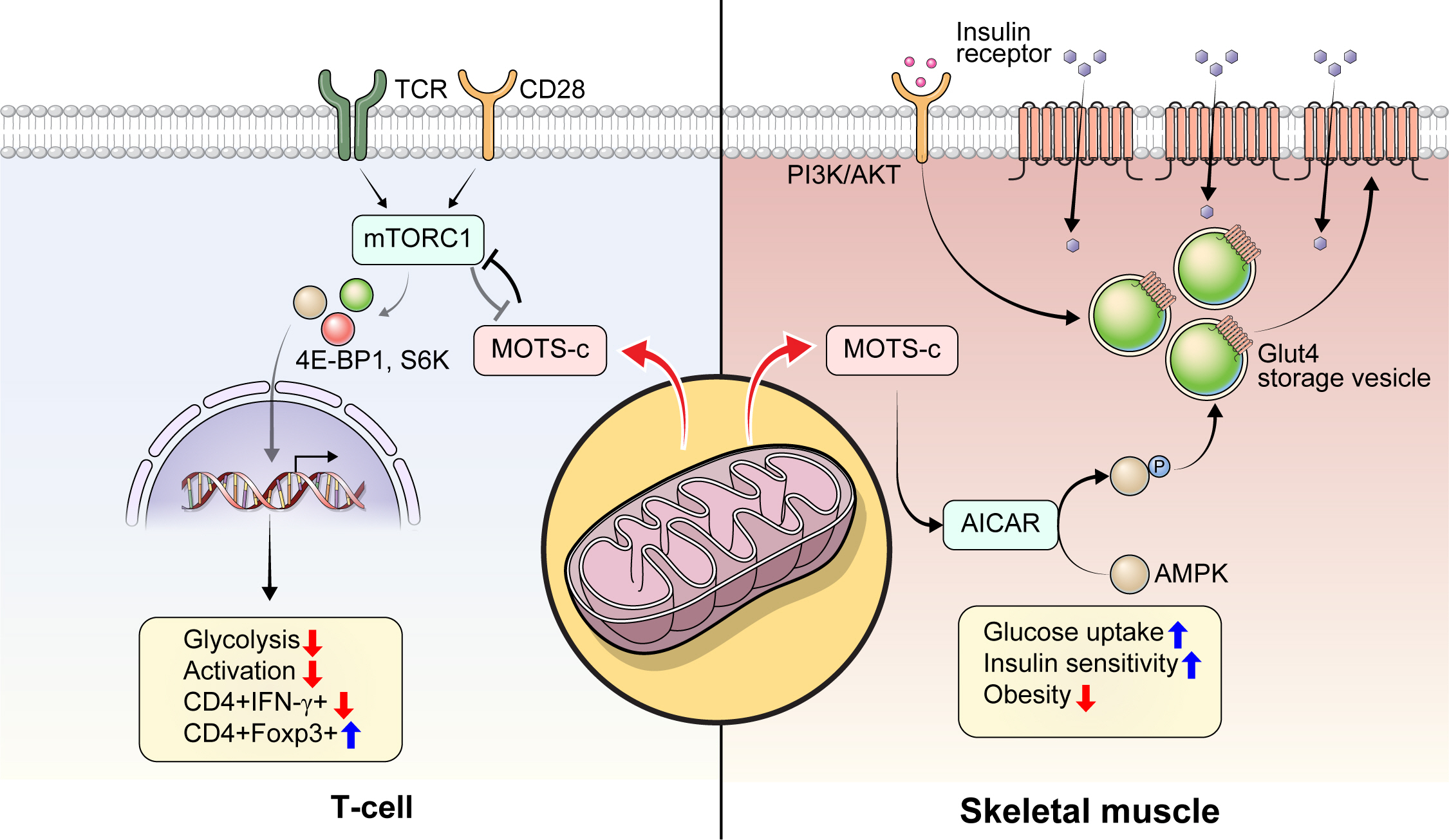
ePub - Mitochondria are complex metabolic organelles with manifold pathophysiological implications in diabetes. Currently published mitochondrial-encoded peptides, which are expressed from the mitochondrial open reading frame of the 12S ribosomal RNA type-c (MOTS-c), 16S rRNA (humanin and short humanin like peptide 1-6 [SHLP1-6]), or small human mitochondrial open reading frame over serine tRNA (SHMOOSE) are associated with regulation of cellular metabolism and insulin action in age-related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus. This review focuses mainly on recent advances in MOTS-c research with regards to diabetes, including both type 1 and type 2. The emerging understanding of MOTS-c in diabetes may provide insight into the development of new therapies for diabetes and other age or senescence-related diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
Satadeepa Kal, Sumana Mahata, Suborno Jati, Sushil K. Mahata
Peptides.2024; 172: 171147. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Stress and Mitokines: Therapeutic Perspectives for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
Benyuan Zhang, Joon Young Chang, Min Hee Lee, Sang-Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi, Minho Shong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 1. CrossRef - Mitochondrial bioenergetics, metabolism, and beyond in pancreatic β-cells and diabetes
Alejandra María Rivera Nieves, Brian Michael Wauford, Accalia Fu
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Its Implications across the Life Span
- Brandy Wicklow, Ravi Retnakaran
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):333-344. Published online February 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0348

- 5,160 View
- 405 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) has historically been perceived as a medical complication of pregnancy that also serves as a harbinger of maternal risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the future. In recent decades, a growing body of evidence has detailed additional lifelong implications that extend beyond T2DM, including an elevated risk of ultimately developing cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, the risk factors that mediate this lifetime cardiovascular risk are evident not only after delivery but are present even before the pregnancy in which GDM is first diagnosed. The concept thus emerging from these data is that the diagnosis of GDM enables the identification of women who are already on an enhanced track of cardiometabolic risk that starts early in life. Studies of the offspring of pregnancies complicated by diabetes now suggest that the earliest underpinnings of this cardiometabolic risk profile may be determined in utero and may first manifest clinically in childhood. Accordingly, from this perspective, GDM is now seen as a chronic metabolic disorder that holds implications across the life span of both mother and child.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ATP5me alleviates high glucose-induced myocardial cell injury
Qingsha Hou, Fang Yan, Xiuling Li, Huanling Liu, Xiang Yang, Xudong Dong
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 129: 111626. CrossRef - Prevalence and Predictors of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Overt Diabetes in Pregnancy: A Secondary Analysis of Nationwide Data from India
Saurav Basu, Vansh Maheshwari, Rutul Gokalani, Chandrakant Lahariya
