
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Role of Fenofibrate Use in Dyslipidemia and Related Comorbidities in the Asian Population: A Narrative Review
- Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Sin Gon Kim, Yu-Cheng Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):184-195. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0168
- 2,377 View
- 347 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
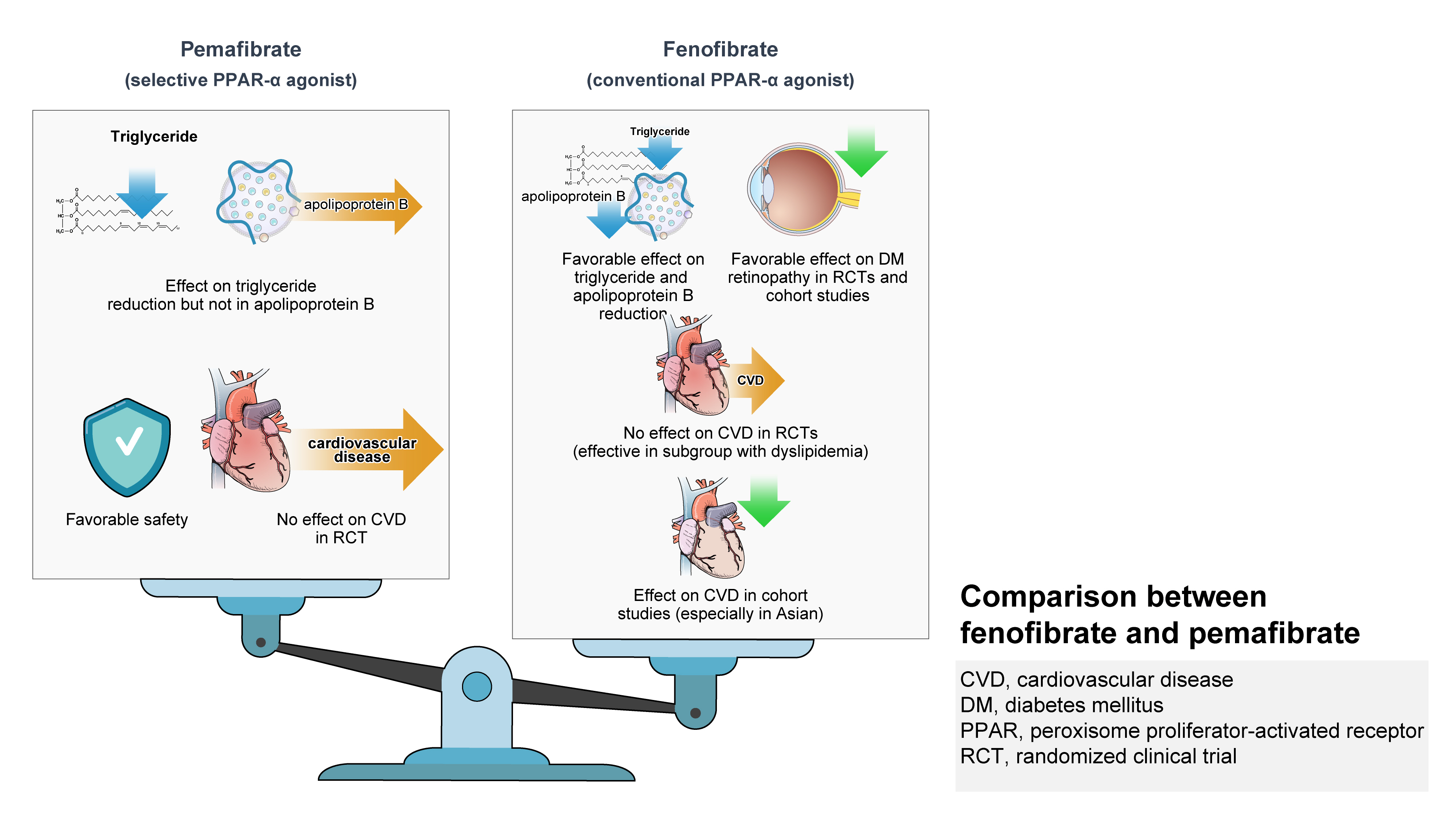
ePub - Hypertriglyceridemia and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) persist despite statin therapy, contributing to residual atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk. Asian subjects are metabolically more susceptible to hypertriglyceridemia than other ethnicities. Fenofibrate regulates hypertriglyceridemia, raises HDL-C levels, and is a recommended treatment for dyslipidemia. However, data on fenofibrate use across different Asian regions are limited. This narrative review summarizes the efficacy and safety data of fenofibrate in Asian subjects with dyslipidemia and related comorbidities (diabetes, metabolic syndrome, diabetic retinopathy, and diabetic nephropathy). Long-term fenofibrate use resulted in fewer cardiovascular (CV) events and reduced the composite of heart failure hospitalizations or CV mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Fenofibrate plays a significant role in improving irisin resistance and microalbuminuria, inhibiting inflammatory responses, and reducing retinopathy incidence. Fenofibrate plus statin combination significantly reduced composite CV events risk in patients with metabolic syndrome and demonstrated decreased triglyceride and increased HDL-C levels with an acceptable safety profile in those with high CV or ASCVD risk. Nevertheless, care is necessary with fenofibrate use due to possible hepatic and renal toxicities in vulnerable individuals. Long-term trials and real-world studies are needed to confirm the clinical benefits of fenofibrate in the heterogeneous Asian population with dyslipidemia.
- Basic Research
- Extracellular Vimentin Alters Energy Metabolism And Induces Adipocyte Hypertrophy
- Ji-Hae Park, Soyeon Kwon, Young Mi Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):215-230. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0332
- 2,382 View
- 201 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
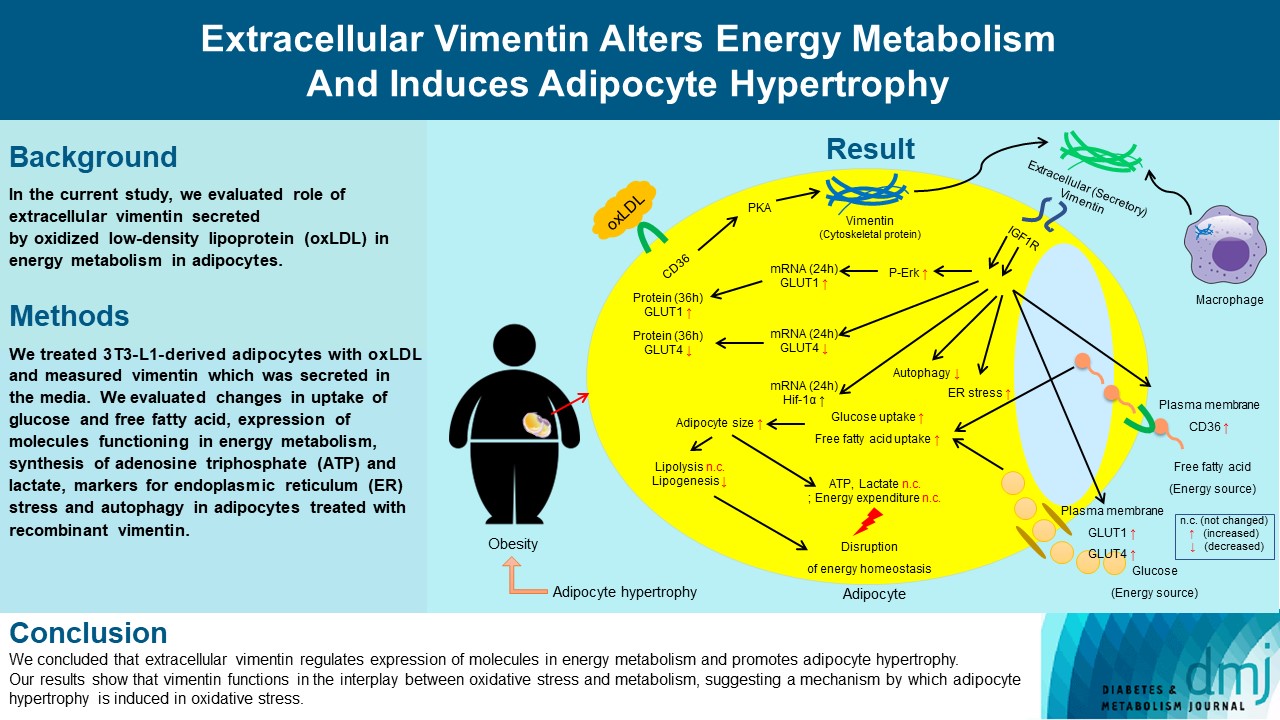
Previous studies have reported that oxidative stress contributes to obesity characterized by adipocyte hypertrophy. However, mechanism has not been studied extensively. In the current study, we evaluated role of extracellular vimentin secreted by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) in energy metabolism in adipocytes.
Methods
We treated 3T3-L1-derived adipocytes with oxLDL and measured vimentin which was secreted in the media. We evaluated changes in uptake of glucose and free fatty acid, expression of molecules functioning in energy metabolism, synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and lactate, markers for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and autophagy in adipocytes treated with recombinant vimentin.
