
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic Research
- DWN12088, A Prolyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitor, Alleviates Hepatic Injury in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Dong-Keon Lee, Su Ho Jo, Eun Soo Lee, Kyung Bong Ha, Na Won Park, Deok-Hoon Kong, Sang-In Park, Joon Seok Park, Choon Hee Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):97-111. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0367
- 1,809 View
- 181 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a liver disease caused by obesity that leads to hepatic lipoapoptosis, resulting in fibrosis and cirrhosis. However, the mechanism underlying NASH is largely unknown, and there is currently no effective therapeutic agent against it. DWN12088, an agent used for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, is a selective prolyl-tRNA synthetase (PRS) inhibitor that suppresses the synthesis of collagen. However, the mechanism underlying the hepatoprotective effect of DWN12088 is not clear. Therefore, we investigated the role of DWN12088 in NASH progression.
Methods
Mice were fed a chow diet or methionine-choline deficient (MCD)-diet, which was administered with DWN12088 or saline by oral gavage for 6 weeks. The effects of DWN12088 on NASH were evaluated by pathophysiological examinations, such as real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, biochemical analysis, and immunohistochemistry. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of hepatic injury were assessed by in vitro cell culture.
Results
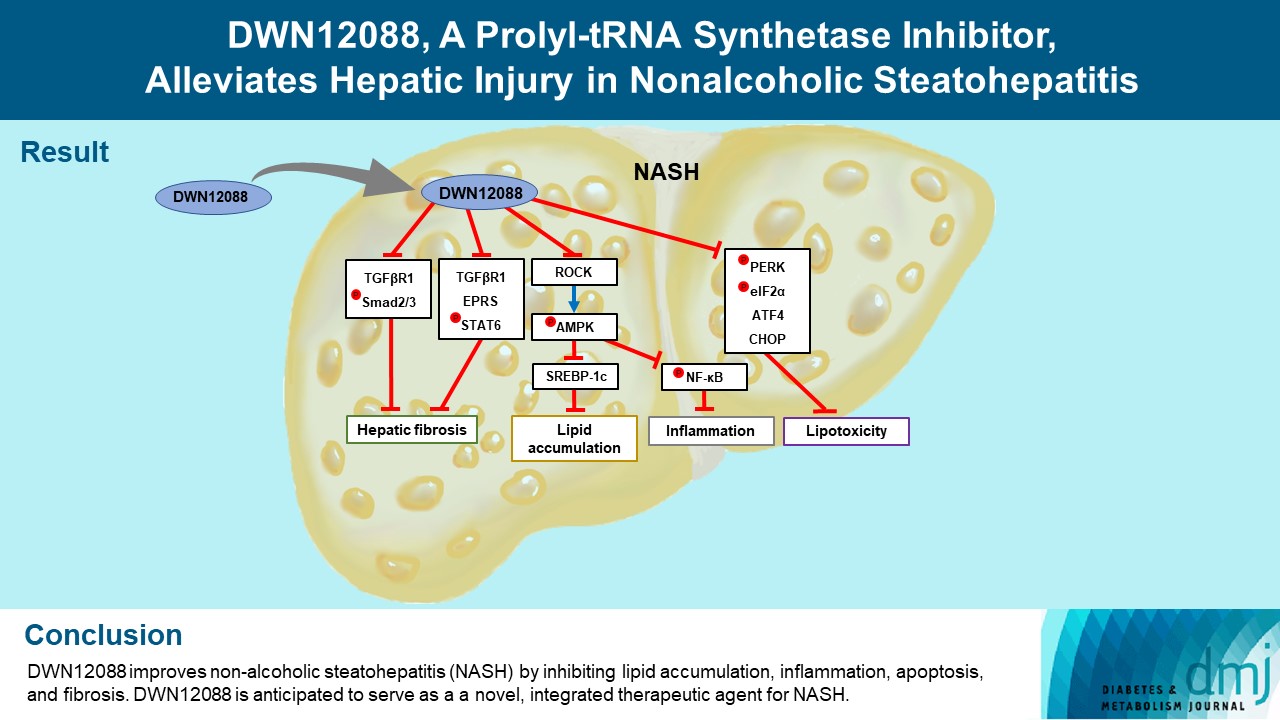
DWN12088 attenuated palmitic acid (PA)-induced lipid accumulation and lipoapoptosis by downregulating the Rho-kinase (ROCK)/AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) and protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)/α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α)/activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4)/C/EBP-homologous protein (CHOP) signaling cascades. PA increased but DWN12088 inhibited the phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) p65 (Ser536, Ser276) and the expression of proinflammatory genes. Moreover, the DWN12088 inhibited transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)-induced pro-fibrotic gene expression by suppressing TGFβ receptor 1 (TGFβR1)/Smad2/3 and TGFβR1/glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) axis signaling. In the case of MCD-diet-induced NASH, DWN12088 reduced hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and lipoapoptosis and prevented the progression of fibrosis.