Preventive Medicine: Research & Reviews.2024; 1(1): 52. CrossRef - Serum betaine and dimethylglycine in mid-pregnancy and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a case-control study
Ziqing Zhou, Yao Yao, Yanan Sun, Xin Wang, Shang Huang, Jianli Hou, Lijun Wang, Fengxiang Wei
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality assessment of videos on social media platforms related to gestational diabetes mellitus in China: A cross-section study
Qin-Yu Cai, Jing Tang, Si-Zhe Meng, Yi Sun, Xia Lan, Tai-Hang Liu
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e29020. CrossRef - Inflammation and decreased cardiovagal modulation are linked to stress and depression at 36th week of pregnancy in gestational diabetes mellitus
Manoharan Renugasundari, Gopal Krushna Pal, Latha Chaturvedula, Nivedita Nanda, K. T. Harichandrakumar, Thiyagarajan Durgadevi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Women with gestational diabetes mellitus, controlled for plasma glucose level, exhibit maternal and fetal dyslipidaemia that may warrant treatment
Barbara J. Meyer, Colin Cortie, Marloes Dekker-Nitert, Helen L. Barrett, Dilys J. Freeman
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 204: 110929. CrossRef - Pregnancy diet to prevent gestational diabetes: study design and dietary assessments
Sylvia H. Ley
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2023; 118(5): 847. CrossRef
- ATP5me alleviates high glucose-induced myocardial cell injury
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
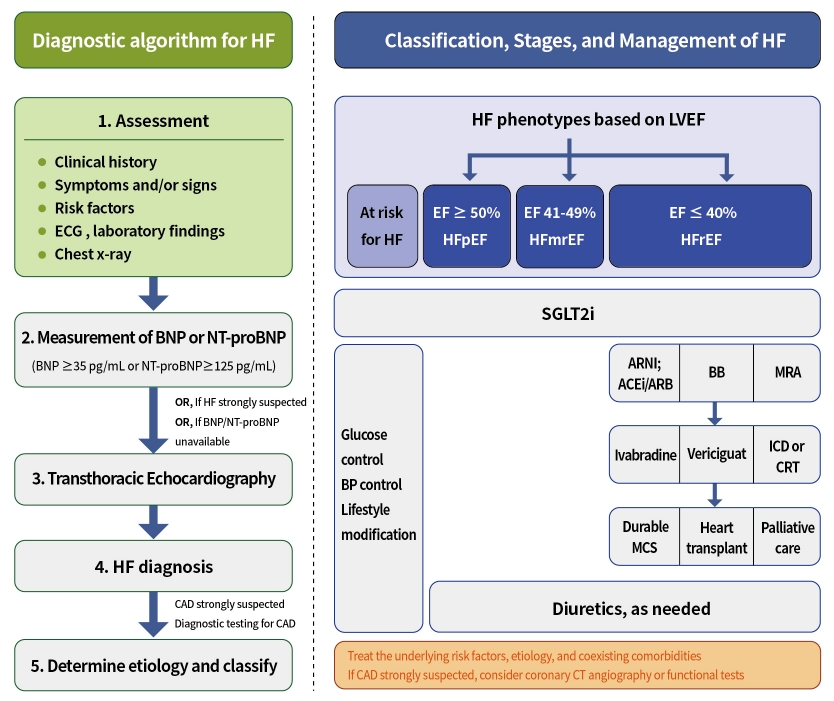
- Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
- Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Society of Heart Failure
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):10-26. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0420
- 4,295 View
- 409 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for the development of heart failure. Furthermore, the prognosis of heart failure is worse in patients with diabetes mellitus than in those without it. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper management of heart failure in patients with diabetes mellitus are important. This review discusses the current criteria for diagnosis and screening tools for heart failure and the currently recommended pharmacological therapies for heart failure. We also highlight the effects of anti-diabetic medications on heart failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Hae Jin Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kyu Yeon Hur, In-Kyung Jeong, Mark Yorek
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin versus glimepiride on cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin: The gemi‐heart study
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Jun Hwa Hong, In‐Chang Hwang, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2181. CrossRef - Optimization of guideline-directed medical treatment for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction
Minjung Bak, Jin-Oh Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(5): 595. CrossRef
- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
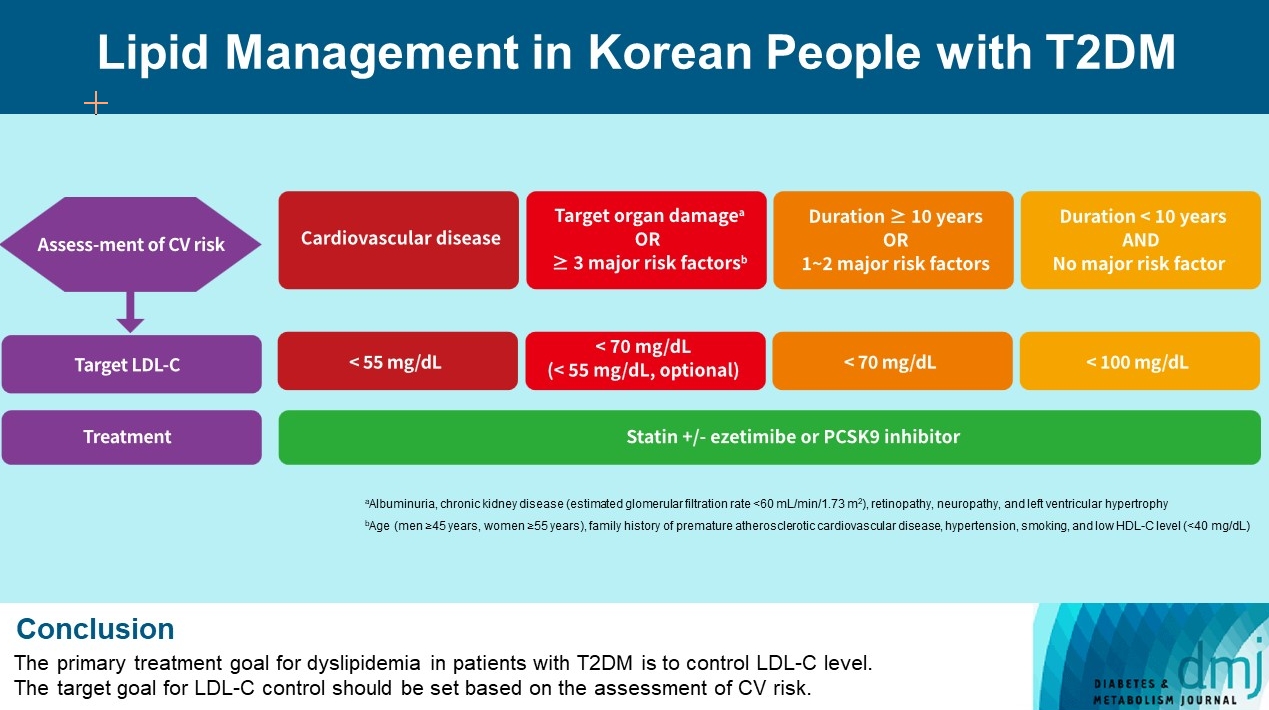
- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
- Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon, on Behalf of Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Clinical Practice Guideline Committee, Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):1-9. Published online January 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0448