Results
Adipocytes secreted vimentin in response to oxLDL. Microscopic evaluation revealed that vimentin treatment induced increase in adipocyte size and increase in sizes of intracellular lipid droplets with increased intracellular triglyceride. Adipocytes treated with vimentin showed increased uptake of glucose and free fatty acid with increased expression of plasma membrane glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1), GLUT4, and CD36. Vimentin treatment increased transcription of GLUT1 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (Hif-1α) but decreased GLUT4 transcription. Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) and 2 were decreased by vimentin treatment. Markers for ER stress were increased and autophagy was impaired in vimentin-treated adipocytes. No change was observed in synthesis of ATP and lactate in the adipocytes treated with vimentin.
Conclusion
We concluded that extracellular vimentin regulates expression of molecules in energy metabolism and promotes adipocyte hypertrophy. Our results show that vimentin functions in the interplay between oxidative stress and metabolism, suggesting a mechanism by which adipocyte hypertrophy is induced in oxidative stress.
- COVID-19
- Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on the Metabolic Control Parameters in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ifan Ali Wafa, Nando Reza Pratama, Nurizzah Farahiyah Sofia, Elsha Stephanie Anastasia, Tiffany Konstantin, Maharani Ayuputeri Wijaya, M. Rifqi Wiyono, Lilik Djuari, Hermina Novida
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):260-272. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0125
- 5,954 View
- 272 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Abrupt implementation of lockdowns during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic affected the management of diabetes mellitus in patients worldwide. Limited access to health facilities and lifestyle changes potentially affected metabolic parameters in patients at risk. We conducted a meta-analysis to determine any differences in the control of metabolic parameters in patients with diabetes, before and during lockdown.
Methods
We performed searches of five databases. Meta-analyses were carried out using random- or fixed-effect approaches to glycaemic control parameters as the primary outcome: glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), random blood glucose (RBG), fasting blood glucose (FBG), time-in-range (TIR), time-above-range (TAR), time-below-range (TBR). Mean difference (MD), confidence interval (CI), and P value were calculated. Lipid profile was a secondary outcome and is presented as a descriptive analysis.
Results
Twenty-one studies enrolling a total of 3,992 patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus (T1DM or T2DM) were included in the study. Patients with T1DM showed a significant improvement of TIR and TAR (MD=3.52% [95% CI, 0.29 to 6.74], I2=76%, P=0.03; MD=–3.36% [95% CI, –6.48 to –0.25], I2=75%, P=0.03), while FBG among patients with T2DM significantly worsened (MD=3.47 mg/dL [95% CI, 1.22 to 5.73], I2=0%, P<0.01). No significant difference was found in HbA1c, RBG, and TBR. Use of continuous glucose monitoring in T1DM facilitated good glycaemic control. Significant deterioration of lipid parameters during lockdown, particularly triglyceride, was observed.
Conclusion
Implementation of lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic did not worsen glycaemic control in patients with diabetes. Other metabolic parameters improved during lockdown, though lipid parameters, particularly triglyceride, worsened. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Disruption of diabetes and hypertension care during the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery approaches in the Latin America and Caribbean region: a scoping review protocol
Samira Barbara Jabakhanji, Oluwabunmi Ogungbe, Sonia Y Angell, Lawrence Appel, David Byrne, Roopa Mehta, John McCaffrey, Lori Rosman, Edward W Gregg, Kunihiro Matsushita
BMJ Open.2024; 14(1): e074443. CrossRef - Influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the achievement of guideline targets for HbA1c, blood pressure, and LDL cholesterol in people with diabetes in Japan
Shingo Kuwajima, Takahito Itoh, Tatsuya Sato, Shoya Ino, Satoru Shibata, Kouhei Ohno, Hiroyuki Hotta, Tomoaki Matsumoto, Hitoshi Ooiwa, Hirofumi Kubo, Takayuki Miki
Diabetology International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: What We Learned From the Lockdown Experience
Catarina Almeida, André Ferreira, Daniela Duarte, Ana Filipa Viegas, André Santos, Alexandra Vaz, Edite Nascimento
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in body weight and glycemic control in association with COVID-19 Shutdown among 23,000 adults with type 2 diabetes
Emily Panza, Kevin E. Kip, Kripa Venkatakrishnan, Oscar C. Marroquin, Rena R. Wing
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(6): 787. CrossRef - The Impact of a Lockdown for the COVID-19 Pandemic on Seasonal HbA1c Variation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Yu-Cheng Cheng, Yu-Hsuan Li, Hsiu-Chen Liu, Chiann-Yi Hsu, Wan-Jen Chang, I-Te Lee, Chin-Li Lu
Life.2023; 13(3): 763. CrossRef - The Impact of Partial Lockdown During COVID-19 Pandemic on Metabolic Control in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ayşe Zülal TOKAÇ, Tuğde Buse UĞUR, Buse Ecem KURUGÖL, Sevilay ALİGÜLÜ, Osman HAYRAN
Journal of Biotechnology and Strategic Health Research.2023; 7(1): 67. CrossRef - Retrospective Study on the Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Northern Taiwan
Hsuan Huang, Hsiao-Ling Su, Chih-Hsung Huang, Yi-Hsin Lin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2539. CrossRef - RIPK1 and RIPK3 inhibitors: potential weapons against inflammation to treat diabetic complications
Dan Ke, Zhen Zhang, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Yucen Dai, Xinhai Sun, Yanhui Chu, Luxin Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - “Does Physical Exercise Promote Health Benefits for Diabetic Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic?”: A Systematic Review
Erivaldo de Souza, Daniela Meneses-Santos, Josué Cruz Santos, Felipe J. Aidar, Carla Roberta de Oliveira Carvalho, Jymmys Lopes dos Santos, Anderson Carlos Marçal
Sports.2023; 11(10): 192. CrossRef - Impact of National Lockdown From COVID-19 Pandemic in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: An Observational Study
Nuntakorn Thongtang, Niracha Chanwimol, Lukana Preechasuk, Varisara Boonyuang, Pinyo Rattanaumpawan, Supawadee Likitmaskul, Apiradee Sriwijitkamol
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2022; 34(6-7): 708. CrossRef
- Disruption of diabetes and hypertension care during the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery approaches in the Latin America and Caribbean region: a scoping review protocol
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients Treated with Statins for Residual Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
- Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jae Myung Yu, Sung Rae Kim, In Kye Lee, Kyung-Ah Han, Sung Hee Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Ji-Oh Mok, Yong-ho Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, So Hun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Ah Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Sung-Ho Her, Won Yong Shin, Mi-Seung Shin, Hyo-Suk Ahn, Seung Ho Kang, Jin-Man Cho, Sang-Ho Jo, Tae-Joon Cha, Seok Yeon Kim, Kyung Heon Won, Dong-Bin Kim, Jae Hyuk Lee, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):78-90. Published online June 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0265
- 9,348 View
- 190 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Cardiovascular risk remains increased despite optimal low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level induced by intensive statin therapy. Therefore, recent guidelines recommend non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) as a secondary target for preventing cardiovascular events. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy and tolerability of omega-3 fatty acids (OM3-FAs) in combination with atorvastatin compared to atorvastatin alone in patients with mixed dyslipidemia.
Methods This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, and phase III multicenter study included adults with fasting triglyceride (TG) levels ≥200 and <500 mg/dL and LDL-C levels <110 mg/dL. Eligible subjects were randomized to ATOMEGA (OM3-FAs 4,000 mg plus atorvastatin calcium 20 mg) or atorvastatin 20 mg plus placebo groups. The primary efficacy endpoints were the percent changes in TG and non-HDL-C levels from baseline at the end of treatment.
