
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Response
- Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
- Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):815-816. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0296
- [Original]
- 2,465 View
- 118 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current Insights on the Use of Insulin and the Potential Use of Insulin Mimetics in Targeting Insulin Signalling in Alzheimer’s Disease
Amy Woodfield, Tatiana Gonzales, Erik Helmerhorst, Simon Laws, Philip Newsholme, Tenielle Porter, Giuseppe Verdile
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15811. CrossRef
- Current Insights on the Use of Insulin and the Potential Use of Insulin Mimetics in Targeting Insulin Signalling in Alzheimer’s Disease
Corrigendum
- New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
- Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):817-818. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0295
- Corrects: Diabetes Metab J 2022;46(4):517
- 2,049 View
- 144 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
Letter
- Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
- Se Hee Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):813-814. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0259
- [Original]
- 2,183 View
- 131 Download
Reviews
- Pathophysiology
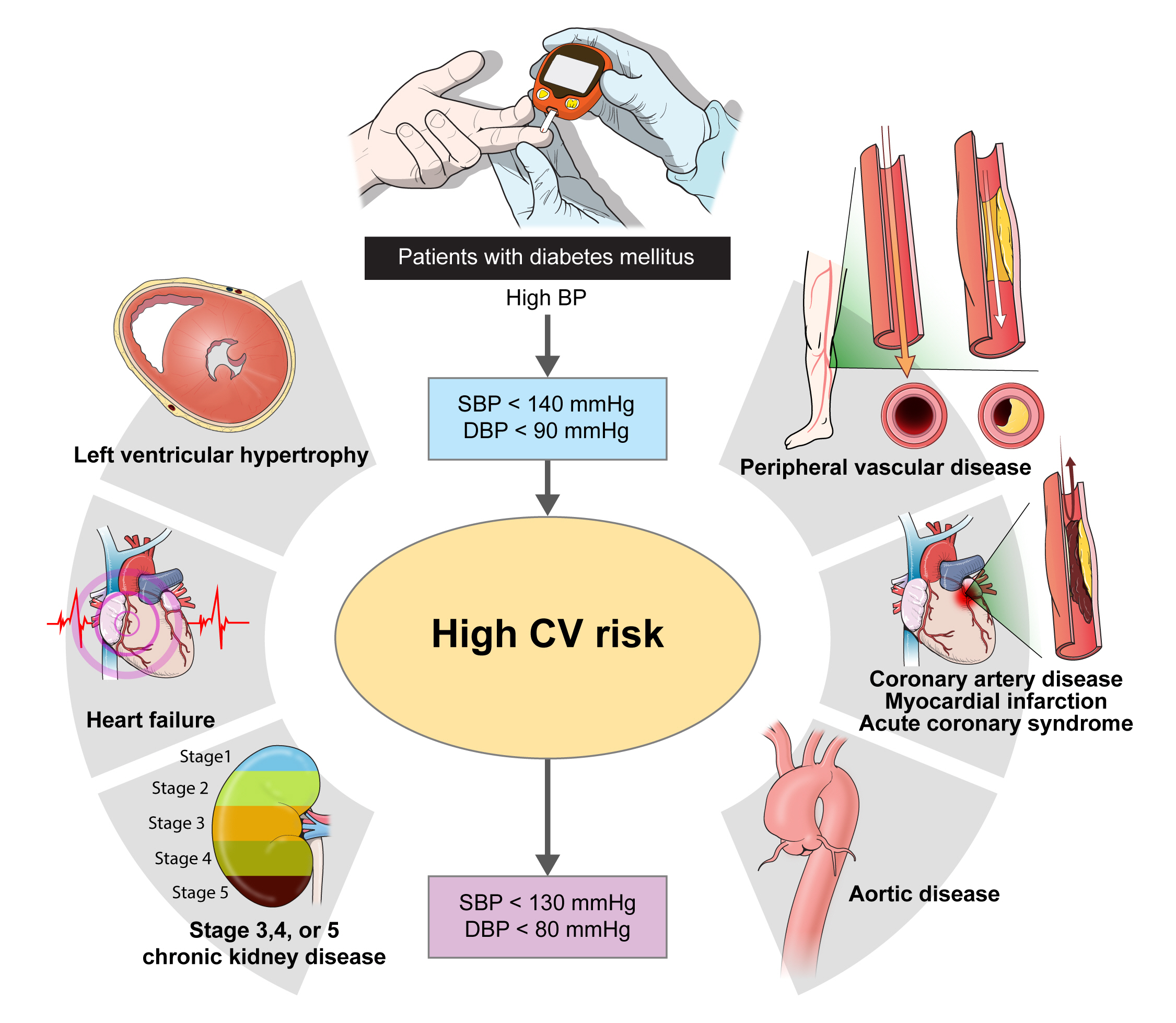
- Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim, on Behalf of the Policy Committee of Korean Society of Hypertension
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):667-674. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0215
- 6,077 View
- 503 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The prevalence of diabetes mellitus continues to increase worldwide, and it is a well-established cardiovascular risk factor. Hypertension is also an important cardiovascular risk factor to be controlled and is common among patients with diabetes mellitus. Optimal blood pressure (BP) goals have been the subject of great debate in the management of hypertension among patients with diabetes mellitus. This review provides detailed results from randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses of clinical outcomes according to the target BP in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. In addition, the target BP in patients with diabetes mellitus recommended by different guidelines was summarized and presented. A target BP of <140/90 mm Hg is recommended for patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus, and BP should be controlled to <130/80 mm Hg in patients with diabetes mellitus who have high-risk clinical features. We hope that this review will be helpful to clinicians and patients by promoting the understanding and appropriate application of BP control in the comprehensive management of patients with diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
Hack-Lyoung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 17. CrossRef - Using Generative AI to Improve the Performance and Interpretability of Rule-Based Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Leon Kopitar, Iztok Fister, Gregor Stiglic
Information.2024; 15(3): 162. CrossRef - Additive interaction of family medical history of diabetes with hypertension on the diagnosis of diabetes among older adults in India: longitudinal ageing study in India
Waquar Ahmed
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging roles of interferon-stimulated gene-15 in age-related telomere attrition, the DNA damage response, and cardiovascular disease
María González-Amor, Beatriz Dorado, Vicente Andrés