- 3,531 View
- 377 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes is an important treatment target as a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Although the primary treatment goal for dyslipidemia is to control low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), achieving this goal remains suboptimal according to recent studies. It is important to set the target goal for LDL-C control based on an accurate risk assessment for CVD. Here, we summarize the latest evidence on lipid management in patients with diabetes and present a consensus of the Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis on the treatment goals of LDL-C according to the duration of diabetes, presence of CVD, target organ damage, or major cardiovascular risk factors. In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and CVD, an LDL-C goal of <55 mg/dL and a reduction in LDL-C level by 50% or more from the baseline is recommended. For the primary prevention of CVD in patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes ≥10 years, major cardiovascular risk factors, or target organ damage, an LDL-C goal of <70 mg/dL is recommended. In patients with T2DM with a duration of diabetes <10 years and no major cardiovascular risk factors, an LDL-C goal of <100 mg/dL is recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Statin Discontinuation in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2024; 13(1): 41. CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 632. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(3): 237. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
- Drug/Regimen
- Machine Learning Approach to Drug Treatment Strategy for Diabetes Care
- Kazuya Fujihara, Hirohito Sone
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):325-332. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0349
- 65,535 View
- 247 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Globally, the number of people with diabetes mellitus has quadrupled in the past three decades, and approximately one in 11 adults worldwide have diabetes mellitus. Since both microvascular and macrovascular diseases in patients with diabetes predispose them to a lower quality of life as well as higher rates of mortality, managing blood glucose levels is of clinical relevance in diabetes care. Many classes of antihyperglycemic drugs are currently approved to treat hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with several new drugs having been developed during the last decade. Diabetes-related complications have been reduced substantially worldwide. Prioritization of therapeutic agents varies according to national guidelines. However, since the characteristics of participants in clinical trials differ from patients in actual clinical practice, it is difficult to apply the results of such trials to clinical practice. Machine learning approaches became highly topical issues in medicine along with rapid technological innovations in the fields of information and communication in the 1990s. However, adopting these technologies to support decision-making regarding drug treatment strategies for diabetes care has been slow. This review summarizes data from recent studies on the choice of drugs for type 2 diabetes mellitus focusing on machine learning approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring antioxidant activities and inhibitory effects against α‐amylase and α‐glucosidase of Elaeocarpus braceanus fruits: insights into mechanisms by molecular docking and molecular dynamics