Results After 8 weeks of treatment, the percent changes from baseline in TG (−29.8% vs. 3.6%,
P <0.001) and non-HDL-C (−10.1% vs. 4.9%,P <0.001) levels were significantly greater in the ATOMEGA group (n =97) than in the atorvastatin group (n =103). Moreover, the proportion of total subjects reaching TG target of <200 mg/dL in the ATOMEGA group was significantly higher than that in the atorvastatin group (62.9% vs. 22.3%,P <0.001). The incidence of adverse events did not differ between the two groups.Conclusion The addition of OM3-FAs to atorvastatin improved TG and non-HDL-C levels to a significant extent compared to atorvastatin alone in subjects with residual hypertriglyceridemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between Omega‐3 Fatty Acid Intake and Dyslipidemia: A Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Tianjiao Wang, Xin Zhang, Na Zhou, Yuxuan Shen, Biao Li, Bingshu E. Chen, Xinzhi Li
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutraceutical support in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
E. V. Gracheva, E. A. Starovoytova, E. S. Kulikov, N. A. Kirillova, S. V. Fedosenko, M. A. Balaganskaya, D. V. Kromka
Rational Pharmacotherapy in Cardiology.2023; 19(3): 298. CrossRef - Effect of coadministration of omega-3 fatty acids with glimepiride on glycemic control, lipid profile, irisin, and sirtuin-1 in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized controlled trial
Rehab H. Werida, Aalaa Ramzy, Youssri Nassief Ebrahim, Maged Wasfy Helmy
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Dietary Interventions on Hypertriglyceridemia: From Public Health to Molecular Nutrition Evidence
Karla Paulina Luna-Castillo, Xochitl Citlalli Olivares-Ochoa, Rocío Guadalupe Hernández-Ruiz, Iris Monserrat Llamas-Covarrubias, Saraí Citlalic Rodríguez-Reyes, Alejandra Betancourt-Núñez, Barbara Vizmanos, Erika Martínez-López, José Francisco Muñoz-Valle
Nutrients.2022; 14(5): 1104. CrossRef - The effect of omega-3 fatty acids and its combination with statins on lipid profile in patients with hypertriglyceridemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yunjiao Yang, Wen Deng, Yanmei Wang, Tongyi Li, Yiding Chen, Cong Long, Qing Wen, Yue Wu, Qiu Chen
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Atorvastatin 40 mg/ω-3 Fatty Acids 4 g Fixed-dose Combination and Atorvastatin 40 mg Monotherapy in Hypertriglyceridemic Patients who Poorly Respond to Atorvastatin 40 mg Monotherapy: An 8-week, Multicenter, Random
Jong Shin Woo, Soon Jun Hong, Dong Hoon Cha, Kee Sik Kim, Moo Hyun Kim, Jun-Won Lee, Myung Ho Jeong, Jin-Ok Jeong, Jun-Hee Lee, Doo Soo Jeon, Eun Joo Cho, Soon Kil Kim, Jun Kwan, Chang Gyu Park, Hae Young Lee, Taek Jong Hong, Jinho Shin, Ho Joong Youn, Do
Clinical Therapeutics.2021; 43(8): 1419. CrossRef - All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Death between Statins and Omega-3 Supplementation: A Meta-Analysis and Network Meta-Analysis from 55 Randomized Controlled Trials
Jeongseon Kim, Tung Hoang, Ji-Myung Kim, So Young Bu, Jeong-Hwa Choi, Eunju Park, Seung-Min Lee, Eunmi Park, Ji Yeon Min, In Seok Lee, So Young Youn, Jee-Young Yeon
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 3203. CrossRef
- Association Between Omega‐3 Fatty Acid Intake and Dyslipidemia: A Continuous Dose–Response Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- You-Cheol Hwang, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):582-589. Published online January 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0124
- 6,611 View
- 185 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The apolipoprotein B/A1 (apoB/A1) ratio is a stronger predictor of future cardiovascular disease than is the level of conventional lipids. Statin and ezetimibe combination therapy have shown additional cardioprotective effects over statin monotherapy.
Methods This was a single-center, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study in Korea. A total of 36 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to either rosuvastatin monotherapy (20 mg/day,
n =20) or rosuvastatin/ezetimibe (5 mg/10 mg/day,n =16) combination therapy for 6 weeks.Results After the 6-week treatment, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apoB reduction were comparable between the two groups (−94.3±15.4 and −62.0±20.9 mg/dL in the rosuvastatin group, −89.9±22.7 and −66.8±21.6 mg/dL in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group,
P =0.54 andP =0.86, respectively). In addition, change in apoB/A1 ratio (−0.44±0.16 in the rosuvastatin group and −0.47±0.25 in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group,P =0.58) did not differ between the two groups. On the other hand, triglyceride and free fatty acid (FFA) reductions were greater in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group than in the rosuvastatin group (−10.5 mg/dL [interquartile range (IQR), −37.5 to 29.5] and 0.0 µEq/L [IQR, −136.8 to 146.0] in the rosuvastatin group, −49.5 mg/dL [IQR, −108.5 to −27.5] and −170.5 µEq/L [IQR, −353.0 to 0.8] in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group,P =0.010 andP =0.049, respectively). Both treatments were generally well tolerated, and there were no differences in muscle or liver enzyme elevation.Conclusion A 6-week combination therapy of low-dose rosuvastatin and ezetimibe showed LDL-C, apoB, and apoB/A1 ratio reduction comparable to that of high-dose rosuvastatin monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Triglyceride and FFA reductions were greater with the combination therapy than with rosuvastatin monotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Moderate-Intensity Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination versus Quadruple-Dose Rosuvastatin Monotherapy: A Meta-Analysis and Systemic Review
Yura Kang, Jung Mi Park, Sang-Hak Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(1): 19. CrossRef - Combination Therapy of Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin for Dyslipidemia: Current Insights
Maya R Chilbert, Dylan VanDuyn, Sara Salah, Collin M Clark, Qing Ma
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2022; Volume 16: 2177. CrossRef - Ezetimibe and diabetes mellitus:a new strategy for lowering cholesterol
V.A. Serhiyenko, A.A. Serhiyenko
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(5): 302. CrossRef - The Effect of Rosuvastatin on Plasma/Serum Levels of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-6, and D-Dimer in People Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Akililu Alemu Ashuro, Yin-Guang Fan, Yuan-Sheng Fu, Dong-Sheng Di, Napoleon Bellua Sam, Hai-Feng Pan, Dong-Qing Ye
AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses.2021; 37(11): 821. CrossRef - Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy and Rosuvastatin Monotherapy on Lipoprotein in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Multicenter Randomized Controlled Study
Jiwoo Lee, You-Cheol Hwang, Woo Je Lee, Jong Chul Won, Kee-Ho Song, Cheol-Young Park, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Joong-Yeol Park
Diabetes Therapy.2020; 11(4): 859. CrossRef - Comparison of Renal Effects of Ezetimibe–Statin Combination versus Statin Monotherapy: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
Jaehyun Bae, Namki Hong, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 798. CrossRef - Combined use of rosuvastatin and ezetimibe improves hepatic steatosis in patients with dyslipidemia
Won Dong Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Seung Up Kim
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 32(12): 1538. CrossRef - Influence of rosuvastatin dose on total fatty acids and free fatty acids in plasma
Cristian I. Ciucanu, Sonia Olariu, Daliborca C. Vlad, Victor Dumitraşcu
Medicine.2020; 99(48): e23356. CrossRef - The effect of switching from statin-monotherapy to statin/ezetimibe combination therapy on lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia: a multicenter open-label study (EUCLID)
Mitsuhide Takeshita, Atsushi Tanaka, Atsushi Kawaguchi, Keiko Sato, Shigeru Toyoda, Teruo Inoue, Koichi Node
Vascular Failure.2020; 4(1): 22. CrossRef - Response: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:582–9)
You-Cheol Hwang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 915. CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J2019;43:582–9)
Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 909. CrossRef - Changes in Plasma Free Fatty Acids Associated with Type-2 Diabetes
Amélie I. S. Sobczak, Claudia A. Blindauer, Alan J. Stewart
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2022. CrossRef
- Moderate-Intensity Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination versus Quadruple-Dose Rosuvastatin Monotherapy: A Meta-Analysis and Systemic Review
- Complications
- Risk Factors for the Development and Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
- Kyung-Jin Yun, Hye Ji Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Hyun Baek, Young Jung Roh, Ki-Ho Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(6):473-481. Published online September 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.6.473
- 4,421 View
- 44 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Some patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) do not develop diabetic kidney disease (DKD) despite the presence of advanced diabetic retinopathy (DR). We aimed to investigate the presence of DKD and its risk factors in patients with T2DM and advanced DR.
Methods We conducted a cross-sectional study in 317 patients with T2DM and advanced DR. The phenotypes of DKD were divided into three groups according to the urine albumin/creatinine ratio (uACR, mg/g) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2): no DKD (uACR <30 and eGFR ≥60), non-severe DKD (uACR ≥30 or eGFR <60), and severe DKD (uACR ≥30 and eGFR <60). Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure, mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level, and HbA1c variability (standard deviation [SD] of serial HbA1c values or HbA1c-SD) were calculated for the preceding 2 years.