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes and Voluntary Exercise on IgA Concentration and Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor Expression in the Submandibular Gland of Rats
Jaebum Park, Yuko Yamamoto, Kouki Hidaka, Satoko Wada-Takahashi, Shun-suke Takahashi, Toshiya Morozumi, Nobuhisa Kubota, Makiko Saita, Juri Saruta, Wakako Sakaguchi, Masahiro To, Tomoko Shimizu, Yuko Mikuni-Takagaki, Keiichi Tsukinoki
Medicina.2023; 59(4): 789. CrossRef - A diabetes update
Zachary Bloomgarden
Journal of Diabetes.2023; 15(7): 542. CrossRef - CARDIOPROTECTIVE AND METABOLIC EFFECTS OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE THERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH SUCH COMORBIDITIES AS ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION, TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS, AND OBESITY
I. P. Dunaieva, N. O. Kravchun, І. A. Ilchenko
Bulletin of Problems Biology and Medicine.2023; 1(2): 211. CrossRef - Hypertensive Heart Failure
Filippos Triposkiadis, Pantelis Sarafidis, Alexandros Briasoulis, Dimitrios E. Magouliotis, Thanos Athanasiou, John Skoularigis, Andrew Xanthopoulos
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(15): 5090. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef
- Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
- Pathophysiology
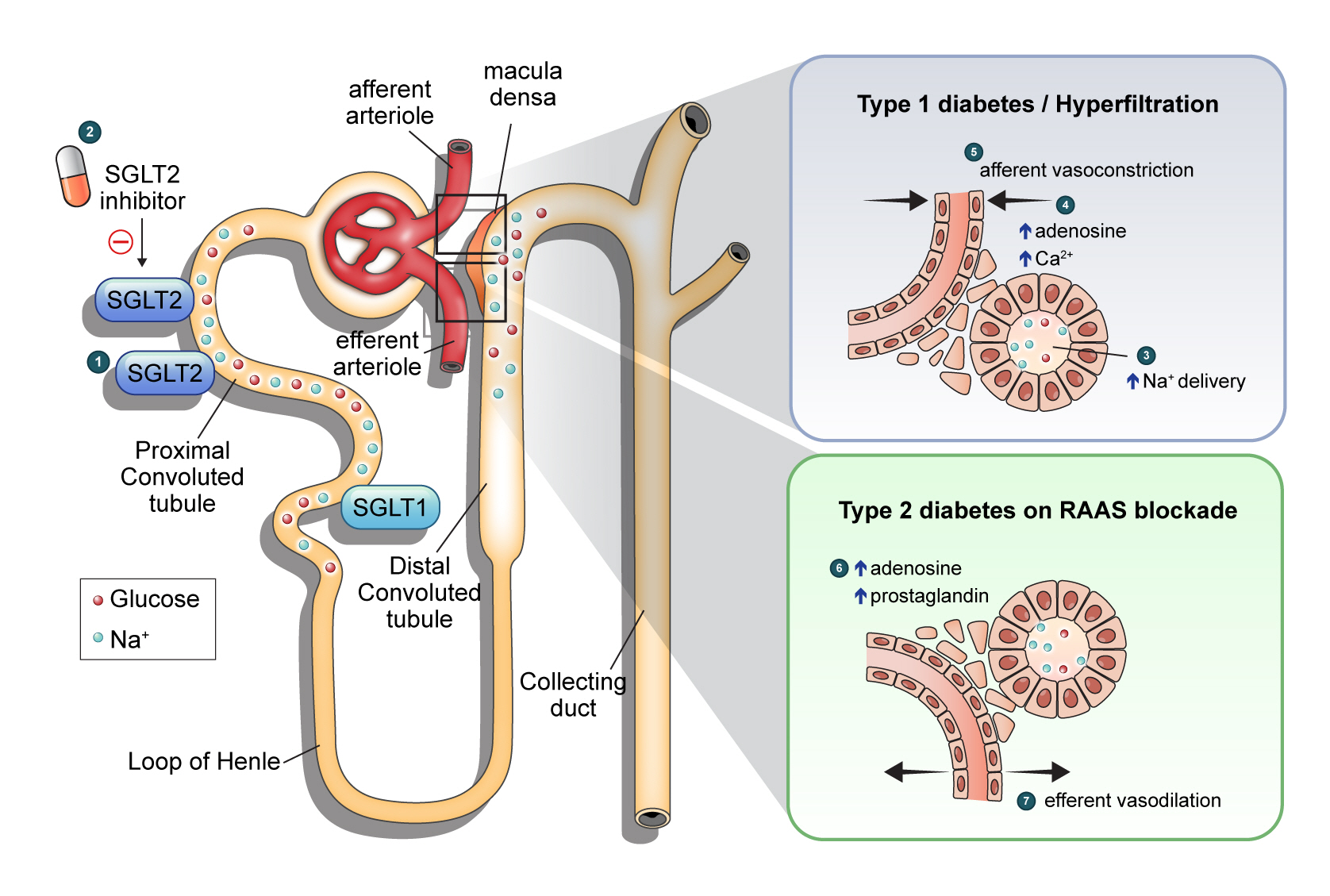
- Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
- Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):543-551. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0209
- 6,348 View
- 673 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a prevalent renal complication of diabetes mellitus that ultimately develops into end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) when not managed appropriately. Substantial risk of ESKD remains even with intensive management of hyperglycemia and risk factors of DKD and timely use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors reduce hyperglycemia primarily by inhibiting glucose and sodium reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule. Currently, their effects expand to prevent or delay cardiovascular and renal adverse events, even in those without diabetes. In dedicated renal outcome trials, SGLT2 inhibitors significantly reduced the risk of composite renal adverse events, including the development of ESKD or renal replacement therapy, which led to the positioning of SGLT2 inhibitors as the mainstay of chronic kidney disease management. Multiple mechanisms of action of SGLT2 inhibitors, including hemodynamic, metabolic, and anti-inflammatory effects, have been proposed. Restoration of tubuloglomerular feedback is a plausible explanation for the alteration in renal hemodynamics induced by SGLT2 inhibition and for the associated renal benefit. This review discusses the clinical rationale and mechanism related to the protection SGLT2 inhibitors exert on the kidney, focusing on renal hemodynamic effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Using intravoxel incoherent motion imaging to evaluate uric acid-induced renal injury and efficacy after treatment
Zhong-Yuan Cheng, Shang-Ao Gong, Ping-Kang Chen, Zong-Chao Yu, Chen Qiu, Ji-Xin Lin, Jia-Bin Mo, Long Qian, You-Zhen Feng, Xiang-Ran Cai
British Journal of Radiology.2024; 97(1153): 274. CrossRef - Rethinking eGFR Comparisons in SGLT2 Inhibitor Research
Yuzuru Ohshiro
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2024; 83(9): e87. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors and Diabetes: Where Does It Come from and Where Does It Go?