Hong Li, Yuanyue Zhang, Zhijia Liu, Chaofan Guo, Maurizio Battino, Shengbao Cai, Junjie Yi
International Journal of Food Science & Technology.2024; 59(1): 343. CrossRef - 3D Convolutional Neural Networks for Predicting Protein Structure for Improved Drug Recommendation
Pokkuluri Kiran Sree, SSSN Usha Devi N
EAI Endorsed Transactions on Pervasive Health and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploring antioxidant activities and inhibitory effects against α‐amylase and α‐glucosidase of Elaeocarpus braceanus fruits: insights into mechanisms by molecular docking and molecular dynamics
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
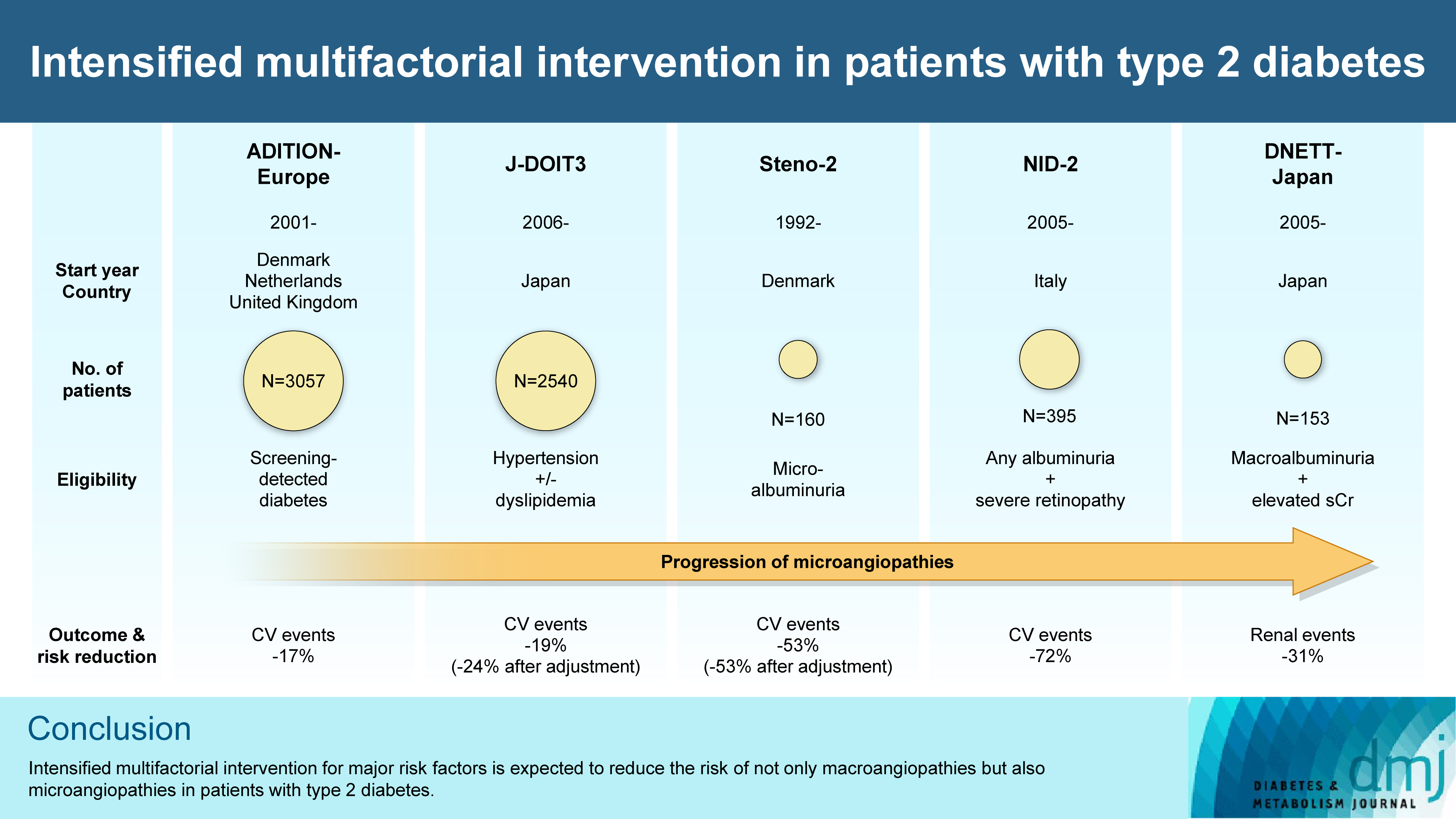
- Intensified Multifactorial Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Takayoshi Sasako, Toshimasa Yamauchi, Kohjiro Ueki
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):185-197. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0325
- 5,022 View
- 357 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - In the management of diabetes mellitus, one of the most important goals is to prevent its micro- and macrovascular complications, and to that end, multifactorial intervention is widely recommended. Intensified multifactorial intervention with pharmacotherapy for associated risk factors, alongside lifestyle modification, was first shown to be efficacious in patients with microalbuminuria (Steno-2 study), then in those with less advanced microvascular complications (the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of Intensive Treatment In People with Screen Detected Diabetes in Primary Care [ADDITION]-Europe and the Japan Diabetes Optimal Treatment study for 3 major risk factors of cardiovascular diseases [J-DOIT3]), and in those with advanced microvascular complications (the Nephropathy In Diabetes-Type 2 [NID-2] study and Diabetic Nephropathy Remission and Regression Team Trial in Japan [DNETT-Japan]). Thus far, multifactorial intervention led to a reduction in cardiovascular and renal events, albeit not necessarily significant. It should be noted that not only baseline characteristics but also the control status of the risk factors and event rates during intervention among the patients widely varied from one trial to the next. Further evidence is needed for the efficacy of multifactorial intervention in a longer duration and in younger or elderly patients. Moreover, now that new classes of antidiabetic drugs are available, it should be addressed whether strict and safe glycemic control, alongside control of other risk factors, could lead to further risk reductions in micro- and macrovascular complications, thereby decreasing all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring mechanisms underlying diabetes comorbidities and strategies to prevent vascular complications
Takayoshi Sasako
Diabetology International.2024; 15(1): 34. CrossRef - Targeting ERS-mitophagy in hippocampal neurons to explore the improvement of memory by tea polyphenols in aged type 2 diabetic rats
Wenjuan Feng, Chenhui Lv, Le Cheng, Xin Song, Xuemin Li, Haoran Xie, Shuangzhi Chen, Xi Wang, Lushan Xue, Cheng Zhang, Jie Kou, Lili Wang, Haifeng Zhao
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2024; 213: 293. CrossRef - Risk of Dementia Among Patients With Diabetes in a Multidisciplinary, Primary Care Management Program