Results The prevalence of no DKD, non-severe DKD, and severe DKD was 37.2% (
n =118), 37.0% (n =117), and 25.8% (n =82), respectively. HbA1c-SD and the triglyceride/high density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio correlated positively with uACR and negatively with eGFR. Multiple linear regression analyses showed that the HbA1c-SD and TG/HDL-C ratio were significantly related with eGFR. Multiple logistic regression analyses after adjusting for several risk factors showed that HbA1c-SD and the TG/HDL-C ratio were significant risk factors for severe DKD.Conclusion The prevalence of DKD was about 60% in patients with T2DM and advanced DR. HbA1c variability and TG/HDL-C ratio may affect the development and progression of DKD in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ocular and Systemic Risk Factors for Disease Worsening Among Patients with NPDR
Charles C. Wykoff, Diana V. Do, Roger A. Goldberg, Dilsher S. Dhoot, Jennifer I. Lim, Weiming Du, Fabiana Q. Silva, Rutvi Desai, Hadi Moini, Kimberly Reed, Alyson J. Berliner, Robert Vitti, W. Lloyd Clark
Ophthalmology Retina.2024; 8(4): 399. CrossRef - Interpretable prediction model for assessing diabetes complication risks in Chinese sufferers
Ye Shiren, Ye Jiangnan, Ye Xinhua, Ni Xinye
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111560. CrossRef - Dose-response association of diabetic kidney disease with routine clinical parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jianbo Guo, Chen Liu, Yifan Wang, Baoyi Shao, Tung Leong Fong, Ngai Chung Lau, Hui Zhang, Haidi Li, Jianan Wang, Xinyu Lu, Anqi Wang, Cheuk Lung Leung, Xin Wei Chia, Fei Li, Xiaoming Meng, Qingyong He, Haiyong Chen
eClinicalMedicine.2024; 69: 102482. CrossRef - Sex-Specific Computed Tomography Abdominal Fat and Skeletal Muscle Characteristics in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients With/Without Comorbid Diabetic Kidney Disease
Jinlei Fan, Liping Zuo, Mingyuan Hou, Bowen Wang, Yueming An, Baoli Hao, Dexin Yu
Academic Radiology.2023; 30(11): 2686. CrossRef - The concordance and discordance of diabetic kidney disease and retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study of 26,809 patients from 5 primary hospitals in China
Zhaoxiang Liu, Xianglan Li, Yanlei Wang, Yanxia Song, Qiang Liu, Junxia Gong, Wenshuang Fan, Chunmei Lv, Chenxiang Cao, Wenhui Zhao, Jianzhong Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ferroptosis: new insight into the mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy
Luxin Li, Yucen Dai, Dan Ke, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Dong Wei, Tongtong Wang, Yanjie Teng, Xiaohuan Yuan, Zhen Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting diabetic kidney disease for type 2 diabetes mellitus by machine learning in the real world: a multicenter retrospective study
Xiao zhu Liu, Minjie Duan, Hao dong Huang, Yang Zhang, Tian yu Xiang, Wu ceng Niu, Bei Zhou, Hao lin Wang, Ting ting Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing screening tools to estimate the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xu Cao, Xiaomei Pei
Technology and Health Care.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Association between serum complements and kidney function in patients with diabetic kidney disease
Meng-chao Liu, Jia-lin Li, Yue-fen Wang, Yuan Meng, Gui-min Zheng, Zhen Cai, Cun Shen, Meng-di Wang, Xiang-gang Zhu, Yang-zi Chen, Yu-lin Wang, Wen-jing Zhao, Wen-quan Niu, Yao-xian Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coagulation Function and Type 2 Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Real-World Observational Study
Meng-chao Liu, Wen-quan Niu, Yue-fen Wang, Yuan Meng, Gui-min Zheng, Zhen Cai, Cun Shen, Xiang-gang Zhu, Meng-di Wang, Jia-lin Li, Wen-jing Zhao, Yao-xian Wang, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Punicalagin alleviates renal injury via the gut-kidney axis in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice
Qinglian Hua, Yaling Han, Haifeng Zhao, Haowen Zhang, Bei Yan, Shengjie Pei, Xin He, Yue Li, Xiangyuan Meng, Lei Chen, Feng Zhong, Duo Li
Food & Function.2022; 13(2): 867. CrossRef - Status and Trends of the Association Between Diabetic Nephropathy and Diabetic Retinopathy From 2000 to 2021: Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
Wenwen Lin, Yayong Luo, Fang Liu, Hangtian Li, Qian Wang, Zheyi Dong, Xiangmei Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Risk Threshold for Hemoglobin A1c Associated With Albuminuria: A Population-Based Study in China
Hong Lian, Hongshi Wu, Jie Ning, Diaozhu Lin, Chulin Huang, Feng Li, Ying Liang, Yiqin Qi, Meng Ren, Li Yan, Lili You, Mingtong Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight change and microvascular outcomes in patients with new-onset diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
Eun Sil Koh, Kyung Do Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Min-Kyung Lee, Ga Eun Nam, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(4): 932. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Dobesilate in Preventing Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Hao Zhang, Shao-Hua Guo, Zheng-Kai Xue, Ya-Ru Zhang, Jia-Rui Wang, Jing-Jin Che, Tong Liu, Hua-Yue Tao, Guang-Ping Li, Seung-Woon Rha, Swapnil-Zaman Ashraful-Haque, Kang-Yin Chen
Clinics.2021; 76: e2942. CrossRef - Elevated TG/HDL-C and non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratios predict mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients
Wenkai Xia, Xiajuan Yao, Yan Chen, Jie Lin, Volker Vielhauer, Hong Hu
BMC Nephrology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Perception Abnormalities Can Predict Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Wei-Ching Fang, Kuei-Mei Chou, Chiao-Yin Sun, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Yung-Chang Chen, Heng-Chih Pan
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2020; 45(6): 926. CrossRef - Association between nonalbumin proteinuria and renal tubular damage of N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase and its clinical relevance in patients with type 2 diabetes without albuminuria
Eugene Han, Mi-Kyung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(3): 255. CrossRef - Detection of Lower Albuminuria Levels and Early Development of Diabetic Kidney Disease Using an Artificial Intelligence-Based Rule Extraction Approach
Yoichi Hayashi
Diagnostics.2019; 9(4): 133. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of liraglutide on expression of CTGF and BMP‐7 in induced diabetic nephropathy
Maggie M. Ramzy, Ahlam M. Abdalla, Nagwa M. Zenhom, Ahmed M. Okasha, Aya E. Abdelkafy, Rabeh K. Saleh
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 120(10): 17512. CrossRef - Are blood lipids associated with microvascular complications among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients? A cross-sectional study in Shanghai, China
Hua Yang, Doris Young, Jian Gao, Yuanzhi Yuan, Minqian Shen, Yuan Zhang, Xueyan Duan, Shanzhu Zhu, Xiaoming Sun
Lipids in Health and Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Discordance in risk factors for the progression of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ki‐Ho Song, Jee‐Sun Jeong, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Yu‐Bae Ahn
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2019; 10(3): 745. CrossRef - Risk factors for the development of micro-vascular complications of type 2 diabetes in a single-centre cohort of patients
Marsida Teliti, Giulia Cogni, Lucia Sacchi, Arianna Dagliati, Simone Marini, Valentina Tibollo, Pasquale De Cata, Riccardo Bellazzi, Luca Chiovato
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2018; 15(5): 424. CrossRef - Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 224. CrossRef - Determinants of the Risk of Diabetic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Retinopathy Independent of Glucose Exposure
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 444. CrossRef
- Ocular and Systemic Risk Factors for Disease Worsening Among Patients with NPDR
- Epidemiology
- Dietary Sodium Intake in People with Diabetes in Korea: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 2008 to 2010
- Myung Shin Kang, Chong Hwa Kim, Su Jin Jeong, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(4):290-296. Published online June 23, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.4.290
- 3,429 View
- 40 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetics are likely to receive advice from their physicians concerning lifestyle changes. To understand how much sodium is consumed by diabetics in Korea, we compared the average daily sodium intake between diabetics and non-diabetics after controlling for confounding factors.
Methods We obtained the sodium intake data for 13,957 individuals who participated in the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), 2008 to 2010, which consisted of a health interview and behavioral and nutritional surveys. The KNHANES uses a stratified, multistage, probability-sampling design, and weighting adjustments were conducted to represent the entire population.