Ji Yoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(1): 9. CrossRef - Cardiorenal outcomes and mortality after sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor initiation in type 2 diabetes patients with percutaneous coronary intervention history
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, BongSeong Kim, Mee Kyung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline eGFR, albuminuria and renal outcomes in patients with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment: an updated meta-analysis
Yunke Ma, Chu Lin, Xiaoling Cai, Suiyuan Hu, Xingyun Zhu, Fang Lv, Wenjia Yang, Linong Ji
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(3): 435. CrossRef - Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on renal risk factors in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Mengnan Li, Jian Zhang, Guimei Yang, Jiaxin Zhang, Minmin Han, Yi Zhang, Yunfeng Liu
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 79(6): 859. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Exposure–Response Analysis of the Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Dapagliflozin and Empagliflozin on Kidney Hemodynamics in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Sjoukje van der Hoek, Jeroen V. Koomen, Erik J. M. van Bommel, Charlotte M. Mosterd, Rosalie A. Scholtes, Anne C. Hesp, Jasper Stevens, Daniel H. van Raalte, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(5): 747. CrossRef - Osteopontin as a Biomarker in Chronic Kidney Disease
Satyesh K. Sinha, Michael Mellody, Maria Beatriz Carpio, Robert Damoiseaux, Susanne B. Nicholas
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1356. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Synthesis and biological profile of benzoxazolone derivatives
Parteek Prasher, Tanisqa Mall, Mousmee Sharma
Archiv der Pharmazie.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SGLT2 inhibitors prevent LPS-induced M1 macrophage polarization and alleviate inflammatory bowel disease by downregulating NHE1 expression
Ye Jin Kim, Jonghwa Jin, Dong-Ho Kim, Daehoon Kim, You Mie Lee, Jun-Kyu Byun, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
Inflammation Research.2023; 72(10-11): 1981. CrossRef
- Using intravoxel incoherent motion imaging to evaluate uric acid-induced renal injury and efficacy after treatment
Editorial
- Beyond Liver Disease: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Kidney Disease
- Eugene Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):564-566. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0203
- 2,341 View
- 130 Download
Reviews
- Drug/Regimen
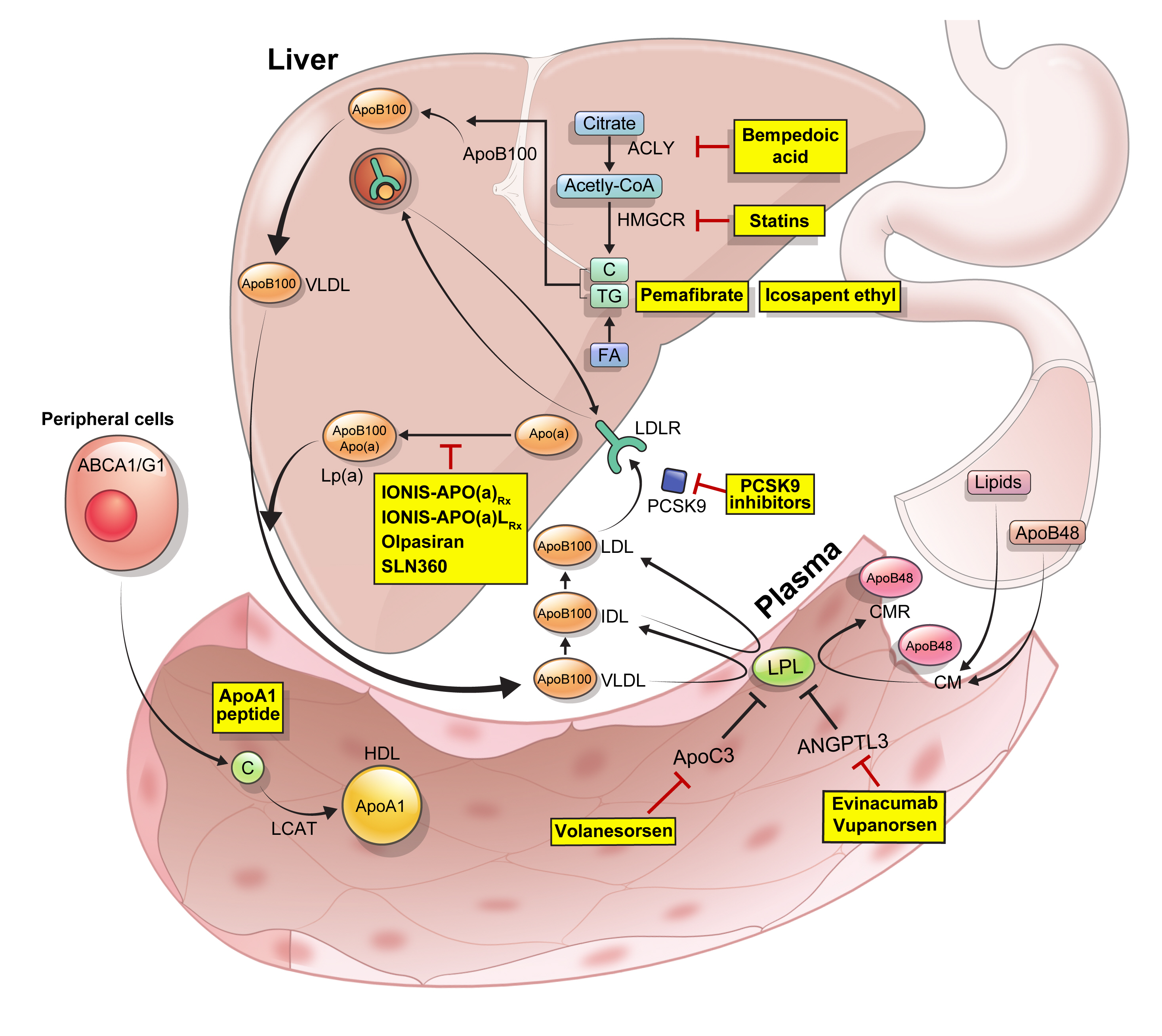
- New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
- Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):517-532. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0198
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2022;46(5):817
- 9,885 View
- 864 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Statins are the cornerstone of the prevention and treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). However, even under optimal statin therapy, a significant residual ASCVD risk remains. Therefore, there has been an unmet clinical need for novel lipid-lowering agents that can target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and other atherogenic particles. During the past decade, several drugs have been developed for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Inclisiran, a small interfering RNA that targets proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9), shows comparable effects to that of PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies. Bempedoic acid, an ATP citrate lyase inhibitor, is a valuable treatment option for the patients with statin intolerance. Pemafibrate, the first selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha modulator, showed a favorable benefit-risk balance in phase 2 trial, but the large clinical phase 3 trial (PROMINENT) was recently stopped for futility based on a late interim analysis. High dose icosapent ethyl, a modified eicosapentaenoic acid preparation, shows cardiovascular benefits. Evinacumab, an angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3) monoclonal antibody, reduces plasma LDL-C levels in patients with refractory hypercholesterolemia. Novel antisense oligonucleotides targeting apolipoprotein C3 (apoC3), ANGPTL3, and lipoprotein(a) have significantly attenuated the levels of their target molecules with beneficial effects on associated dyslipidemias. Apolipoprotein A1 (apoA1) is considered as a potential treatment to exploit the athero-protective effects of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), but solid clinical evidence is necessary. In this review, we discuss the mode of action and clinical outcomes of these novel lipid-lowering agents beyond statins.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of adherence in patients with chronic diseases
Michel Burnier
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 119: 1. CrossRef - Bempedoic acid: new evidence and recommendations on use
Kristina Paponja, Ivan Pećin, Željko Reiner, Maciej Banach
Current Opinion in Lipidology.2024; 35(1): 41. CrossRef - Genetic insights into repurposing statins for hyperthyroidism prevention: a drug-target Mendelian randomization study
Anqi Huang, Xinyi Wu, Jiaqi Lin, Chiju Wei, Wencan Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting host-specific metabolic pathways—opportunities and challenges for anti-infective therapy
Monika I. Konaklieva, Balbina J. Plotkin
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) and Atherosclerosis: Does Hypolipidemic Treatment Have an Effect?