Kailu Wang, Shi Zhao, Eric Kam-Pui Lee, Susan Zi-May Yau, Yushan Wu, Chi-Tim Hung, Eng-Kiong Yeoh
JAMA Network Open.2024; 7(2): e2355733. CrossRef - Causes of In-Hospital Death and Pharmaceutical Associations with Age of Death during a 10-Year Period (2011–2020) in Individuals with and without Diabetes at a Japanese Community General Hospital
Minae Hosoki, Taiki Hori, Yousuke Kaneko, Kensuke Mori, Saya Yasui, Seijiro Tsuji, Hiroki Yamagami, Saki Kawata, Tomoyo Hara, Shiho Masuda, Yukari Mitsui, Kiyoe Kurahashi, Takeshi Harada, Shingen Nakamura, Toshiki Otoda, Tomoyuki Yuasa, Akio Kuroda, Itsur
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(5): 1283. CrossRef - External validation of a minimal-resource model to predict reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate in people with type 2 diabetes without diagnosis of chronic kidney disease in Mexico: a comparison between country-level and regional performance
Camilla Sammut-Powell, Rose Sisk, Ruben Silva-Tinoco, Gustavo de la Pena, Paloma Almeda-Valdes, Sonia Citlali Juarez Comboni, Susana Goncalves, Rory Cameron
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gut Microbiota Targeted Approach by Natural Products in Diabetes Management: An Overview
Priyanka Sati, Praveen Dhyani, Eshita Sharma, Dharam Chand Attri, Arvind Jantwal, Rajni Devi, Daniela Calina, Javad Sharifi-Rad
Current Nutrition Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes: Further Insights into the Power of Weight Loss and Exercise
Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 302. CrossRef - Sarcopenia: Loss of mighty armor against frailty and aging
Takayoshi Sasako, Kohjiro Ueki
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(10): 1145. CrossRef
- Exploring mechanisms underlying diabetes comorbidities and strategies to prevent vascular complications
- Basic Research
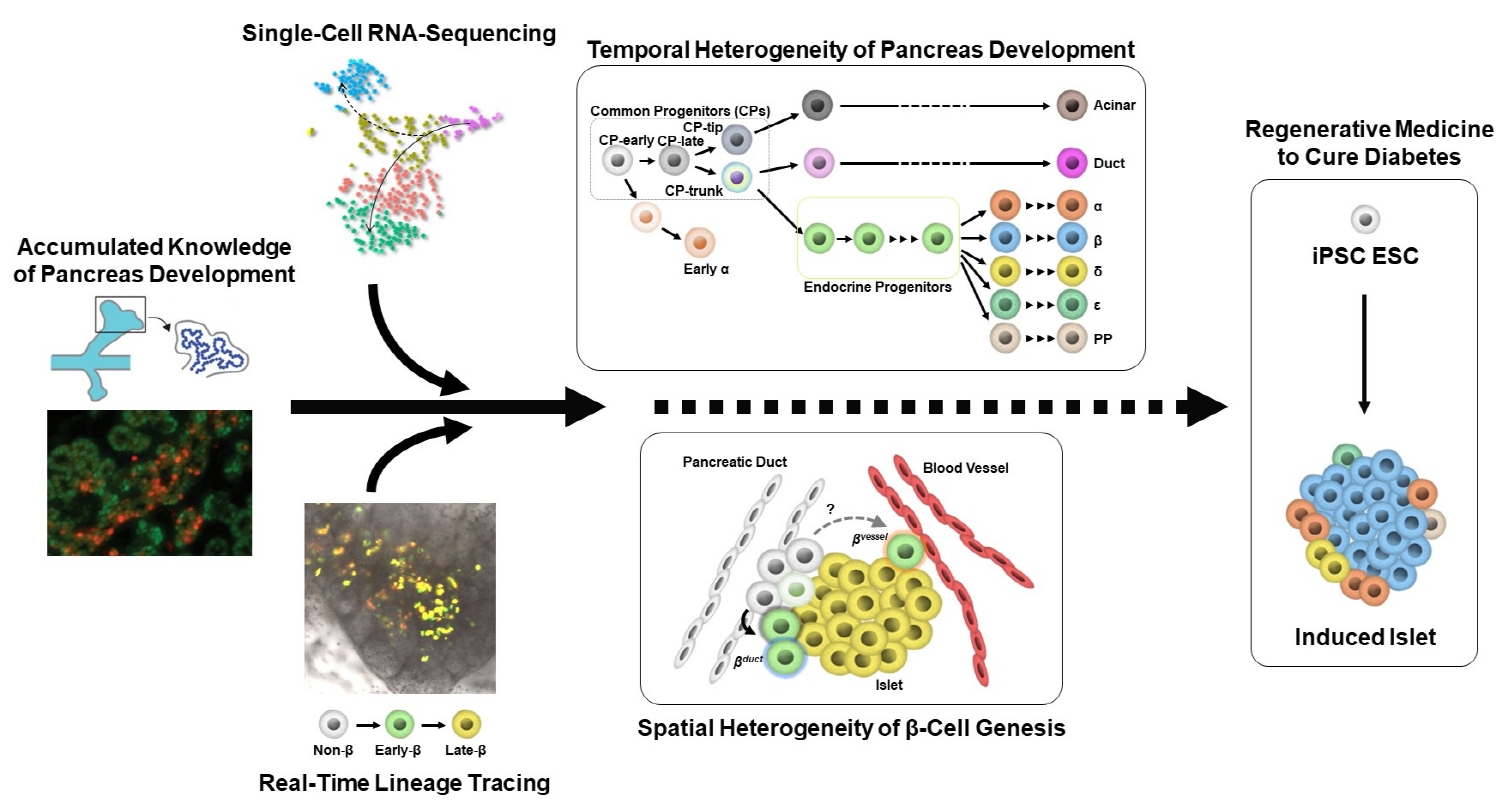
- Heterogeneity of Islet Cells during Embryogenesis and Differentiation
- Shugo Sasaki, Takeshi Miyatsuka
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):173-184. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0324
- 3,709 View
- 248 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes is caused by insufficient insulin secretion due to β-cell dysfunction and/or β-cell loss. Therefore, the restoration of functional β-cells by the induction of β-cell differentiation from embryonic stem (ES) and induced-pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, or from somatic non-β-cells, may be a promising curative therapy. To establish an efficient and feasible method for generating functional insulin-producing cells, comprehensive knowledge of pancreas development and β-cell differentiation, including the mechanisms driving cell fate decisions and endocrine cell maturation is crucial. Recent advances in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technologies have opened a new era in pancreas development and diabetes research, leading to clarification of the detailed transcriptomes of individual insulin-producing cells. Such extensive high-resolution data enables the inference of developmental trajectories during cell transitions and gene regulatory networks. Additionally, advancements in stem cell research have not only enabled their immediate clinical application, but also has made it possible to observe the genetic dynamics of human cell development and maturation in a dish. In this review, we provide an overview of the heterogeneity of islet cells during embryogenesis and differentiation as demonstrated by scRNA-seq studies on the developing and adult pancreata, with implications for the future application of regenerative medicine for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Newly discovered knowledge pertaining to glucagon and its clinical applications