Results Our analysis revealed that, overall, diabetics tended to have lower sodium intake (4,910.2 mg) than healthy individuals (5,188.2 mg). However, both diabetic and healthy individuals reported higher sodium intake than is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO). Stratified subgroup analyses revealed that the sodium intake (4,314.2 mg) among newly diagnosed diabetics was higher among women when compared to patients with known diabetes (3,812.5 mg,
P =0.035). Female diabetics with cardiovascular disease had lower average sodium intake compared to those without cardiovascular disease after adjusting for sex, age, body mass index, and total energy intake (P =0.058). Sodium intake among male diabetics with hypercholesterolemia (P =0.011) and female diabetics with hypertriglyceridemia (P =0.067) tended to be higher than that among those who without dyslipidemia.Conclusion The average sodium intake of diabetics in Korea was higher than the WHO recommends. Sodium intake in newly diagnosed diabetics was significantly higher than that in non-diabetics and previously diagnosed diabetics among females. Prospective studies are needed to identify the exact sodium intake.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Salt Intake in Adults with Diabetes and Hypertension: The Longitudinal Study of Adult Health-Brasil Study
Natália Gonçalves Ribeiro, Deborah F. Lelis, Rosane H. Griep, Sandhi M. Barreto, Maria del Carmen B Molina, Maria I. Schmidt, Bruce B. Duncan, Isabela Bensenor, Paulo A. Lotufo, José G. Mill, Marcelo Perim Baldo
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different diets on glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes: A literature review
Maryam E Al-Adwi, Zinab M Al-Haswsa, Karmen M Alhmmadi, Yasmin A Eissa, Aya Hamdan, Hiba Bawadi, Reema F Tayyem
Nutrition and Health.2023; 29(2): 215. CrossRef - Dietary salt intake predicts future development of metabolic syndrome in the general population
Hiroyuki Takase, Kazusa Hayashi, Fumihiko Kin, Suguru Nakano, Masashi Machii, Shin Takayama, Tomonori Sugiura, Yasuaki Dohi
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(1): 236. CrossRef - High Sodium Intake, as Assessed by Urinary Sodium Excretion, Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Sarcopenia
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Seung-Soon Im, Hye Soon Kim, Taeg Kyu Kwon, Byoung Kuk Jang
Gut and Liver.2023; 17(3): 456. CrossRef - Trends of Dietary Intakes and Metabolic Diseases in Japanese Adults: Assessment of National Health Promotion Policy and National Health and Nutrition Survey 1995–2019
Muhammad Fauzi, Indri Kartiko-Sari, Hemant Poudyal
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2350. CrossRef - Determinants of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Adults in Dill-Chora Referral Hospital, Dire Dawa, East Ethiopia
Tewodros Getnet Amera, Yibekal Manaye Tefera, Tameru Menberu, Aminu Mohammed Yassin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 3565. CrossRef - Dietary sodium and cardiovascular morbidity/mortality: a brief commentary on the ‘J-shape hypothesis’
Christiana Tsirimiagkou, Kalliopi Karatzi, Antonios Argyris, Eirini D. Basdeki, Panagiota Kaloudi, Mary Yannakoulia, Athanase D. Protogerou
Journal of Hypertension.2021; 39(12): 2335. CrossRef - Associations of Dietary Salt and Its Sources with Hemoglobin A1c in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Not Taking Anti-Diabetic Medications: Analysis Based on 6-Month Intervention with a Moderate Low-Carbohydrate Diet
Hajime Haimoto, Takashi Murase, Shiho Watanabe, Keiko Maeda, Kenji Wakai
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4569. CrossRef - Association of rheumatoid arthritis and high sodium intake with major adverse cardiovascular events: a cross-sectional study from the seventh Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jeong-Hyeon Bae, Min-Young Shin, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, You-Jung Ha
BMJ Open.2021; 11(12): e056255. CrossRef - Nineteen-year trends in fermented food consumption and sodium intake from fermented foods for Korean adults from 1998 to 2016
Sang Young Kim, Jeanne H Freeland-Graves, Hyun Ja Kim
Public Health Nutrition.2020; 23(3): 515. CrossRef - Dietary Sodium Intake and Health Indicators: A Systematic Review of Published Literature between January 2015 and December 2019
Katherine J Overwyk, Zerleen S Quader, Joyce Maalouf, Marlana Bates, Jacqui Webster, Mary G George, Robert K Merritt, Mary E Cogswell
Advances in Nutrition.2020; 11(5): 1174. CrossRef - Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 461. CrossRef - Factors Predicting Sodium Intake of Korean Americans with Type 2 Diabetes
Jisook Ko, Kim B. Kim, Gayle M. Timmerman, Angela P. Clark, Miyong Kim
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health.2018; 20(3): 641. CrossRef - Evaluation of the association between the number of natural teeth and anemia among Korean adults using nationally representative data
Kyungdo Han, Jun‐Beom Park
Journal of Periodontology.2018; 89(10): 1184. CrossRef - Clinical implications of age and sex in the prevalence of periodontitis in Korean adults with diabetes
Kyungdo Han, Jun‑Beom Park
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between underweight and tooth loss among Korean adults
In-Seok Song, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Jun Ryu, Jun-Beom Park
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The Science of Salt: A regularly updated systematic review of the implementation of salt reduction interventions (March–August 2016)
Joseph Alvin Santos, Kathy Trieu, Thout Sudhir Raj, JoAnne Arcand, Claire Johnson, Jacqui Webster, Rachael McLean
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2017; 19(4): 439. CrossRef - Salt-sensitive genes and their relation to obesity
Yong-Pil Cheon, Myoungsook Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2017; 50(3): 217. CrossRef
- Salt Intake in Adults with Diabetes and Hypertension: The Longitudinal Study of Adult Health-Brasil Study
- Impact of Serum Triglyceride and High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels on Early-Phase Insulin Secretion in Normoglycemic and Prediabetic Subjects
- Masanori Shimodaira, Tomohiro Niwa, Koji Nakajima, Mutsuhiro Kobayashi, Norinao Hanyu, Tomohiro Nakayama
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(4):294-301. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.4.294
- 3,228 View
- 28 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Increased triglycerides (TGs) and decreased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels are established as diabetic risks for nondiabetic subjects. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship among TG, HDL-C, TG/HDL-C ratio, and early-phase insulin secretion in normoglycemic and prediabetic subjects.
Methods We evaluated 663 Japanese subjects who underwent the 75-g oral glucose tolerance test. On the basis of these results, the subjects were divided into four groups: those with normal glucose tolerance (NGT;
n =341), isolated impaired fasting glucose (i-IFG;n =211), isolated impaired glucose tolerance (i-IGT;n =71), and combined IFG and IGT (IFG+IGT;n =40). Insulin secretion was estimated by the insulinogenic index (IGI) (Δinsulin/Δglucose [30 to 0 minutes]) and disposition index (DI) (IGI/homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance).Results In prediabetic subjects (i-IFG, i-IGT, and IFG+IGT), linear regression analyses revealed that IGI and DI were positively correlated with HDL-C levels. Moreover, in subjects with i-IGT and (IFG+IGT), but not with i-IFG, the indices of insulin secretion were negatively correlated with the log-transformed TG and TG/HDL-C ratio. In both the subjects with i-IGT, multivariate linear regression analyses revealed that DI was positively correlated with HDL-C and negatively with log-transformed TG and TG/HDL-C ratio. On the other hand, in subjects with NGT, there was no association between insulin secretion and lipid profiles.
Conclusion These results revealed that serum TG and HDL-C levels have different impacts on early-phase insulin secretion on the basis of their glucose tolerance status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The protective effects of lipoxin A4 on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Chinese prospective cohort study
Sudan Wang, Xiaoyan Qian, Chao Shen, Qian Sun, Yang Jing, Bingyue Liu, Kexin Zhang, Mengyuan Li, Junrong Wang, Hui Zhou, Chen Dong
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interaction between the GCKR rs1260326 variant and serum HDL cholesterol contributes to HOMA-β and ISIMatusda in the middle-aged T2D individuals
Min Shen, Liying Jiang, Hechun Liu, Hao Dai, Hemin Jiang, Yu Qian, Zhixiao Wang, Shuai Zheng, Heng Chen, Tao Yang, Qi Fu, Kuanfeng Xu
Journal of Human Genetics.2023; 68(12): 835. CrossRef - Elevated triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio as a risk factor for progression to prediabetes: a 5-year retrospective cohort study in Japan
Masanori Shimodaira, Yu Minemura, Tomohiro Nakayama
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association ofTG/HDLCratio trajectory and risk of type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study inChina
Yanyan Zhang, Pei Qin, Yanmei Lou, Ping Zhao, Xue Li, Ranran Qie, Xiaoyan Wu, Minghui Han, Shengbing Huang, Yang Zhao, Dechen Liu, Yuying Wu, Yang Li, Xingjin Yang, Yang Zhao, Yifei Feng, Changyi Wang, Jianping Ma, Xiaolin Peng, Hongen Chen, Dan Zhao, Sha
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(5): 402. CrossRef - Triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor similar to the triglyceride–glucose index for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome using International Diabetes Federation criteria of insulin resistance in obese adolescents: a cross-sectio
Nazlı Nur Aslan Çin, Hülya Yardımcı, Nevra Koç, Seyit Ahmet Uçaktürk, Mehtap Akçil Ok
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 33(6): 777. CrossRef - Comparison of Serum PCSK9 Levels in Subjects with Normoglycemia, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Impaired Glucose Tolerance
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Seong-Su Moon, Hochan Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 480. CrossRef - Triglycerides/glucose index is a useful surrogate marker of insulin resistance among adolescents
B Kang, Y Yang, E Y Lee, H K Yang, H-S Kim, S-Y Lim, J-H Lee, S-S Lee, B-K Suh, K-H Yoon
International Journal of Obesity.2017; 41(5): 789. CrossRef - The TyG index may predict the development of cardiovascular events
Laura Sánchez‐Íñigo, David Navarro‐González, Alejandro Fernández‐Montero, Juan Pastrana‐Delgado, Jose Alfredo Martínez
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2016; 46(2): 189. CrossRef - TyG Index Change Is More Determinant for Forecasting Type 2 Diabetes Onset Than Weight Gain
David Navarro-González, Laura Sánchez-Íñigo, Alejandro Fernández-Montero, Juan Pastrana-Delgado, Jose Alfredo Martinez
Medicine.2016; 95(19): e3646. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids for hypertriglyceridaemia management in Korea