Petros Adamidis, Despoina Pantazi, Iraklis Moschonas, Evangelos Liberopoulos, Alexandros Tselepis
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2024; 11(3): 72. CrossRef - Modulating effects of crocin on lipids and lipoproteins: Mechanisms and potential benefits
Habib Yaribeygi, Mina Maleki, Farin Rashid-Farrokhi, Payman Raise Abdullahi, Mohammad Amin Hemmati, Tannaz Jamialahmadi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Heliyon.2024; 10(7): e28837. CrossRef - Assessing the Benefits of Lifestyle Influences on Cardiovascu-lar Health After Acute Coronary Syndrome
Marius Rus, Claudia Elena Stanis, Paula Marian, Lilliana Oana Pobirci, Loredana Ioana Banszki, Veronica Huplea, Gheorghe Adrian Osiceanu, Bianca-Maria Pop, Gabriela Dogaru, Felicia Liana Andronie-Cioara
Balneo and PRM Research Journal.2024; 15(Vol.15, no): 660. CrossRef - Liver cancer cells as the model for developing liver-targeted RNAi therapeutics
Beibei Hou, Linhui Qin, Linfeng Huang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2023; 644: 85. CrossRef - Insights into Causal Cardiovascular Risk Factors from Mendelian Randomization
C. M. Schooling, J. V. Zhao
Current Cardiology Reports.2023; 25(2): 67. CrossRef - Secoisolariciresinol diglucoside and anethole ameliorate lipid abnormalities, oxidative injury, hypercholesterolemia, heart, and liver conditions
Sana Noreen, Habib‐ur Rehman, Tabussam Tufail, Huma Badar Ul Ain, Chinaza Godswill Awuchi
Food Science & Nutrition.2023; 11(6): 2620. CrossRef - Colesterol remanente, riesgo vascular y prevención de la arteriosclerosis
Xavier Pintó, Marta Fanlo, Virginia Esteve, Jesús Millán, Agustín Blanco, Mariano Blasco, José Luís Díaz Díaz, Ángel Díaz Rodríguez, Alipio Mangas, Vicente Pascual, Juan Pedro Botet, Pablo Pérez Martínez
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis.2023; 35(4): 206. CrossRef - Evolving Management of Low‐Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: A Personalized Approach to Preventing Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Across the Risk Continuum
Michael J. Wilkinson, Norman E. Lepor, Erin D. Michos
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The cell origins of foam cell and lipid metabolism regulated by mechanical stress in atherosclerosis
Zhi Ouyang, Jian Zhong, Junyi Shen, Ye Zeng
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Metabolism: Key Regulators of Their Flux
Alejandro Gugliucci
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4399. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol, vascular risk, and prevention of atherosclerosis
Xavier Pintó, Marta Fanlo, Virginia Esteve, Jesús Millán
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis (English Edition).2023; 35(4): 206. CrossRef - Antibiotics and Lipid-Modifying Agents: Potential Drug–Drug Interactions and Their Clinical Implications
Marios Spanakis, Danny Alon-Ellenbogen, Petros Ioannou, Nikolaos Spernovasilis
Pharmacy.2023; 11(4): 130. CrossRef - Advances in Treatment of Dyslipidemia
Jill Dybiec, Wiktoria Baran, Bartłomiej Dąbek, Piotr Fularski, Ewelina Młynarska, Ewa Radzioch, Jacek Rysz, Beata Franczyk
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13288. CrossRef - Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α in Lipoprotein Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Elena Valeria Fuior, Evangelia Zvintzou, Theodosios Filippatos, Katerina Giannatou, Victoria Mparnia, Maya Simionescu, Anca Violeta Gafencu, Kyriakos E. Kypreos
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2696. CrossRef - Preparation, characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study of ginsenoside Rb1-PLGA nanoparticles
Lixin Du, Huiling Lu, Yifei Xiao, Zhihua Guo, Ya Li
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dysregulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis in Ovarian Cancer
Zahraa Qusairy, Anne Gangloff, Shuk On Annie Leung
Current Oncology.2023; 30(9): 8386. CrossRef - Riesgo residual. Conclusiones
Ángel Cequier, José Luis Zamorano
Revista Española de Cardiología Suplementos.2023; 23: 25. CrossRef - Causal effects of circulating lipids and lipid-lowering drugs on the risk of urinary stones: a Mendelian randomization study
Zilong Tan, Jing Hong, Aochuan Sun, Mengdi Ding, Jianwu Shen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of residual cardiovascular risk: trends and frontiers
Lin Wang, Sutong Wang, Chaoyuan Song, Yiding Yu, Yuehua Jiang, Yongcheng Wang, Xiao Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Understanding on the Genetic Basis of Key Metabolic Disorders: A Review
Kenneth Francis Rodrigues, Wilson Thau Lym Yong, Md. Safiul Alam Bhuiyan, Shafiquzzaman Siddiquee, Muhammad Dawood Shah, Balu Alagar Venmathi Maran
Biology.2022; 11(9): 1308. CrossRef - Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 575. CrossRef
- The role of adherence in patients with chronic diseases
- Others
- Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):552-563. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0193

- 5,701 View
- 277 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Recently, medical research using big data has become very popular, and its value has become increasingly recognized. The Korean National Health Information Database (NHID) is representative of big data that combines information obtained from the National Health Insurance Service collected for claims and reimbursement of health care services and results obtained from general health examinations provided to all Korean adults. This database has several strengths and limitations. Given the large size, various laboratory data, and questionnaires obtained from medical check-ups, their longitudinal nature, and long-term accumulation of data since 2002, carefully designed studies may provide valuable information that is difficult to obtain from other forms of research. However, consideration of possible bias and careful interpretation when defining causal relationships is also important because the data were not collected for research purposes. After the NHID became publicly available, research and publications based on this database have increased explosively, especially in the field of diabetes and metabolism. This article reviews the history, structure, and characteristics of the Korean NHID. Recent trends in big data research using this database, commonly used operational diagnosis, and representative studies have been introduced. We expect further progress and expansion of big data research using the Korean NHID.