Dan Kawamori, Shugo Sasaki
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(7): 829. CrossRef
- Newly discovered knowledge pertaining to glucagon and its clinical applications
- Basic Research
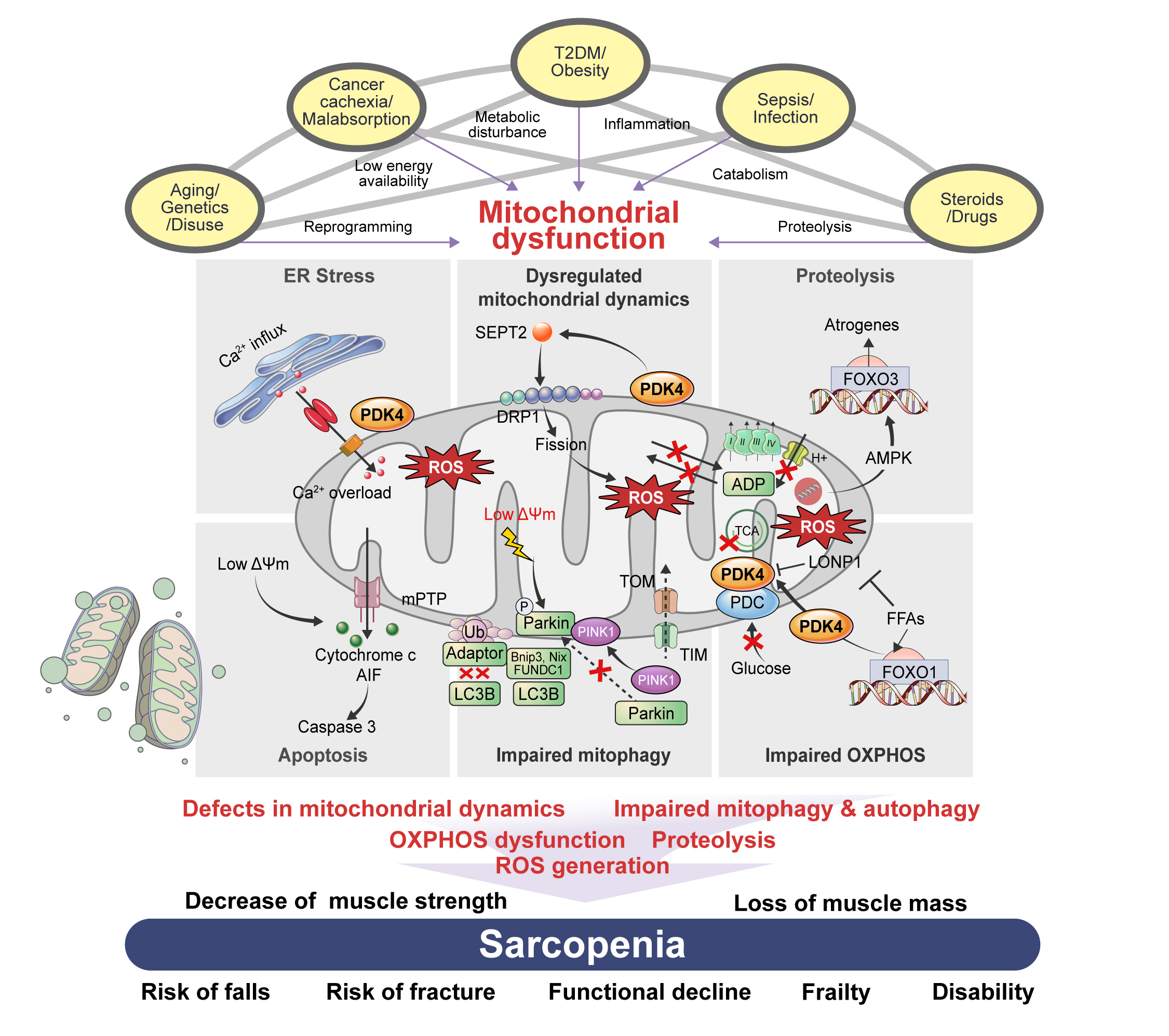
- The Link between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Sarcopenia: An Update Focusing on the Role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4
- Min-Ji Kim, Ibotombi Singh Sinam, Zerwa Siddique, Jae-Han Jeon, In-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):153-163. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0305
- 4,828 View
- 366 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Sarcopenia, defined as a progressive loss of muscle mass and function, is typified by mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of mitochondrial resilience. Sarcopenia is associated not only with aging, but also with various metabolic diseases characterized by mitochondrial dyshomeostasis. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs) are mitochondrial enzymes that inhibit the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which controls pyruvate entry into the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the subsequent adenosine triphosphate production required for normal cellular activities. PDK4 is upregulated in mitochondrial dysfunction-related metabolic diseases, especially pathologic muscle conditions associated with enhanced muscle proteolysis and aberrant myogenesis. Increases in PDK4 are associated with perturbation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondrial quality control, which are emerging as a central mechanism in the pathogenesis of metabolic disease-associated muscle atrophy. Here, we review how mitochondrial dysfunction affects sarcopenia, focusing on the role of PDK4 in mitochondrial homeostasis. We discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of PDK4 on mitochondrial dysfunction in sarcopenia and show that targeting mitochondria could be a therapeutic target for treating sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis, activatory effects, molecular docking and ADME studies as rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase activators of ureido phenyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives
Mustafa Oğuzhan Kaya, Tuna Demirci, Ümit Çalışır, Oğuzhan Özdemir, Yeşim Kaya, Mustafa Arslan
Research on Chemical Intermediates.2024; 50(1): 437. CrossRef - Unraveling the causes of sarcopenia: Roles of neuromuscular junction impairment and mitochondrial dysfunction
Yanmei Miao, Leiyu Xie, Jiamei Song, Xing Cai, Jinghe Yang, Xinglong Ma, Shaolin Chen, Peng Xie
Physiological Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic clues to aging: exploring the role of circulating metabolites in frailty, sarcopenia and vascular aging related traits and diseases
Zonghao Qian, Yuzhen Huang, Yucong Zhang, Ni Yang, Ziwei Fang, Cuntai Zhang, Le Zhang
Frontiers in Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 Protects Cardiomyocytes from lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mitochondrial Damage by Reducing Lactate Accumulation