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, Y. J. Jeong, S. J. Yang, S. J. Baik, H. Lee, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, I.-Y. Choi, H. W. Yim, K.-H. Yoon
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(5): 508. CrossRef - Relationship between insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion rate: not necessarily hyperbolic
S. H. Kim, A. Silvers, J. Viren, G. M. Reaven
Diabetic Medicine.2016; 33(7): 961. CrossRef - The triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio as a predictor of insulin resistance but not of β cell function in a Chinese population with different glucose tolerance status
Meicen Zhou, Lixin Zhu, Xiangli Cui, Linbo Feng, Xuefeng Zhao, Shuli He, Fan Ping, Wei Li, Yuxiu Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactive effects of C-reactive protein levels on the association between APOE variants and triglyceride levels in a Taiwanese population
Semon Wu, Lung-An Hsu, Ming-Sheng Teng, Jeng-Feng Lin, Hsin-Hua Chou, Ming-Cheng Lee, Yi-Ming Wu, Cheng-Wen Su, Yu-Lin Ko
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipoproteins and β-Cell Functions: From Basic to Clinical Data
Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(4): 274. CrossRef
- The protective effects of lipoxin A4 on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Chinese prospective cohort study
- Beneficial Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Low Density Lipoprotein Particle Size in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Already under Statin Therapy
- Myung Won Lee, Jeong Kyung Park, Jae Won Hong, Kwang Joon Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Chul Woo Ahn, Young Duk Song, Hong Keun Cho, Seok Won Park, Eun Jig Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(3):207-211. Published online June 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.3.207
- 4,182 View
- 46 Download
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Beyond statin therapy for reducing low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), additional therapeutic strategies are required to achieve more optimal reduction in cardiovascular risk among diabetic patients with dyslipidemia. To evaluate the effects and the safety of combined treatment with omega-3 fatty acids and statin in dyslipidemic patients with type 2 diabetes, we conducted a randomized, open-label study in Korea. Patients with persistent hypertriglyceridemia (≥200 mg/dL) while taking statin for at least 6 weeks were eligible. Fifty-one patients were randomized to receive either omega-3 fatty acid 4, 2 g, or no drug for 8 weeks while continuing statin therapy. After 8 weeks of treatment, the mean percentage change of low density lipoprotein (LDL) particle size and triglyceride (TG) level was greater in patients who were prescribed 4 g of omega-3 fatty acid with statin than in patients receiving statin monotherapy (2.8%±3.1% vs. 2.3%±3.6%,
P =0.024; -41.0%±24.1% vs. -24.2%±31.9%,P =0.049). Coadministration of omega-3 fatty acids with statin increased LDL particle size and decreased TG level in dyslipidemic patients with type 2 diabetes. The therapy was well tolerated without significant adverse effects.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy: insulin resistance, lipid profile, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Martin-Yurii Markevich, Volodymyr Segin, Victoria Serhiyenko, Alexandr Serhiyenko
InterConf.2023; (35(163)): 213. CrossRef - Atherogenic features of the fatty acid profile of erythrocyte membranes of patients with fatty liver disease of mixed genesis
M. V. Kruchinina, A. V. Belkovets, M. V. Parulikova, A. A. Gromov
Ateroscleroz.2023; 19(4): 350. CrossRef - Omega-3 supplementation in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) – a review of clinical trials and cohort
Vitoria Melo, Thomas Silva, Thaissa Silva, Juliana Freitas, Joselita Sacramento, Mirian Vazquez, Edilene Araujo
Endocrine Regulations.2022; 56(1): 66. CrossRef - Nutrigenetics, omega-3 and plasma lipids/lipoproteins/apolipoproteins with evidence evaluation using the GRADE approach: a systematic review
Justine Keathley, Véronique Garneau, Valérie Marcil, David M Mutch, Julie Robitaille, Iwona Rudkowska, Gabriela Magdalena Sofian, Sophie Desroches, Marie-Claude Vohl
BMJ Open.2022; 12(2): e054417. CrossRef - N-3 fatty acid supplementation mediates lipid profile, including small dense LDL, when combined with statins: a randomized double blind placebo controlled trial
Gediz Dogay Us, Sohail Mushtaq
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of omega-3 fatty acids and its combination with statins on lipid profile in patients with hypertriglyceridemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yunjiao Yang, Wen Deng, Yanmei Wang, Tongyi Li, Yiding Chen, Cong Long, Qing Wen, Yue Wu, Qiu Chen
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Study of the Healthy Effects of Different Fat Ratios Mixtures of Omega-3 to Omega-6 in Male Mice with Alloxan-Induced Diabetes
Ali. M. Atallah, Faryal. F. Hussein
Tikrit journal for agricultural sciences.2021; 21(4): 129. CrossRef - Omega-3 Fatty Acids as Druggable Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Disorders
Neha M. Chitre, Nader H. Moniri, Kevin S. Murnane
CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets.2020; 18(10): 735. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Patients Treated with Statins for Residual Hypertriglyceridemia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jae Myung Yu, Sung Rae Kim, In Kye Lee, Kyung-Ah Han, Sung Hee Choi, Soo-Kyung Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Ji-Oh Mok, Yong-ho Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, So Hun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Ah Lee, Chang Beom Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Sung-Ho Her,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 78. CrossRef - The combination of canagliflozin and omega-3 fatty acid ameliorates insulin resistance and cardiac biomarkersviamodulation of inflammatory cytokines in type 2 diabetic rats
Mohammed Mohsen Safhi, Tarique Anwer, Gyas Khan, Rahimullah Siddiqui, Sivagurunathan Moni Sivakumar, Mohammad Firoz Alam
The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology.2018; 22(5): 493. CrossRef - Effect of diets rich in either saturated fat or n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and supplemented with long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipoprotein profiles
C B Dias, N Amigo, L G Wood, X Correig, M L Garg
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2017; 71(11): 1297. CrossRef - Effects of 12-week supplementation of marine Omega-3 PUFA-based formulation Omega3Q10 in older adults with prehypertension and/or elevated blood cholesterol
Tian Shen, Guoqiang Xing, Jingfen Zhu, Shuxian Zhang, Yong Cai, Donghua Li, Gang Xu, Evan Xing, Jianyu Rao, Rong Shi
Lipids in Health and Disease.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of dietary saturated and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the incorporation of long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids into blood lipids
C B Dias, L G Wood, M L Garg
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2016; 70(7): 812. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids for hypertriglyceridaemia management in Korea
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, Y. J. Jeong, S. J. Yang, S. J. Baik, H. Lee, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, I.-Y. Choi, H. W. Yim, K.-H. Yoon
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(5): 508. CrossRef - Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Diabetic Nephropathy Progression in Patients with Diabetes and Hypertriglyceridemia
Eugene Han, Yujung Yun, Gyuri Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Jin Wang, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong Soo Cha, Beom Seok Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Wolf-Hagen Schunck
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(5): e0154683. CrossRef - The clinical relevance of omega-3 fatty acids in the management of hypertriglyceridemia
James Backes, Deborah Anzalone, Daniel Hilleman, Julia Catini
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Supercritical fluid extraction of grape seeds: extract chemical composition, antioxidant activity and inhibition of nitrite production in LPS-stimulated Raw 264.7 cells
Concepción Pérez, María Luisa Ruiz del Castillo, Carmen Gil, Gracia Patricia Blanch, Gema Flores
Food & Function.2015; 6(8): 2607. CrossRef - Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids May Attenuate Streptozotocin-Induced Pancreatic β-Cell Death via Autophagy Activation in Fat1 Transgenic Mice
Won-Min Hwang, Dong-Ho Bak, Dong Ho Kim, Ju Young Hong, Seung-Yun Han, Keun-Young Park, Kyu Lim, Dong-Mee Lim, Jae Gu Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 569. CrossRef - Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, fibrates and niacin as therapeutic options in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia: A review of the literature
Matthew K. Ito
Atherosclerosis.2015; 242(2): 647. CrossRef - Nutraceuticals and dyslipidaemia: Beyond the common therapeutics
Pietro Scicchitano, Matteo Cameli, Maria Maiello, Pietro Amedeo Modesti, Maria Lorenza Muiesan, Salvatore Novo, Pasquale Palmiero, Pier Sergio Saba, Roberto Pedrinelli, Marco Matteo Ciccone
Journal of Functional Foods.2014; 6: 11. CrossRef - The effect of dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on plasma lipids and lipoproteins of C57BL/6 mice is age and sex specific
K.A. Balogun, R.S. Randunu, S.K. Cheema
Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids.2014; 91(1-2): 39. CrossRef - Gene-diet interactions with polymorphisms of the MGLL gene on plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and size following an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation: a clinical trial
Catherine Ouellette, Iwona Rudkowska, Simone Lemieux, Benoit Lamarche, Patrick Couture, Marie-Claude Vohl
Lipids in Health and Disease.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Saturated fat consumption may not be the main cause of increased blood lipid levels
C.B. Dias, R. Garg, L.G. Wood, M.L. Garg
Medical Hypotheses.2014; 82(2): 187. CrossRef
- Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy: insulin resistance, lipid profile, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
- Postprandial Triglyceride Is Associated with Fasting Triglyceride and HOMA-IR in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
- Seo Hee Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Hee Kwan Won, Jae Hoon Moon, Kwang Joon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):404-410. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.404
- 4,127 View
- 41 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Recent studies indicate postprandial triglyceride (TG) had a better association with cardiovascular events and metabolic syndrome than fasting TG. The authors of the present study investigated the metabolic and clinical relevance of postprandial TG.