Conclusion
Our findings provide new insights about DWN12088, namely that it plays an important role in the overall improvement of NASH. Hence, DWN12088 shows great potential to be developed as a new integrated therapeutic agent for NASH.
- Basic Research
- Beneficial Effects of a Curcumin Derivative and Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptor I Inhibitor Combination on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
- Kyung Bong Ha, Eun Soo Lee, Na Won Park, Su Ho Jo, Soyeon Shim, Dae-Kee Kim, Chan Mug Ahn, Choon Hee Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):500-513. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0110
- 2,223 View
- 145 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Curcumin 2005-8 (Cur5-8), a derivative of curcumin, improves fatty liver disease via AMP-activated protein kinase activation and autophagy regulation. EW-7197 (vactosertib) is a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) receptor I and may scavenge reactive oxygen species and ameliorate fibrosis through the SMAD2/3 canonical pathway. This study aimed to determine whether co-administering these two drugs having different mechanisms is beneficial.
Methods
Hepatocellular fibrosis was induced in mouse hepatocytes (alpha mouse liver 12 [AML12]) and human hepatic stellate cells (LX-2) using TGF-β (2 ng/mL). The cells were then treated with Cur5-8 (1 μM), EW-7197 (0.5 μM), or both. In animal experiments were also conducted during which, methionine-choline deficient diet, Cur5-8 (100 mg/kg), and EW-7197 (20 mg/kg) were administered orally to 8-week-old C57BL/6J mice for 6 weeks.
Results
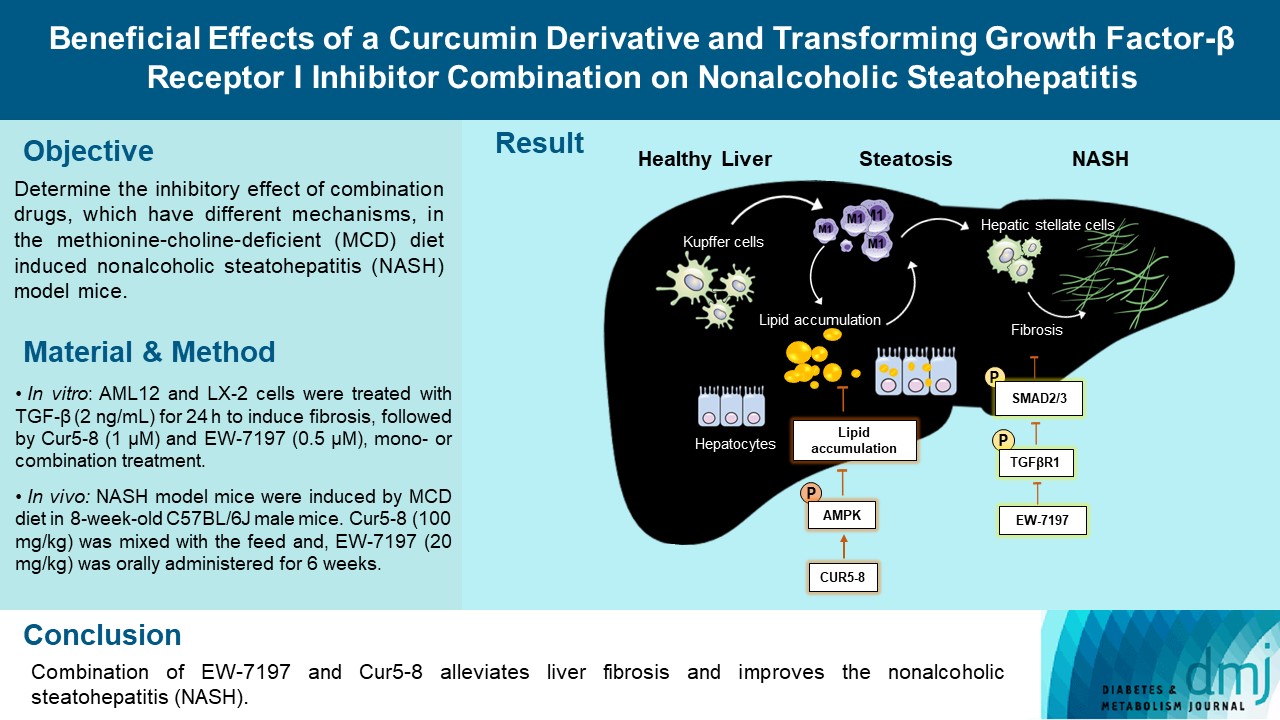
TGF-β-induced cell morphological changes were improved by EW-7197, and lipid accumulation was restored on the administration of EW-7197 in combination with Cur5-8. In a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-induced mouse model, 6 weeks of EW-7197 and Cur5-8 co-administration alleviated liver fibrosis and improved the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score.
Conclusion
Co-administering Cur5-8 and EW-7197 to NASH-induced mice and fibrotic hepatocytes reduced liver fibrosis and steatohepatitis while maintaining the advantages of both drugs. This is the first study to show the effect of the drug combination against NASH and NAFLD. Similar effects in other animal models will confirm its potential as a new therapeutic agent.
- Drug/Regimen
- Evogliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Caused by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Mice