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Repeated detection of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease increases the incidence risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Mee Kyoung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 180. CrossRef - Diabetes severity and the risk of depression: A nationwide population-based study
Yunjung Cho, Bongsung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 351: 694. CrossRef - Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol is an independent risk factor for the incidence of chronic kidney disease in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Soo Yeon Jang, Minwoong Kang, Eyun Song, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111639. CrossRef - Association of the Intensive Blood Pressure Target and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the Population With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Study in Korea
Soo‐Young Yoon, Ji Yoon Kong, Su Jin Jeong, Jin Sug Kim, Hyeon Seok Hwang, Kyunghwan Jeong
Journal of the American Heart Association.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 290. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease
Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
npj Parkinson's Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Comorbidity Differences by Trajectory Groups as a Reference for Identifying Patients at Risk for Late Mortality in Childhood Cancer Survivors: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hyery Kim, Hae Reong Kim, Sung Han Kang, Kyung-Nam Koh, Ho Joon Im, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41203. CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the Relationship Between Psychiatry Visit and Suicide After Deliberate Self-harm: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hye Hyeon Kim, Chanyoung Ko, Ji Ae Park, In Han Song, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41261. CrossRef - Reply
Yeonghee Eun, Hyungjin Kim, Jaejoon Lee
Arthritis & Rheumatology.2023; 75(6): 1081. CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Comparison of Cefepime with Piperacillin/Tazobactam Treatment in Patients with Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
Bo-Guen Kim, Danbee Kang, Kyung Hoon Min, Juhee Cho, Kyeongman Jeon
Antibiotics.2023; 12(6): 984. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome increases thyroid cancer risk in young adults: a population-based cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(4): 526. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High Body Weight Variability
Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 163. CrossRef - Physical activity and reduced risk of fracture in thyroid cancer patients after thyroidectomy — a nationwide cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Jeonghoon Ha, Chaiho Jeong, Jun-Young Heu, Se-Won Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Hyun Baek
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Response to comments of Lai et al. “Proposal of one option for patient-centered, heterogeneous selection of antidiabetic drug”
Sunyoung Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110864. CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Increased risk of ischemic stroke associated with elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase level in adult cancer survivors: a population-based cohort study
Kyuwoong Kim, Hyeyun Jung, Edvige Di Giovanna, Tae Joon Jun, Young-Hak Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
Ye-Seul Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101000. CrossRef - Possible Applications of the Korean Experience in the Development of Croatian Healthcare System
Predrag Bejakovic, Romina P Družeta, Ohmin Kwon
Science, Art and Religion.2023; 2(1--2): 26. CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Alcohol consumption and the risk of liver disease: a nationwide, population-based study
Sang Yi Moon, Minkook Son, Yeo Wool Kang, Myeongseok Koh, Jong Yoon Lee, Yang Hyun Baek
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef - Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide propensity-score matched cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 194: 110187. CrossRef - Chronic viral hepatitis accelerates lung function decline in smokers
Suh-Young Lee, Sun-Sin Kim, So-Hee Lee, Heung-Woo Park
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2022; 23(6): 2159. CrossRef
- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Response
- Clinical Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Study (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46: 658-62)
- Hwi Seung Kim, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):665-666. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0166
- [Original]
- 2,371 View
- 130 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Type 2 diabetes mellitus pharmacological remission with dapagliflozin plus oral semaglutide
Maria Elena Lunati, Vincenzo Cimino, Davide Bernasconi, Alessandra Gandolfi, Paola Silvia Morpurgo, Camilla Tinari, Elisa Lazzaroni, Laura Baruffaldi, Milena Muratori, Laura Montefusco, Ida Pastore, Antonio Rossi, Ivano Giuseppe Franzetti, Fabrizio Murato
Pharmacological Research.2024; 199: 107040. CrossRef
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus pharmacological remission with dapagliflozin plus oral semaglutide
Letter