Methods In a cross-sectional retrospective study, the authors of the present study compared fasting and postprandial TG and analyzed the relationship between postprandial TG and various demographic and metabolic parameters in 639 Korean subjects with type 2 diabetes (T2D, group I,
n =539) and impaired fasting glucose (IFG, group II,n =100) after ingestion of a standardized liquid meal (total 500 kcal, 17.5 g fat, 68.5 g carbohydrate, and 17.5 g protein).Results Fasting and postprandial TG were significantly correlated (
r =0.973,r =0.937,P <0.001) in group I and II, respectively. Of the variables, total cholesterol, waist circumference and body mass index were significantly correlated with fasting and postprandial TG in both groups. Only postprandial TG showed a significant correlation with glucose metabolic parameters (e.g., postprandial glucose, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR], and fasting C-peptide) in subjects with T2D. Multiple regression analysis showed fasting TG and HOMA-IR could be predictable variables for postprandial TG in subjects with T2D.Conclusion Postprandial TG was very strongly correlated with fasting TG. The authors of the present study suggest insulin resistance may be more associated with postprandial TG than fasting TG in Korean T2D patients on a low-fat diet.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impaired ketogenesis is associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes
Sejeong Lee, Jaehyun Bae, Doo Ri Jo, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Postprandial lipaemia following consumption of a meal enriched with medium chain saturated and/or long chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. A randomised cross-over study
Grace Austin, Jessica JA. Ferguson, Rohith N. Thota, Harjinder Singh, Tracy Burrows, Manohar L. Garg
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(2): 420. CrossRef - Effects of fatty acids composition in a breakfast meal on the postprandial lipid responses: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Yuanhang Yao, Sheri Xueqi Pek, Darel Wee Kiat Toh, Xuejuan Xia, Jung Eun Kim
International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition.2020; 71(7): 793. CrossRef - The Forgotten Lipids: Triglycerides, Remnant Cholesterol, and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Pratik B Sandesara, Salim S Virani, Sergio Fazio, Michael D Shapiro
Endocrine Reviews.2019; 40(2): 537. CrossRef - Determinant of postprandial triglyceride levels in healthy young adults
Tri J.E. Tarigan, Anandhara I. Khumaedi, Syahidatul Wafa, Michael Johan, Murdani Abdullah, Ingrid S. Surono, Dicky L. Tahapary
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(3): 1917. CrossRef - Impact of the triglyceride level on coronary plaque components in female patients with coronary artery disease treated with statins
Motoki Yamashita, Atsushi Iwata, Yuta Kato, Makito Futami, Satoshi Imaizumi, Takashi Kuwano, Amane Ike, Makoto Sugihara, Hiroaki Nishikawa, Bo Zhang, Shin’ichiro Yasunaga, Keijiro Saku, Shin-ichiro Miura
Heart and Vessels.2018; 33(10): 1175. CrossRef - Biomarker potential of C-peptide for screening of insulin resistance in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals
Haseeb A. Khan, Samia H. Sobki, Aishah Ekhzaimy, Isra Khan, Mona A. Almusawi
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2018; 25(8): 1729. CrossRef - Postprandial C‐peptide to glucose ratio as a predictor of β‐cell function and its usefulness for staged management of type 2 diabetes
Eun Young Lee, Sena Hwang, Seo Hee Lee, Yong‐ho Lee, A Ra Choi, Youngki Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(5): 517. CrossRef - Genetics and Causality of Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Robert S. Rosenson, Michael H. Davidson, Benjamin J. Hirsh, Sekar Kathiresan, Daniel Gaudet
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2014; 64(23): 2525. CrossRef - The effect of insulin resistance on postprandial triglycerides in Korean type 2 diabetic patients
Kyeong Hye Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Acta Diabetologica.2014; 51(1): 15. CrossRef - Acute effects of an oral supplement of (−)-epicatechin on postprandial fat and carbohydrate metabolism in normal and overweight subjects
Gabriela Gutiérrez-Salmeán, Pilar Ortiz-Vilchis, Claudia M. Vacaseydel, Ivan Rubio-Gayosso, Eduardo Meaney, Francisco Villarreal, Israel Ramírez-Sánchez, Guillermo Ceballos
Food & Function.2014; 5(3): 521. CrossRef - A comparative study of broccoli sprouts powder and standard triple therapy on cardiovascular risk factors following H.pylori eradication: a randomized clinical trial in patients with type 2 diabetes
Parvin Mirmiran, Zahra Bahadoran, Mahdieh Golzarand, Homayoun Zojaji, Fereidoun Azizi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of higher resistin levels with inflammatory activation and endothelial dysfunction in patients with essential hypertension
Chang FANG, Juan LEI, Shu-xian ZHOU, Yu-ling ZHANG, Gui-yi YUAN, Jing-feng WANG
Chinese Medical Journal.2013; 126(4): 646. CrossRef - Epicardial adipose tissue thickness is an indicator for coronary artery stenosis in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients: its assessment by cardiac magnetic resonance
Hyun Kim, Kwang Kim, Hye-Jeong Lee, Hee Yu, Jae Moon, Eun Kang, Bong Cha, Hyun Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Young Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012; 11(1): 83. CrossRef
- Impaired ketogenesis is associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes
- Clinical Characteristics of Type 2 Diabetes Patients according to Family History of Diabetes
- Seung Uk Jeong, Dong Gu Kang, Dae Ho Lee, Kang Woo Lee, Dong-Mee Lim, Byung Joon Kim, Keun-Yong Park, Hyoun-Jung Chin, Gwanpyo Koh
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(4):222-228. Published online August 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.4.222
- 3,496 View
- 26 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has a strong genetic component, and its prevalence is notably increased in the family members of T2DM patients. However, there are few studies about the family history of T2DM. We carried out this study to assess the influences of family history on clinical characteristics in T2DM patients.
Methods This is a cross-sectional study involving 651 T2DM patients. Patient history and physical examination were performed and fasting blood was taken. If any first degree relative was diabetic, a family history of diabetes was considered to exist.
Results Among the total 621 patients, 38.4% had a family history of diabetes. Patients with a family history had a younger age, higher weight, younger age at diagnosis and higher triglyceride level than did those without a family history. Dyslipidemia medication and metabolic syndrome were more prevalent in familial diabetes. Sex, blood pressure, previous treatment for diabetes, HbA1c, C-peptide, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol were not different between familial and non-familial diabetes. Upon multiple linear regression analysis, the family history of diabetes remained significantly associated with serum triglyceride level.
Conclusion In T2DM patients with a family history of diabetes, the disease tended to develop earlier. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk factors are more prevalent in familial T2DM than they were in non-familial T2DM. These results support the necessity of earlier screening for diabetes in family members of T2DM patients and more active prevention against cardiovascular disease in T2DM patients with a family history.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: Comprehensive Cellular and Molecular Mechanistic Insights
Praise Tatenda Nhau, Mlindeli Gamede, Ntethelelo Sibiya
Pathophysiology.2024; 31(2): 197. CrossRef - Evolutionary algorithm for the optimization of meal intake and insulin administration in patients with type 2 diabetes
Eva Gonzalez-Flo, Elaheh Kheirabadi, Carlos Rodriguez-Caso, Javier Macía
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Cytokines (IL-17 and IL-33), FGF-18, and WNT-5 in the Pathogenesis of Patients with Established Type II Diabetes
Przha Mohammed, Kawa Amin
Journal of Zankoy Sulaimani - Part A.2023; 25(2): 11. CrossRef - Cellular Chitchatting: Exploring the Role of Exosomes as Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Giulia Germena, Laura Cecilia Zelarayán, Rabea Hinkel
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined associations of family history and self-management with age at diagnosis and cardiometabolic risk in 86,931 patients with type 2 diabetes: Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) Register from 11 countries
Johnny T. K. Cheung, Eric Lau, Cyrus C. T. Tsui, Edmond L. N. Siu, Naomi K. W. Tse, Nicole Y. L. Hui, Ronald C. W. Ma, Alice P. S. Kong, Amy Fu, Vanessa Lau, Weiping Jia, Wayne H. H. Sheu, Leorino Sobrepena, K. H. Yoon, Alexander T. B. Tan, Yook-Chin Chia
BMC Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Capsaicin, its clinical significance in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy
Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla, Bongani B. Nkambule, Ilenia Cirilli, Fabio Marcheggiani, Sihle E. Mabhida, Khanyisani Ziqubu, Yonela Ntamo, Babalwa Jack, Tawanda M. Nyambuya, Sidney Hanser, Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 153: 113439. CrossRef - Safety profile of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: A brief summary
Annamaria Mascolo, Raffaella Di Napoli, Nunzia Balzano, Donato Cappetta, Konrad Urbanek, Antonella De Angelis, Lucia Scisciola, Irene Di Meo, Maria Giuseppa Sullo, Concetta Rafaniello, Liberata Sportiello
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of triglycerides and waist circumference on insulin resistance and β-cell function in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes
Fahd Ahmed, Molham AL-Habori, Ebtesam Al-Zabedi, Riyadh Saif-Ali
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Orientin Improves Substrate Utilization and the Expression of Major Genes Involved in Insulin Signaling and Energy Regulation in Cultured Insulin-Resistant Liver Cells
Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje, Sinenhlanhla X. H. Mthembu, Andani Tshiitamune, Ndivhuwo Muvhulawa, Fikile T. Mthiyane, Khanyisani Ziqubu, Christo J. F. Muller, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Molecules.2021; 26(20): 6154. CrossRef - Identification of Pre-Diabetic Biomarkers in the Progression of Diabetes Mellitus
Jae-Ho Lee, Do-Young Kim, Rubee Pantha, Eun-Ho Lee, Jae-Hoon Bae, Eugene Han, Dae-Kyu Song, Taeg Kyu Kwon, Seung-Soon Im
Biomedicines.2021; 10(1): 72. CrossRef - Shared (epi)genomic background connecting neurodegenerative diseases and type 2 diabetes
Valerio Caputo, Andrea Termine, Claudia Strafella, Emiliano Giardina, Raffaella Cascella
World Journal of Diabetes.2020; 11(5): 155. CrossRef - Family history of diabetes in both parents is strongly associated with impaired residual β‐cell function in Japanese type 2 diabetes patients
Minoru Iwata, Yutaka Kamura, Hisae Honoki, Kaori Kobayashi, Manabu Ishiki, Kunimasa Yagi, Yasuo Fukushima, Atsuko Takano, Hiromi Kato, Shihou Murakami, Kiyohiro Higuchi, Chikaaki Kobashi, Kazuhito Fukuda, Yukiko Koshimizu, Kazuyuki Tobe
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(3): 564. CrossRef - The relationship between age of onset and risk factors including family history and life style in Korean population with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Jin-Won Noh, Jin Hee Jung, Jeong Eun Park, Jung Hwa Lee, Kang Hee Sim, Jumin Park, Min Hee Kim, Ki-Bong Yoo
Journal of Physical Therapy Science.2018; 30(2): 201. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Subjects with Sulfonylurea-Dependent Type 2 Diabetes
Se Hee Min, Soo Heon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 509. CrossRef - Nutritional Assessment of Type II Diabetic Patients
El-Sayed H. Bakr
Pakistan Journal of Nutrition.2015; 14(6): 308. CrossRef
- COVID-19-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: Comprehensive Cellular and Molecular Mechanistic Insights
- Effects of Adding omega-3 Fatty Acids to Simvastatin on Lipids, Lipoprotein Size and Subspecies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Hypertriglyceridemia.