- Mi-Jin Kim, Na-young Kim, Yun-A Jung, Seunghyeong Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Sungwoo Lee, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):186-192. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0271
- 5,679 View
- 97 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Renal fibrosis is considered to be the final common outcome of chronic kidney disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have demonstrated protective effects against diabetic kidney disease. However, the anti-fibrotic effect of evogliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, has not been studied. Here, we report the beneficial effects of evogliptin on unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis in mice. Evogliptin attenuated UUO-induced renal atrophy and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting demonstrated that evogliptin treatment inhibits pro-fibrotic gene expressions and extracellular matrix production.
In vitro findings showed that the beneficial effects of evogliptin on renal fibrosis are mediated by inhibition of the transforming growth factor-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. The present study demonstrates that evogliptin is protective against UUO-induced renal fibrosis, suggesting that its clinical applications could extend to the treatment of kidney disease of non-diabetic origin.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
Birte Ohm, Isabelle Moneke, Wolfgang Jungraithmayr
British Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 180(22): 2846. CrossRef - Linagliptin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis mouse model via inhibition of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Biwei Pei, Na Zhang, Tingting Pang, Gengyun Sun
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(4): 995. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Evogliptin Directly Inhibits Inflammatory and Fibrotic Signaling in Isolated Liver Cells
Hye-Young Seo, So-Hee Lee, Eugene Han, Jae Seok Hwang, Sol Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11636. CrossRef - Optimization and validation of a fluorogenic dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzymatic assay in human plasma
Hyunyee Yoon, Su Hee Cho, Yu Rim Seo, Kyung-Sang Yu, Sung Sup Park, Moon Jung Song
Analytical Biochemistry.2021; 612: 113952. CrossRef - Use of Anti-Diabetic Agents in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Bench to Bedside
Sungjin Chung, Gheun-Ho Kim
Life.2021; 11(5): 389. CrossRef - Targeting Dermal Fibroblast Subtypes in Antifibrotic Therapy: Surface Marker as a Cellular Identity or a Functional Entity?