Tangtian Chen, Qiumin Xie, Bin Tan, Qin Yi, Han Xiang, Rui Wang, Qin Zhou, Bolin He, Jie Tian, Jing Zhu, Hao Xu
Inflammation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats
Majid Mohabbat, Hamid Arazi
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroprotective Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Dichloroacetate: Targeting Metabolic Disorders in Nervous System Diseases
Yue Zhang, Meiyan Sun, Hongxiang Zhao, Zhengyan Wang, Yanan Shi, Jianxin Dong, Kaifang Wang, Xi Wang, Xingyue Li, Haiyan Qi, Xiaoyong Zhao
International Journal of Nanomedicine.2023; Volume 18: 7559. CrossRef
- Synthesis, activatory effects, molecular docking and ADME studies as rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase activators of ureido phenyl substituted 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives
- Technology/Device
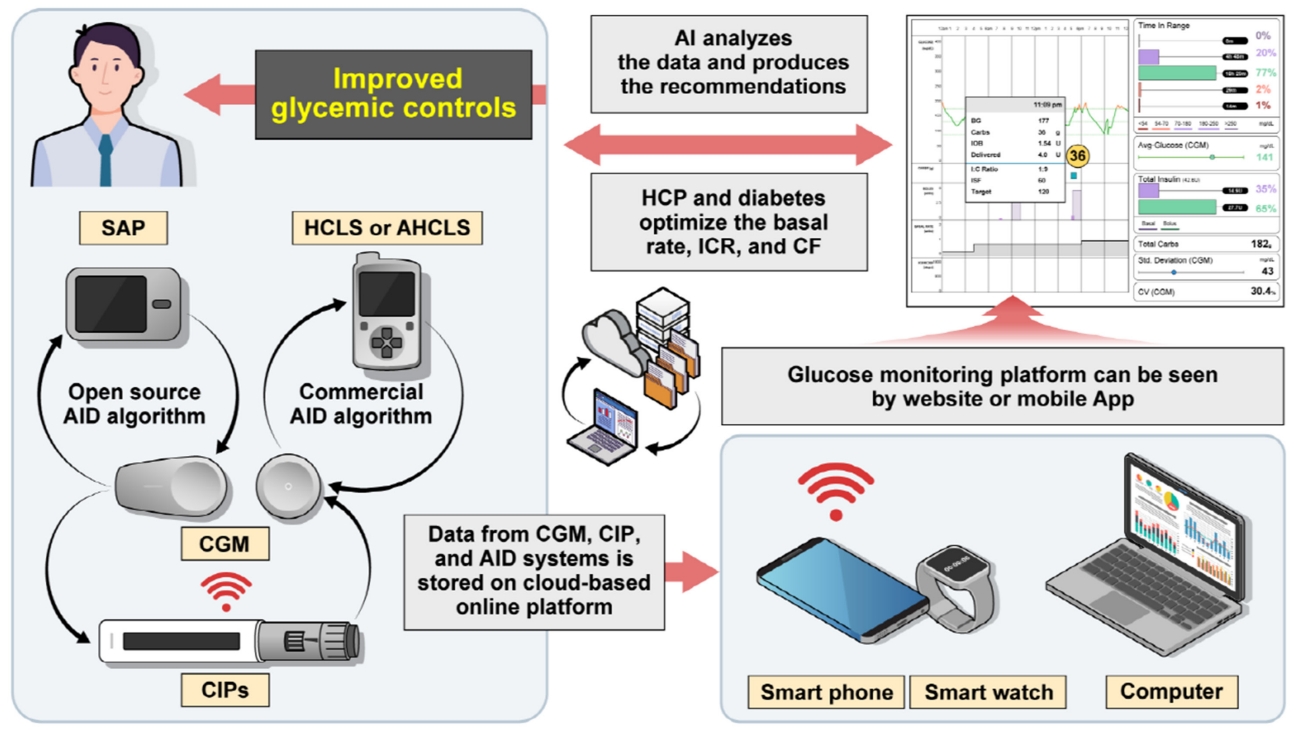
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):27-41. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0271
- 6,169 View
- 383 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology has evolved over the past decade with the integration of various devices including insulin pumps, connected insulin pens (CIPs), automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, and virtual platforms. CGM has shown consistent benefits in glycemic outcomes in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with insulin. Moreover, the combined effect of CGM and education have been shown to improve glycemic outcomes more than CGM alone. Now a CIP is the expected future technology that does not need to be worn all day like insulin pumps and helps to calculate insulin doses with a built-in bolus calculator. Although only a few clinical trials have assessed the effectiveness of CIPs, they consistently show benefits in glycemic outcomes by reducing missed doses of insulin and improving problematic adherence. AID systems and virtual platforms made it possible to achieve target glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetes while minimizing hypoglycemia, which has always been challenging in T1DM. Now fully automatic AID systems and tools for diabetes decisions based on artificial intelligence are in development. These advances in technology could reduce the burden associated with insulin treatment for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advances in the precision control strategy of artificial pancreas
Wuyi Ming, Xudong Guo, Guojun Zhang, Yinxia Liu, Yongxin Wang, Hongmei Zhang, Haofang Liang, Yuan Yang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Health in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Dorothy Avoke, Abdallah Elshafeey, Robert Weinstein, Chang H. Kim, Seth S. Martin
Endocrine Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Outcomes During Early Use of the MiniMed™ 780G Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System with Guardian™ 4 Sensor
Toni L. Cordero, Zheng Dai, Arcelia Arrieta, Fang Niu, Melissa Vella, John Shin, Andrew S. Rhinehart, Jennifer McVean, Scott W. Lee, Robert H. Slover, Gregory P. Forlenza, Dorothy I. Shulman, Rodica Pop-Busui, James R. Thrasher, Mark S. Kipnes, Mark P. Ch
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(9): 652. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - APSec1.0: Innovative Security Protocol Design with Formal Security Analysis for the Artificial Pancreas System
Jiyoon Kim, Jongmin Oh, Daehyeon Son, Hoseok Kwon, Philip Virgil Astillo, Ilsun You