- Won Jun Kim, Chang Beom Lee, Cheol Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Dae Jung Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seung Jin Han, Hong Keum Cho
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(6):494-502. Published online December 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.6.494
- 2,559 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
omega-3 fatty acids are known to improve lipid profiles, the distribution of lipoprotein subclasses, and secondary prevention against post-myocardial infarction. Rare reports have emerged of synergistic results of omega-3 fatty acids with simvastatin in cases of type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertriglyceridemia. The purpose of this study was to determine the combined relationship of omega-3 fatty acids plus simvastatin on lipid, lipoprotein size and the types of subspecies. METHODS: This randomized, multi-center, comparison study evaluated eight weeks of combination therapy (omega-3 fatty acids (Omacor) 4 g/day plus simvastatin 20 mg/day) or monotherapy (simvastatin 20 mg/day) for at least six weeks in 62 diabetic patients. Subjects with a triglyceride concentration of more than 200 mg/dL were eligible for inclusion. RESULTS: No significant differences for omega-3 fatty acids + simvastatin versus simvastatin alone were observed for triglycerides (-22.7% vs. -14.3%, P = 0.292), HDL peak particle size (+2.8% vs. -0.4%, P = 0.076), LDL mean particle size (+0.4% vs -0.1%, P = 0.376) or LDL subspecies types, although the combination therapy showed a tendency toward lower triglycerides, larger HDL, and LDL particle sizes than did the monotherapy. There were no significant differences between the two groups in regard to HDL-C, LDL-C, or HbA1c levels. There were no serious adverse events and no abnormalities in the laboratory values associated with this study. CONCLUSION: omega-3 fatty acids were a safeform of treatment in hypertriglyceridemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. But, regarding efficacy, a much larger sample size and longer-term follow-up may be needed to distinguish between the effects of combination therapy and monotherapy.
- Relationship between Menopausal Status and Metabolic Syndrome Components in Korean Women.
- Jang Hyun Koh, Mi Young Lee, Soo Min Nam, Joong Kyung Sung, Pil Moon Jung, Jin Kyu Noh, Jang Yel Shin, Young Goo Shin, Choon Hee Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(3):243-251. Published online June 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.3.243
- 2,346 View
- 35 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Postmenopausal status is associated with a 60% increased risk for metabolic syndrome. It is thought to be associated with decreased estrogens and increased abdominal obesity in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between metabolic syndrome components and menopausal status. METHODS: A total of 1,926 women were studied and divided into three groups according to their menstrual stage (premenopausal, perimenopausal or postmenopausal). The presence of metabolic syndrome was assessed using the National Cholesterol Education Program's (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel III criteria. RESULTS: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome was 7.1% in premenopause, 9.8% in perimenopause, and 24.2% in postmenopause. The strong correlation was noted between the metabolic syndrome score and waist circumference in postmenopause (r = 0.56, P < 0.01) and perimenopause (r = 0.60, P < 0.01). Along the menopausal transition, the risk of metabolic syndrome increased with high triglyceride after the age-adjusted (odds ratio (OR) 1.517 [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.014~2.269] in perimenopausal women and OR 1.573 [95% CI 1.025~2.414] in postmenopausal women). In addition, the prevalence of metabolic syndromeincreased in accordance with elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) levels. CONCLUSION: Triglyceride and waist circumference were important metabolic syndrome components, though ALT and GGT may also be related for predicting metabolic syndrome during the transition to menopause. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interaction between major dietary patterns and cardiorespiratory fitness on metabolic syndrome in Iranian adults: a cross-sectional study
Hossein Shahinfar, Mahtab Ghanbari, Yahya Jalilpiran, Nastaran Payande, Mahshid Shahavandi, Nadia Babaei, Kurosh Djafarian, Cain C. C. Clark, Sakineh Shab-Bidar
Nutrition Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Wild Ginseng Complex Pharmacopuncture Combined with Hyperthermia on Abdominal Obesity in Post-Menopause Women: Case Report
Jeong-Eun Yoo
Journal of Korean Medicine for Obesity Research.2016; 16(2): 133. CrossRef - Factors associated with metabolic syndrome in climacteric women of southern Brazil
A. D. Rodrigues, H. Theodoro, K. G. Mendes, V. M. Paniz, D. de Lorenzi, M. T. Anselmo Olinto
Climacteric.2012; 16(1): 96. CrossRef - Effects of Web-based Health Education on Blood Glucose and Blood Pressure Improvement in Postmenopausal Women with Impaired Fasting Blood Glucose
Jeong-Ah Oh, Hee-Seung Kim, Min-Jeong Park, Hye-Sun Shim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(5): 724. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Related Risk Factors of Elderly Residents in Andong Rural Area 2. Based on the Biochemical Measurements and Nutrient Intakes
Hye-Sang Lee, Chong-Suk Kwon
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2010; 39(10): 1459. CrossRef - The Association between Serum GGT Concentration and Diabetic Peripheral Polyneuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Ho Chan Cho
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(2): 111. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Related Risk Factors of Elderly Residents in Andong Rural Area 1. Based on the Anthropometric Measurements and Health Behaviors
Hye-Sang Lee, Chong-Suk Kwon
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2010; 39(4): 511. CrossRef
- Interaction between major dietary patterns and cardiorespiratory fitness on metabolic syndrome in Iranian adults: a cross-sectional study
- Rosiglitazone Activates AMPK and Improves Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in OLETF Rats.
- Eun Hee Cho, Ki Up Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(2):141-148. Published online April 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.2.141
- 1,799 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Insulin resistance is very common in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Glitazones improve insulin sensitivity by acting as a selective agonist of the peroxisome proliferators -activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma), and were shown to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in skeletal muscle and the liver. Glitazones were also shown to reduce hepatic lipogenesis. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the protective mechanism of rosiglitazone on NAFLD is associated with AMPK activation. METHODS: Twelve OLETF rats were divided into 2 groups (control, treatment, n = 6 each). LETO rats served as controls. At 35 weeks of age, treatment group received rosiglitazone 4 mg/kg daily for 3 days. Fasting plasma glucose, insulin, free fatty acid, lactate and triglycerides were measured. Liver tissues from each group were processed for histological and hepatic triglyceride content analysis and western blotting. RESULTS: Fasting plasma glucose, insulin and triglycerides levels were significantly lower in treatment group than in control group. Histologic examination disclosed decreased hepatic steatosis in treatment group. Hepatic triglyceride content was also decreased in treatment group. Sterol regulatory binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and fatty acid synthase (FAS) expression were increased and AMPK phosphorylation was reduced in OLETF rats compared with LETO rats, and these changes were reversed by rosiglitazone treatment. CONCLUSION: Rosiglitazone reduced hepatic steatosis in OLETF rats, and activated AMPK in the liver. These results suggest the role of AMPK activation in the protective action of rosiglitazone on NAFLD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Small Rice Bowl-Based Meal Plan for Energy and Marcronutrient Intake in Korean Men with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
Hee Jung Ahn, Kyung Ah Han, Jin Young Jang, Jae Hyuk Lee, Kang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(3): 273. CrossRef
- Small Rice Bowl-Based Meal Plan for Energy and Marcronutrient Intake in Korean Men with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
- Acquired Generalized Lipodystrophy with Severe Insulin Resistant Diabetes Mellitus.
- Jung Min Lee, Tae Seo Sohn, Hyun Shik Son
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(6):487-491. Published online November 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.6.487
- 1,663 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acquired generalized lipodystrophy is a rare disease, and often follows autoimmune disease, prodromal infection, HIV infection. The clinical characteristics are generalized absence of fat, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, absence of ketosis, elevated basal metabolic rate, severe hypertriglyceridemia, and hepatomegaly. Here we experience and report a case of 16-year-old female patient who has clinical features of acquired generalized lipodystrophy with severe insulin resistant diabetes mellitus without any prodromal states.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