Xin Huang, Yimin Khoong, Chengyao Han, Dai Su, Hao Ma, Shuchen Gu, Qingfeng Li, Tao Zan
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study with open‐label extension (the EVERGREEN study)
Gyuri Kim, Soo Lim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ie B. Park, Kyu J. Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park, Su K. Kwon, Hye S. Kim, Seok W. Park, Sin G. Kim, Min K. Moon, Eun S. Kim, Choon H. Chung, Kang S. Park, Mikyung Kim, Dong J. Chung, Chang B. Lee, Tae H. Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(9): 1527. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Efficacy and safety of novel dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitor evogliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Aishwarya Krishnamurthy, LokeshKumar Sharma, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 24(5): 434. CrossRef
- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
- Basic Research
- Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Attenuates Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis by Negatively Regulating TGF-β-p53-Smad2/3-Mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via Activation of AKT
- Sundong Lin, Lechu Yu, Yongqing Ni, Lulu He, Xiaolu Weng, Xuemian Lu, Chi Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):158-172. Published online October 28, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0235
- 5,765 View
- 113 Download
- 38 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is required for renal fibrosis, which is a characteristic of diabetic nephropathy (DN). Our previous study demonstrated that fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) prevented DN associated with the suppressing renal connective tissue growth factor expression, a key marker of renal fibrosis. Therefore, the effects of FGF21 on renal fibrosis in a DN mouse model and the underlying mechanisms were investigated in this study.
Methods Type 1 diabetes mellitus was induced in C57BL/6J mice by intraperitoneal injections of multiple low doses of streptozotocin. Then, diabetic and non-diabetic mice were treated with or without FGF21 in the presence of pifithrin-α (p53 inhibitor) or 10-[4′-(N,N-Diethylamino)butyl]-2-chlorophenoxazine hydrochloride (10-DEBC) hydrochloride (Akt inhibitor) for 4 months.
Results DN was diagnosed by renal dysfunction, hypertrophy, tubulointerstitial lesions, and glomerulosclerosis associated with severe fibrosis, all of which were prevented by FGF21. FGF21 also suppressed the diabetes-induced renal EMT in DN mice by negatively regulating transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-induced nuclear translocation of Smad2/3, which is required for the transcription of multiple fibrotic genes. The mechanistic studies showed that FGF21 attenuated nuclear translocation of Smad2/3 by inhibiting renal activity of its conjugated protein p53, which carries Smad2/3 into the nucleus. Moreover pifithrin-α inhibited the FGF21-induced preventive effects on the renal EMT and subsequent renal fibrosis in DN mice. In addition, 10-DEBC also blocked FGF21-induced inhibition of renal p53 activity by phosphorylation of mouse double minute-2 homolog (MDM2).
Conclusion FGF21 prevents renal fibrosis via negative regulation of the TGF-β/Smad2/3-mediated EMT process by activation of the Akt/MDM2/p53 signaling pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epithelial–mesenchymal plasticity in kidney fibrosis
Sudarat Hadpech, Visith Thongboonkerd
genesis.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Wenhui Zhong, Yuheng Jiang, Huizhen Wang, Xiang Luo, Tao Zeng, Huimi Huang, Ling Xiao, Nan Jia, Aiqing Li
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119620. CrossRef - Platelet concentrates may affect the formation of pathological scars by regulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition
Ju Tian, Dandan Shi, Chenyan Long, Jing Ding, Huimin You, Xiaoying He, Biao Cheng
Medical Hypotheses.2024; 182: 111227. CrossRef - Cadherin-responsive hydrogel combined with dental pulp stem cells and fibroblast growth factor 21 promotes diabetic scald repair via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and necroptosis