- Clinical Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Study (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46: 658-62)
- Tomoyuki Kawada
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):663-664. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0131
- [Original]
- 2,404 View
- 139 Download
Review
- Pathophysiology
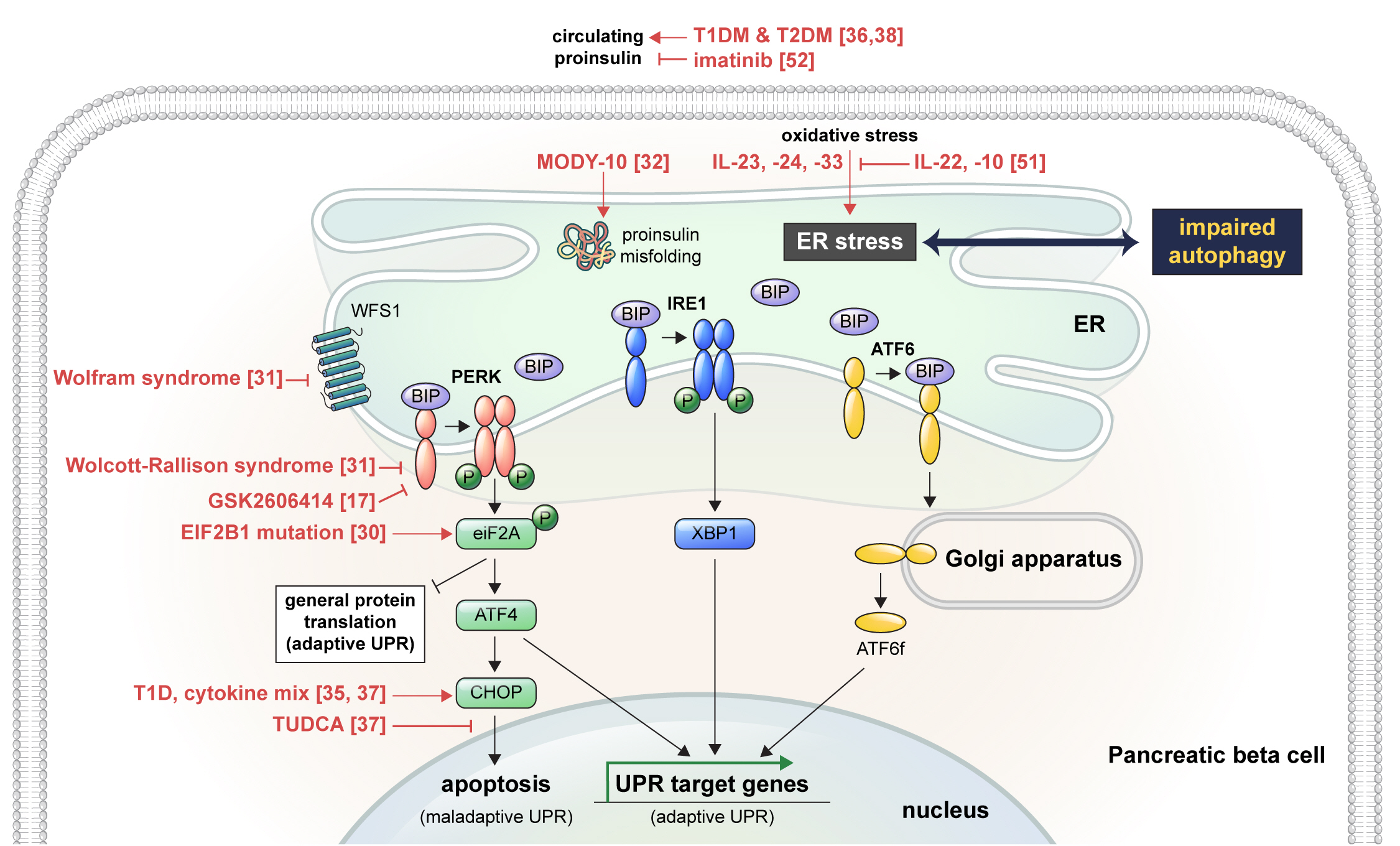
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Dysregulated Autophagy in Human Pancreatic Beta Cells
- Seoil Moon, Hye Seung Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):533-542. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0070
- 4,505 View
- 250 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Pancreatic beta cell homeostasis is crucial for the synthesis and secretion of insulin; disruption of homeostasis causes diabetes, and is a treatment target. Adaptation to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress through the unfolded protein response (UPR) and adequate regulation of autophagy, which are closely linked, play essential roles in this homeostasis. In diabetes, the UPR and autophagy are dysregulated, which leads to beta cell failure and death. Various studies have explored methods to preserve pancreatic beta cell function and mass by relieving ER stress and regulating autophagic activity. To promote clinical translation of these research results to potential therapeutics for diabetes, we summarize the current knowledge on ER stress and autophagy in human insulin-secreting cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucolipotoxicity Suppressed Autophagy and Insulin Contents in Human Islets, and Attenuation of PERK Activity Enhanced Them in an ATG7-Dependent Manner
Seoil Moon, Ji Yoon Lim, Mirang Lee, Youngmin Han, Hongbeom Kim, Wooil Kwon, Jin-Young Jang, Mi Na Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 231. CrossRef - Endoplasmic reticulum stress: A possible connection between intestinal inflammation and neurodegenerative disorders
Giorgio Vivacqua, Romina Mancinelli, Stefano Leone, Rosa Vaccaro, Ludovica Garro, Simone Carotti, Ludovica Ceci, Paolo Onori, Luigi Pannarale, Antonio Franchitto, Eugenio Gaudio, Arianna Casini
Neurogastroenterology & Motility.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pancreatic islet remodeling in cotadutide-treated obese mice
Renata Spezani, Thatiany Souza Marinho, Luiz E. Macedo Cardoso, Marcia Barbosa Aguila, Carlos Alberto Mandarim-de-Lacerda
Life Sciences.2023; 327: 121858. CrossRef - Modulation of Unfolded Protein Response Restores Survival and Function of β-Cells Exposed to the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A
Laura Maria Daian, Gabriela Tanko, Andrei Mircea Vacaru, Luiza Ghila, Simona Chera, Ana-Maria Vacaru
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2023. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Identification and analysis of type 2 diabetes-mellitus-associated autophagy-related genes
Kun Cui, Zhizheng Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sestrin2 in diabetes and diabetic complications
Xiaodan Zhang, Zirui Luo, Jiahong Li, Yaxuan Lin, Yu Li, Wangen Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Crosstalk between autophagy and insulin resistance: evidence from different tissues
Asie Sadeghi, Maryam Niknam, Mohammad Amin Momeni-Moghaddam, Maryam Shabani, Hamid Aria, Alireza Bastin, Maryam Teimouri, Reza Meshkani, Hamed Akbari
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta cell lipotoxicity in the development of type 2 diabetes: the need for species-specific understanding
Patricia Thomas, Meurig T. Gallagher, Gabriela Da Silva Xavier
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Glucolipotoxicity Suppressed Autophagy and Insulin Contents in Human Islets, and Attenuation of PERK Activity Enhanced Them in an ATG7-Dependent Manner
Original Articles
- Type 1 Diabetes
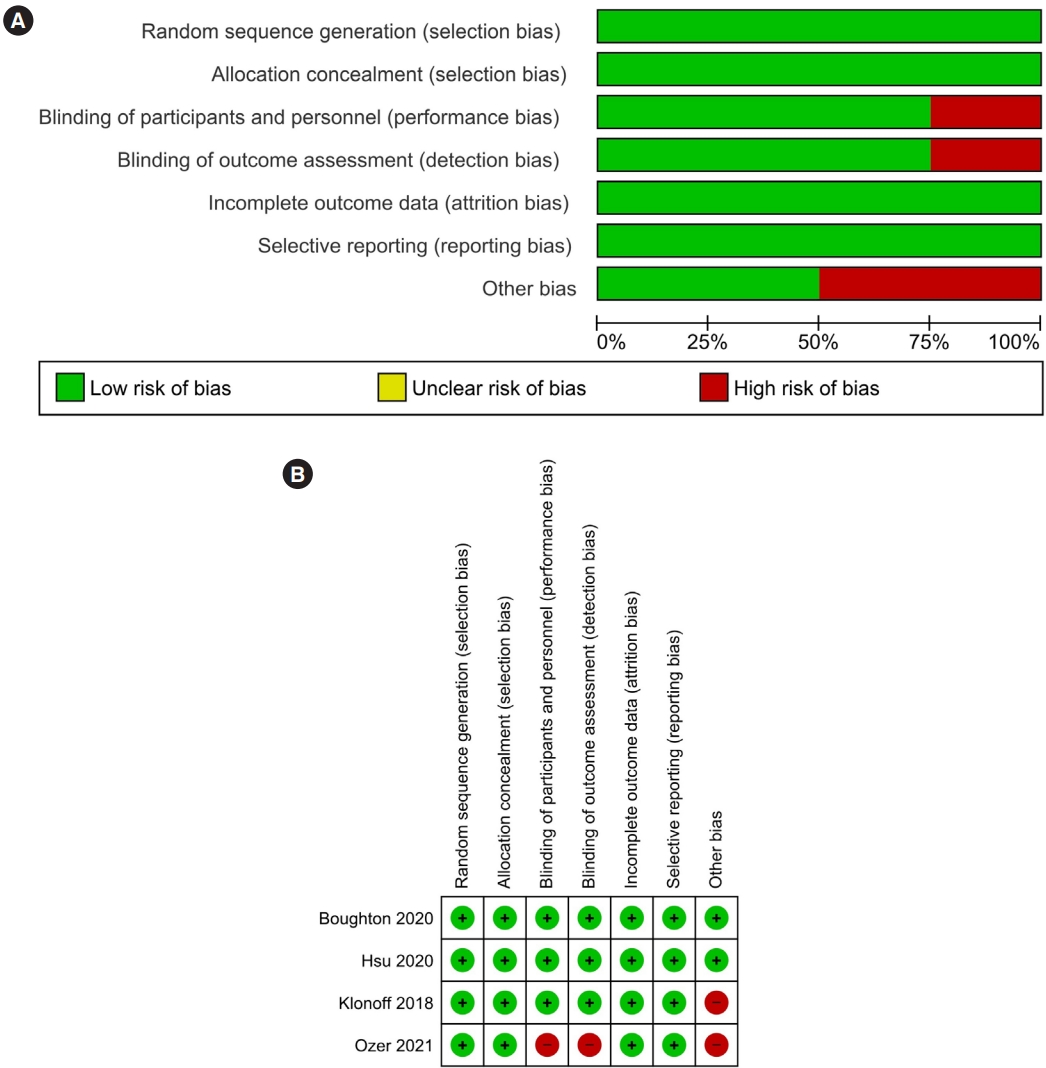
- Performance of Fast-Acting Aspart Insulin as Compared to Aspart Insulin in Insulin Pump for Managing Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
- Deep Dutta, Ritin Mohindra, Kunal Mahajan, Meha Sharma
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):72-81. Published online June 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0035
- 4,858 View
- 250 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
No meta-analysis has analysed efficacy and safety of fast-acting aspart insulin (FIAsp) with insulin pump in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).
Methods
Electronic databases were searched for randomised controlled trials (RCTs) involving T1DM patients on insulin pump receiving FIAsp in intervention arm, and placebo/active comparator insulin in control arm. Primary outcome was to evaluate changes in 1- and 2-hour post-prandial glucose (1hPPG and 2hPPG). Secondary outcomes were to evaluate alterations in percentage time with blood glucose <3.9 mmol/L (hypoglycaemia), time in range (TIR) blood glucose 3.9 to 10 mmol/L, insulin requirements and adverse events.
Results
Data from four RCTs involving 640 patients was analysed. FIAsp use in insulin pump was associated with significantly greater lowering of 1hPPG (mean difference [MD], –1.35 mmol/L; 95% confidence interval [CI], –1.72 to –0.98; P<0.01; I2=63%) and 2hPPG (MD, –1.19 mmol/L; 95% CI, –1.38 to –1.00; P<0.01; I2=0%) as compared to controls. TIR was comparable among groups (MD, 1.06%; 95% CI, –3.84 to 5.96; P=0.67; I2=70%). Duration of blood glucose <3.9 mmol/L was lower in FIAsp group, approaching significance (MD, –0.91%; 95% CI, –1.84 to 0.03; P=0.06; I2=0%). Total hypoglycaemic episodes (risk ratio [RR], 1.35; 95% CI, 0.55 to 3.31; P=0.51; I2=0%), severe hypoglycaemia (RR, 2.26; 95% CI, 0.77 to 6.66; P=0.14), infusion site reactions (RR, 1.35; 95% CI, 0.63 to 2.93; P=0.77; I2=0%), and treatment-emergent adverse events (RR, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.80 to 1.60; P=0.50; I2=0%) were comparable.