Sensors.2023; 23(12): 5501. CrossRef - Advances and Development of Electronic Neural Interfaces
Xue Jiaxiang, Liu Zhixin
Journal of Computing and Natural Science.2023; : 147. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Metabolic Control in a Cohort of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Coeliac Disease
Flavia Amaro, Maria Alessandra Saltarelli, Marina Primavera, Marina Cerruto, Stefano Tumini
Endocrines.2023; 4(3): 595. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 472. CrossRef - The Growing Challenge of Diabetes Management in an Aging Society
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 630. CrossRef - Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos, Ranjit M. Anjana, Viswanathan Mohan, Charlotte Steenblock, Stefan R. Bornstein
Exploration of Endocrine and Metabolic Disease.2023; 1(1): 16. CrossRef - An Observational Pilot Study of a Tailored Environmental Monitoring and Alert System for Improved Management of Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Mohammed Alotaibi, Fady Alnajjar, Badr A Alsayed, Tareq Alhmiedat, Ashraf M Marei, Anas Bushnag, Luqman Ali
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 3799. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
- Basic Research
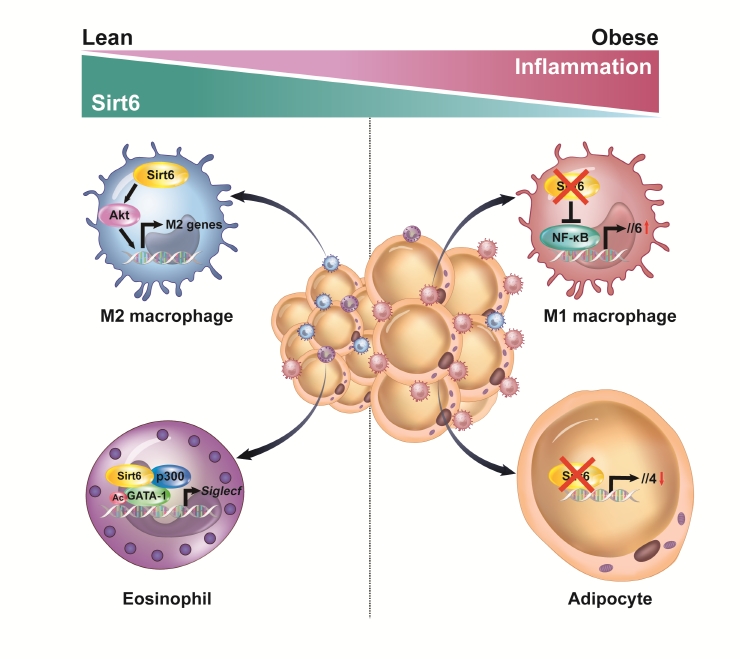
- Multiple Roles of Sirtuin 6 in Adipose Tissue Inflammation
- Eun Ju Bae, Byung-Hyun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):164-172. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0270
- 3,698 View
- 229 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Adipose tissue (AT) inflammation is strongly associated with obesity-induced insulin resistance. When subjected to metabolic stress, adipocytes become inflamed and secrete a plethora of cytokines and chemokines, which recruit circulating immune cells to AT. Although sirtuin 6 (Sirt6) is known to control genomic stabilization, aging, and cellular metabolism, it is now understood to also play a pivotal role in the regulation of AT inflammation. Sirt6 protein levels are reduced in the AT of obese humans and animals and increased by weight loss. In this review, we summarize the potential mechanism of AT inflammation caused by impaired action of Sirt6 from the immune cells’ point of view. We first describe the properties and functions of immune cells in obese AT, with an emphasis on discrete macrophage subpopulations which are central to AT inflammation. We then highlight data that links Sirt6 to functional phenotypes of AT inflammation. Importantly, we discuss in detail the effects of Sirt6 deficiency in adipocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils on insulin resistance or AT browning. In our closing perspectives, we discuss emerging issues in this field that require further investigation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Increased Expression of Sirtuin 6 in the Prevention of Premature Aging Pathomechanisms
Adrianna Dzidek, Olga Czerwińska-Ledwig, Małgorzata Żychowska, Wanda Pilch, Anna Piotrowska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9655. CrossRef - Exploring the Influence of Age, Gender and Body Mass Index on Colorectal Cancer Location
Dorel Popovici, Cristian Stanisav, Sorin Saftescu, Serban Negru, Radu Dragomir, Daniel Ciurescu, Razvan Diaconescu
Medicina.2023; 59(8): 1399. CrossRef
- The Role of Increased Expression of Sirtuin 6 in the Prevention of Premature Aging Pathomechanisms

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