Wenjie Lu, Juan Zhao, Xiong Cai, Yutian Wang, Wenwei Lin, Yaoping Fang, Yunyang Wang, Jinglei Ao, Jiahui Shou, Jiake Xu, Sipin Zhu
Materials Today Bio.2024; 24: 100919. CrossRef - Sodium butyrate ameliorated diabetic nephropathy-associated tubulointerstitial inflammation by modulating the tight junctions of renal tubular epithelial cells
Tingting Yang, Lin Li, Cai Heng, Pian Sha, Yiying Wang, Jiaming Shen, Zhenzhou Jiang, Sitong Qian, Chujing Wei, Hao Yang, Xia Zhu, Tao Wang, Mengying Wu, Jianyun Wang, Qian Lu, Xiaoxing Yin
Food & Function.2024; 15(5): 2628. CrossRef - Urinary Excretion of Biomolecules Related to Cell Cycle, Proliferation, and Autophagy in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Anton I. Korbut, Vyacheslav V. Romanov, Vadim V. Klimontov
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 487. CrossRef - FGF21 Inhibits Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-induced Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Injury by Regulating the PPARγ/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Ruixue Li, Xi Liu
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Timosaponin BII inhibits TGF‐β mediated epithelial‐mesenchymal transition through Smad‐dependent pathway during pulmonary fibrosis
Dali Ding, Xuebin Shen, Lizhen Yu, Yueyue Zheng, Yao Liu, Wei Wang, Li Liu, Zitong Zhao, Sihui Nian, Limin Liu
Phytotherapy Research.2023; 37(7): 2787. CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) endocrines et fibrogenèse pulmonaire
M. Ghanem, A. Mailleux, B. Crestani
Revue des Maladies Respiratoires.2023; 40(3): 239. CrossRef - Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Kidney Diseases: Potential and Challenges
Fukun Chen, NaNa Chen, Chunjuan Xia, Hongyue Wang, Lishi Shao, Chen Zhou, Jiaping Wang
Cell Transplantation.2023; 32: 096368972311642. CrossRef - MicroRNA functional metal-organic framework nanocomposite for efficient inhibition of drug-resistant breast cancer cells
Yuxin Shen, Yao Zhang, Xiyue Gao, Mengdi Shang, Yanfei Cai, Zhaoqi Yang
Emergent Materials.2023; 6(5): 1537. CrossRef - Downregulation of a potential therapeutic target NPAS2, regulated by p53, alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition via suppressing HES1
Yingying Chen, Zhong He, Bo Zhao, Rui Zheng
Cellular Signalling.2023; 109: 110795. CrossRef - KLF5/MDM2 Axis Modulates Oxidative Stress and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Lens Epithelial Cells: The Role in Diabetic Cataract
Xiao Li, Doudou Chen, Bowen Ouyang, Shengnan Wang, Yawei Li, Li Li, Siquan Zhu, Guangying Zheng
Laboratory Investigation.2023; 103(11): 100226. CrossRef - MAP3K19 Promotes the Progression of Tuberculosis-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Through Activation of the TGF-β/Smad2 Signaling Pathway
Yu Xia, Haiyue Wang, Meihua Shao, Xuemei Liu, Feng Sun
Molecular Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus intestinal damp-heat syndrome and the therapeutic effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction from the perspective of exosomal miRNA
LiSha He, Tingting Bao, Yingying Yang, Han Wang, Chengjuan Gu, Jia Chen, Tiangang Zhai, Xinhui He, Mengyi Wu, Linhua Zhao, Xiaolin Tong
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 285: 114786. CrossRef - Cardamomin protects from diabetes-induced kidney damage through modulating PI3K/AKT and JAK/STAT signaling pathways in rats
Chan Gao, Xiao Fei, Ming Wang, Qi Chen, Ning Zhao
International Immunopharmacology.2022; 107: 108610. CrossRef - Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Predicts Short-Term Prognosis in Patients With Acute Heart Failure: A Prospective Cohort Study
Guihai Wu, Shenglin Wu, Jingyi Yan, Shanshan Gao, Jinxiu Zhu, Minghui Yue, Zexin Li, Xuerui Tan
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Fibrotic Diseases
Min-Qi Jia, Cha-Xiang Guan, Jia-Hao Tao, Yong Zhou, Liang-Jun Yan
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Circ_FOXP1 promotes the growth and survival of high glucose-treated human trophoblast cells through the regulation of miR-508-3p/SMAD family member 2 pathway