Conclusion
FIAsp use in insulin pump is associated with better post-prandial glycaemic control with no increased hypoglycaemia or glycaemic variability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of Ultra-rapid Lispro Insulin in Managing Type-1 and Type-2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Deep Dutta, Lakshmi Nagendra, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 27(6): 467. CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of Ultra-rapid Lispro Insulin in Managing Type-1 and Type-2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Basic Research
- Peroxisomal Fitness: A Potential Protective Mechanism of Fenofibrate against High Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice
- Songling Jiang, Md Jamal Uddin, Xiaoying Yu, Lingjuan Piao, Debra Dorotea, Goo Taeg Oh, Hunjoo Ha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):829-842. Published online June 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0274
- 4,885 View
- 292 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been increasing in association with the epidemic of obesity and diabetes. Peroxisomes are single membrane-enclosed organelles that play a role in the metabolism of lipid and reactive oxygen species. The present study examined the role of peroxisomes in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced NAFLD using fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) agonist.
Methods
Eight-week-old male C57BL/6J mice were fed either a normal diet or HFD for 12 weeks, and fenofibrate (50 mg/kg/day) was orally administered along with the initiation of HFD.
Results
HFD-induced liver injury as measured by increased alanine aminotransferase, inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid accumulation was effectively prevented by fenofibrate. Fenofibrate significantly increased the expression of peroxisomal genes and proteins involved in peroxisomal biogenesis and function. HFD-induced attenuation of peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation was also significantly restored by fenofibrate, demonstrating the functional significance of peroxisomal fatty acid oxidation. In Ppara deficient mice, fenofibrate failed to maintain peroxisomal biogenesis and function in HFD-induced liver injury.
Conclusion
The present data highlight the importance of PPARα-mediated peroxisomal fitness in the protective effect of fenofibrate against NAFLD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacological potential of ginseng and ginsenosides in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Young-Su Yi
Journal of Ginseng Research.2024; 48(2): 122. CrossRef - Fenofibrate alleviates NAFLD by enhancing the PPARα/PGC-1α signaling pathway coupling mitochondrial function
Xuemei Wang, Jieying Wang, Cao Ying, Yuan Xing, Xuan Su, Ke Men
BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 184. CrossRef - Current Therapeutical Approaches Targeting Lipid Metabolism in NAFLD
Manuela Vitulo, Elisa Gnodi, Giulia Rosini, Raffaella Meneveri, Roberto Giovannoni, Donatella Barisani
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(16): 12748. CrossRef - PPARα agonist fenofibrate prevents postoperative cognitive dysfunction by enhancing fatty acid oxidation in mice
Tiantian Liu, Xinlu Chen, Ziqi Wei, Xue Han, Yujia Liu, Zhengliang Ma, Tianjiao Xia, Xiaoping Gu
Translational Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fenofibrate enhances lipid deposition via modulating PPARγ, SREBP-1c, and gut microbiota in ob/ob mice fed a high-fat diet
Ying Zhang, Xiu-Bin Jia, Yun-Chao Liu, Wen-Qian Yu, Yan-Hong Si, Shou-Dong Guo
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Pharmacological potential of ginseng and ginsenosides in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Drug/Regimen
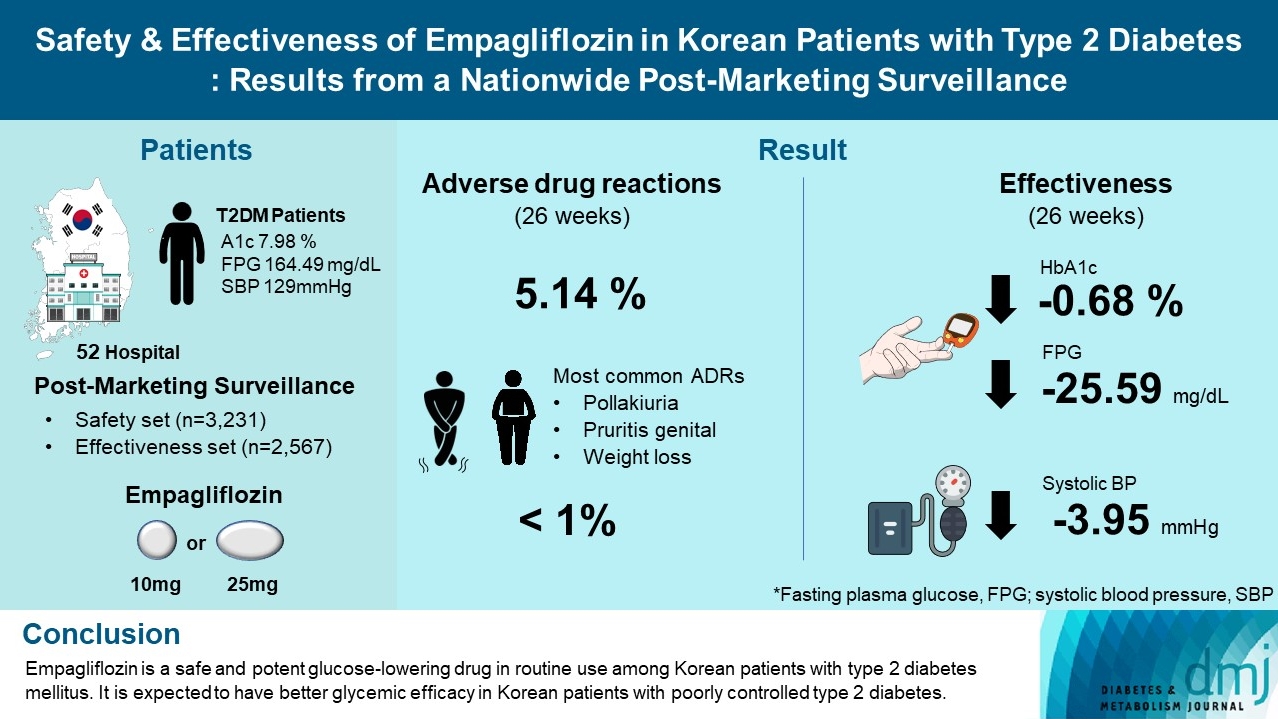
- Safety and Effectiveness of Empagliflozin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Nationwide Post-Marketing Surveillance
- Jun Sung Moon, Nam Hoon Kim, Jin Oh Na, Jae Hyoung Cho, In-Kyung Jeong, Soon Hee Lee, Ji-Oh Mok, Nan Hee Kim, Dong Jin Chung, Jinhong Cho, Dong Woo Lee, Sun Woo Lee, Kyu Chang Won
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):82-91. Published online June 20, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0356
- 5,955 View
- 295 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To evaluate the safety and effectiveness of empagliflozin in routine clinical settings, we collected and assessed the clinical profiles of Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods
This was a post-marketing surveillance study of empagliflozin 10 and 25 mg. Information on adverse events and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) was collected as safety data sets. Available effectiveness outcomes, including glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level, fasting plasma glucose, body weight, and blood pressure, were assessed.