Mingqun Li, Yuqin Huang, Hongli Xi, Wei Zhang, Ziwu Xiang, Lingyun Wang, Xuanyu Li, Hongyan Guo
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(9): 1067. CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factor 21 attenuates the progression of hyperuricemic nephropathy through inhibiting inflammation, fibrosis and oxidative stress
Xinghao Jiang, Qing Wu, Yeboah Kwaku Opoku, Yimeng Zou, Dan Wang, Changhui Hu, Guiping Ren
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology.2022; 131(6): 474. CrossRef - Myokines: Novel therapeutic targets for diabetic nephropathy
Ming Yang, Shilu Luo, Jinfei Yang, Wei Chen, Liyu He, Di Liu, Li Zhao, Xi Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dojuksan ameliorates tubulointerstitial fibrosis through irisin-mediated muscle-kidney crosstalk
Songling Jiang, Dal-Seok Oh, Debra Dorotea, Eunjung Son, Dong-Seon Kim, Hunjoo Ha
Phytomedicine.2021; 80: 153393. CrossRef - Chromatin accessibility of kidney tubular cells under stress reveals key transcription factor mediating acute and chronic kidney disease
Yuexian Xing, Qi Wang, Jing Zhang, Wenju Li, Aiping Duan, Jingping Yang, Zhihong Liu
The FEBS Journal.2021; 288(18): 5446. CrossRef - Small molecules against the origin and activation of myofibroblast for renal interstitial fibrosis therapy
Ya-long Feng, Wen-bo Wang, Yue Ning, Hua Chen, Pei Liu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 139: 111386. CrossRef - FGF21 prevents low-protein diet-induced renal inflammation in aged mice
Han Fang, Sujoy Ghosh, Landon C. Sims, Kirsten P. Stone, Cristal M. Hill, Denisha Spires, Daria V. Ilatovskaya, Christopher D. Morrison, Thomas W. Gettys, Krisztian Stadler
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2021; 321(3): F356. CrossRef - IFN-α-2b Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblasts via the TGFβ/Smad Signaling Pathway to Reduce Postoperative Epidural Fibrosis
Zhendong Liu, Hui Chen, Zhehao Fan, Jihang Dai, Yu Sun, Lianqi Yan, Rui Wang, Xiaolei Li, Jingcheng Wang
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2021; 41(8): 271. CrossRef - FOXN3 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via modulating the AKT/MDM2/p53 axis in human glioma
Chaojia Wang, Hanjun Tu, Ling Yang, Chunming Ma, Juntao Hu, Jie Luo, Hui Wang
Aging.2021; 13(17): 21587. CrossRef - Regulation and Potential Biological Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Chronic Kidney Disease
Xue Zhou, Yuefeng Zhang, Ning Wang
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Multiple Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factor in Diabetic Nephropathy
Junyu Deng, Ye Liu, Yiqiu Liu, Wei Li, Xuqiang Nie
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 5273. CrossRef - Exercise Training Alleviates Cardiac Fibrosis through Increasing Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Regulating TGF-β1-Smad2/3-MMP2/9 Signaling in Mice with Myocardial Infarction
Yixuan Ma, Yixin Kuang, Wenyan Bo, Qiaoqin Liang, Wenfei Zhu, Mengxin Cai, Zhenjun Tian
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(22): 12341. CrossRef - Snai1-induced partial epithelial–mesenchymal transition orchestrates p53–p21-mediated G2/M arrest in the progression of renal fibrosis via NF-κB-mediated inflammation
Ruochen Qi, Jiyan Wang, Yamei Jiang, Yue Qiu, Ming Xu, Ruiming Rong, Tongyu Zhu
Cell Death & Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Destruction of the blood-retina barrier in diabetic retinopathy depends on angiotensin-converting enzyme-mediated TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway activation
Ping Sun, Ning Xu, Yan Li, Yang Han
International Immunopharmacology.2020; 85: 106686. CrossRef Chrysophanol Inhibits the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy via Inactivation of TGF-β Pathway
Chuan Guo, Yarong Wang, Yuanlin Piao, Xiangrong Rao, Dehai Yin
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2020; Volume 14: 4951. CrossRef
- Epithelial–mesenchymal plasticity in kidney fibrosis
- The Effect of alpha-Lipoic Acid on Proteinuria and Renal TGFbeta Expression in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Rat Model.
- Seok Woo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Dong Sun Kim, Tae Wha Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(1):21-29. Published online February 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.1.21
- 2,369 View
- 19 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It is well known that renal TGFbeta expression is related to the development of diabetic nephropathy. Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), a potent antioxidant and cofactor of mitochondrial respiratory enzymes, can improve the insulin resistance and the vascular endothelial dysfunction, and suppresses the development of diabetic vascular complications. This study was undertaken to investigate whether ALA could reduce urinary protein excretion and renal TGFbeta protein expression in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus animal model, Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rat. METHODS: Obese 30 male OLETF rats were randomly divided to 3 groups at the age of 30 weeks. The rats in the Control group fed normal rat chow while the rats in the ALA group were fed with rat chow containing ALA (0.5% of food weight). Ten rats in the Pair-fed group were fed with normal rat chow, but were given the same amount of food as consumed by the ALA group. During 5 weeks of ALA feeding, food intake and body weight were checked in metabolic chamber. Blood glucose levels, HbA1c and urinary protein excretion were measured at 30 weeks and 35 weeks of age, and renal TGFbeta protein expression at 35 weeks of age was measured by Western blot and represented by relative unit (RU). Immunohistochemical staining for TGFbeta protein in renal tissue was also examined at 35 weeks of age. RESULTS: Food intake, body weight, blood glucose levels, HbA1c and urinary protein excretion among the Control, ALA and Pair-fed groups at 30 weeks of age were not different. At 35 weeks of age, food intake was significantly decreased in the ALA group than the Control group (Control group vs. ALA group, 27.7 +/- 1.1 g/day vs. 22.4 +/- 1.4 g/day, P < 0.001), and body weight was significantly decreased in the ALA group than the Control and Pair-fed groups (Control group: 694.4 +/- 10.3 g, ALA group: 600.4 +/- 7.4 g, Pair-fed group: 685.4 +/- 11.6 g, P < 0.001). Blood glucose levels were significantly decreased in the ALA group than the Control and Pair-fed groups (Control group: 157.7 +/- 4.6 mg/dL, ALA group: 130.7 +/- 4.8 mg/dL, Pair-fed group: 153.7 +/- 3.3 mg/dL, P < 0.001) although blood glucose levels from 30 weeks to 34 weeks of age and HbA1c at 35 weeks of age were not different among the groups. Urinary protein excretion and renal TGFbeta protein expression were significantly decreased in the ALA group than the Control and Pair-fed groups (urinary protein excretion, Control group: 5.033 +/- 0.254 mg/mgCr, ALA group: 3.633 +/- 0.303 mg/mgCr, Pair-fed group: 4.977 +/- 0.339 mg/mgCr, P < 0.001; renal TGFbeta protein expression, Control group: 7.09 +/- 0.17 RU, ALA group: 4.14 +/- 0.26 RU, Pair-fed group: 7.00 +/- 0.29 RU, P < 0.001). In the ALA group at 35 weeks of age, urinary protein excretion and renal TGFbeta protein expression were positively related in the Control, ALA and Pair-fed groups (Control group, r = 0.847, P = 0.002; ALA group, r = 0.954, P < 0.001; Pair-fed group, r = 0.858, P = 0.002). TGFbeta staining in glomeruli was observed in all groups but was decreased in the ALA group at 35 weeks of age. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that ALA may prevent the increase of food intake, body weight, blood glucose, urinary protein excretion and renal TGFbeta protein expression in obese type 2 diabetic rat model. The effect of ALA on diabetic nephropathy presented as proteinuria and renal TGFbeta expression in diabetic patients needs to be further clarified. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dietary alpha-lipoic acid boosts growth, immune-antioxidant traits, behavior, and transcriptomes of antioxidant, apoptosis, and immune-related genes to combat cold stress in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
Amany Behairy, Hanan A. Ghetas, Noura A. Abd-Allah, Walaa El-Houseiny, Ahmed H. Arisha, Mohamed M. M. Metwally, Basma A. Elshafey, Adham A. Al-Sagheer, Engy M. M. Mohamed
Aquaculture International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Dietary alpha-lipoic acid boosts growth, immune-antioxidant traits, behavior, and transcriptomes of antioxidant, apoptosis, and immune-related genes to combat cold stress in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