Results
The incidence rate of ADRs was 5.14% in the safety dataset (n=3,231). Pollakiuria, pruritis genital, and weight loss were the most common ADRs. ADRs of special interest accounted for only 1.18%, and there were no serious events that led to mortality or hospitalization. In the effectiveness data set (n=2,567), empagliflozin significantly reduced the mean HbA1c level and body weight during the study period by –0.68%±1.39% and –1.91±3.37 kg (both P<0.0001), respectively. In addition, shorter disease duration, absence of dyslipidemia, and higher baseline HbA1c levels were identified as the clinical features characteristic of a “responder” to empagliflozin therapy.
Conclusion
Empagliflozin is a safe and potent glucose-lowering drug in routine use among Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. It is expected to have better glycemic efficacy in Korean patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin in Bangladeshi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (EFFISAEM Study)
Mohammad Saifuddin, Ajit Kumar Paul, Sultana Marufa Shefin, Md. Jahangir Alam, Shahjada Selim, Sunjida Islam, Tanjina Hossain, Sadiqa Tuqan, Nusrat Sultana, Marufa Mustari, Ramen Chandra Basak, Kazi Ali Aftab, Indrajit Prasad, Mohammad Rafiq Uddin, Shoma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Tolerability of Two Empagliflozin Formulations in Healthy Korean Subjects
Xu Jiang, Sungyeun Bae, Deok Yong Yoon, Shin Jung Park, Jaeseong Oh, Joo-Youn Cho, Kyung-Sang Yu
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2023; Volume 17: 2137. CrossRef - Comparative safety of different sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chun Xing Li, Li Yan Liu, Chen Xiao Zhang, Xu Hua Geng, Si Meng Gu, Yu Qiao Wang, Hua Liu, Qing Xie, Shuo Liang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin in Bangladeshi Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (EFFISAEM Study)
- Drug/Regimen
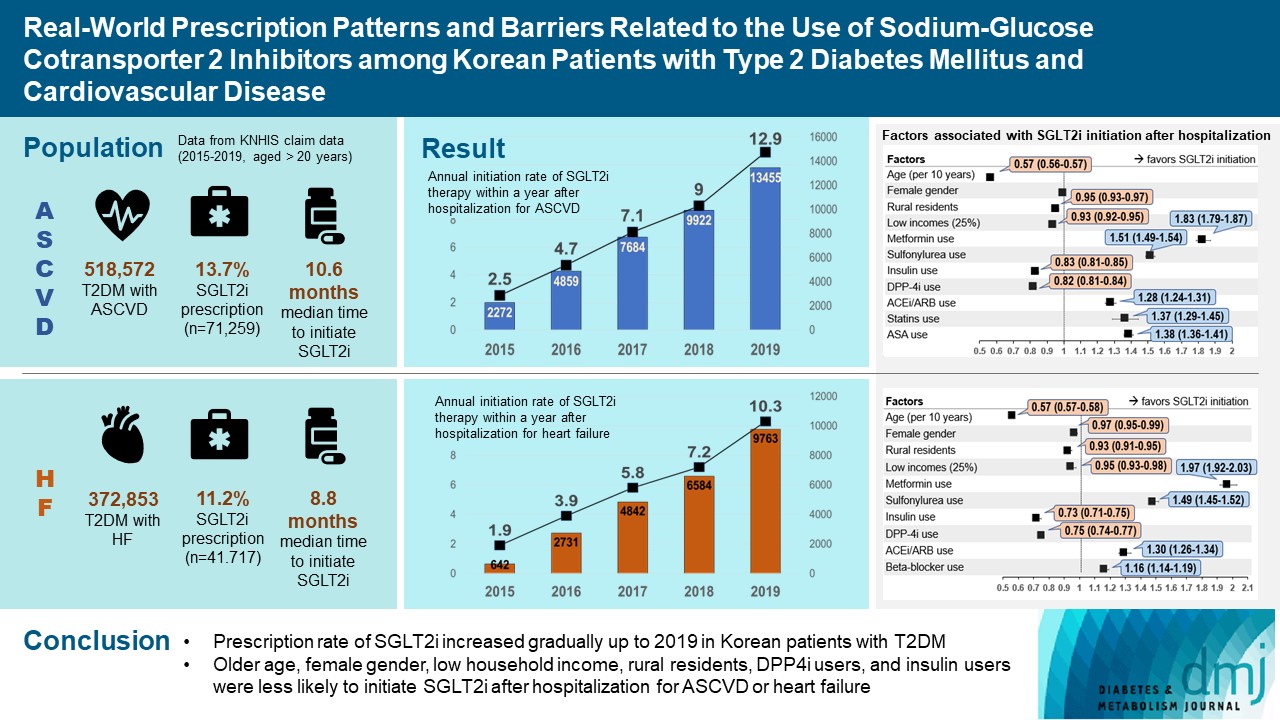
- Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
- Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):701-712. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0002
- 4,905 View
- 319 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate prescription trends and clinical factors of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) use according to the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or heart failure (HF) in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Prescription patterns of SGLT2i use between 2015 and 2019 were determined using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database of claims.
Results
Of all patients with T2DM (n=4,736,493), the annual prescription rate of SGLT2i increased every year in patients with ASCVD (from 2.2% to 10.7%) or HF (from 2.0% to 11.1%). After the first hospitalization for ASCVD (n=518,572), 13.7% (n=71,259) of patients initiated SGLT2i with a median of 10.6 months. After hospitalization for HF (n=372,853), 11.2% (n=41,717) of patients initiated SGLT2i after a median of 8.8 months. In multivariate regression for hospitalization, older age (per 10 years, odds ratio [OR], 0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.56 to 0.57), lower household income (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.92 to 0.95), rural residents (OR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) users (OR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.81 to 0.84) were associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in ASCVD. Additionally, female gender (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99) was associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in HF.
Conclusion
The prescription rate of SGLT2i increased gradually up to 2019 but was suboptimal in patients with ASCVD or HF. After the first hospitalization for ASCVD or HF, older age, female gender, low household income, rural residents, and DPP-4i users were less likely to initiate SGLT2i. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(3): 285. CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Hospital Readmissions for Fluid Overload among Individuals with Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease: Risk Factors and Multivariable Prediction Models
Jiashen Cai, Dorothy Huang, Hanis Binte Abdul Kadir, Zhihua Huang, Li Choo Ng, Andrew Ang, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Yong Mong Bee, Wei Yi Tay, Chieh Suai Tan, Cynthia C. Lim
Nephron.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Prescribing patterns of SGLT-2 inhibitors for patients with heart failure: A two-center analysis
Teja Chakrala, Roshni O. Prakash, Justin Kim, Hanzhi Gao, Umar Ghaffar, Jaymin Patel, Alex Parker, Bhagwan Dass
American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.2023; 28: 100286. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors with DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin in patients with acute myocardial infarction and diabetes mellitus
Young Sang Lyu, Seok Oh, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Myung Ho Jeong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





