
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Iron Overload and the Risk of Diabetes in the General Population: Results of the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey Cohort Study
- He Gao, Jinying Yang, Wenfei Pan, Min Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):307-318. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0287
- 5,072 View
- 196 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Recent studies have found that there are significant associations between body iron status and the development of diabetes. In the present study, we aimed to analyze the association among iron overload (IO), insulin resistance (IR), and diabetes in Chinese adults, and to explore the sex difference.
Methods
Men and women (age >19 years) who participated in the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey and did not have diabetes at baseline were followed between 2009 and 2015 (n=5,779). Over a mean of 6 years, 75 participants were diagnosed with incident diabetes. Logistic regression was used to assess the risk factors associated with IO. Cox proportional hazard regression was used to estimate the risk of incident diabetes and to determine whether the risk differed among subgroups. Causal mediation analysis (CMA) was used to explore the mechanism linking IO and diabetes.
Results
According to sex-stratified multivariable-adjusted Cox proportional hazards regression, IO increased the risk of incident diabetes. Women with IO had a higher risk of diabetes than men. Subgroup analysis with respect to age showed that the association between IO and diabetes was stronger in older women and younger men (P<0.001). CMA showed that liver injury (alanine transaminase) and lipid metabolism abnormalities (triglyceride, apolipoprotein B) contributed to the association between IO and diabetes.
Conclusion
IO is associated with diabetes and this association is sex-specific. IO may indirectly induce IR via liver injury and lipid metabolism abnormalities, resulting in diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative susceptibility mapping for iron monitoring of multiple subcortical nuclei in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sana Mohammadi, Sadegh Ghaderi, Fatemeh Sayehmiri, Mobina Fathi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Ferritin Concentrations in the General Population: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Anthropometric, Metabolic, and Dietary Correlates
Cara Övermöhle, Sabina Waniek, Gerald Rimbach, Katharina Susanne Weber, Wolfgang Lieb
The Journal of Nutrition.2023; 153(5): 1524. CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Iron overload induces islet β cell ferroptosis by activating ASK1/P-P38/CHOP signaling pathway
Ling Deng, Man-Qiu Mo, Jinling Zhong, Zhengming Li, Guoqiao Li, Yuzhen Liang
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15206. CrossRef - The role of ferroptosis in metabolic diseases
Ling Xie, Bin Fang, Chun Zhang
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2023; 1870(6): 119480. CrossRef - Epidemiological and transcriptome data identify potential key genes involved in iron overload for type 2 diabetes
Xuekui Liu, Xiu Hong, Shiqiang Jiang, Rui Li, Qian Lv, Jie Wang, Xiuli Wang, Manqing Yang, Houfa Geng, Yang Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum iron and liver transaminases based on a large adult women population
Andong He, Zhuoping Zhou, Lili Huang, Ka Cheuk Yip, Jing Chen, Ruiling Yan, Ruiman Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum ferritin and uric acid levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Chinese population
Fangli Zhou, Xiaoli He, Dan Liu, Yan Ye, Haoming Tian, Li Tian
PeerJ.2023; 11: e16267. CrossRef - The Role of Iron Overload in Diabetic Cognitive Impairment: A Review
Ji-Ren An, Qing-Feng Wang, Gui-Yan Sun, Jia-Nan Su, Jun-Tong Liu, Chi Zhang, Li Wang, Dan Teng, Yu-Feng Yang, Yan Shi
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3235. CrossRef - The Association Between METS-IR and Serum Ferritin Level in United States Female: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on NHANES
Han Hao, Yan Chen, Ji Xiaojuan, Zhang Siqi, Chu Hailiang, Sun Xiaoxing, Wang Qikai, Xing Mingquan, Feng Jiangzhou, Ge Hongfeng
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress on Relationship Between Iron Overload and Lower Limb Arterial Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Zhongjing Wang, Shu Fang, Sheng Ding, Qin Tan, Xuyan Zhang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 2259. CrossRef - Iron deficiency in cardiac surgical patients
L Hof, O Old, A.U. Steinbicker, P Meybohm, S Choorapoikayil, K Zacharowski
Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica.2022; 73(4): 235. CrossRef
- Quantitative susceptibility mapping for iron monitoring of multiple subcortical nuclei in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Sex Differences in the Effects of CDKAL1 Variants on Glycemic Control in Diabetic Patients: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
- Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Young Sun Hong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):879-889. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0265
- 65,535 View
- 178 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Using long-term data from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study, we defined poor glycemic control and investigated possible risk factors, including variants related to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In addition, we evaluated interaction effects among risk factors for poor glycemic control.
Methods
Among 436 subjects with newly diagnosed diabetes, poor glycemic control was defined based on glycosylated hemoglobin trajectory patterns by group-based trajectory modeling. For the variants related to T2DM, genetic risk scores (GRSs) were calculated and divided into quartiles. Risk factors for poor glycemic control were assessed using a logistic regression model.
Results
Of the subjects, 43% were in the poor-glycemic-control group. Body mass index (BMI) and triglyceride (TG) were associated with poor glycemic control. The risk for poor glycemic control increased by 11.0% per 1 kg/m2 increase in BMI and by 3.0% per 10 mg/dL increase in TG. The risk for GRS with poor glycemic control was sex-dependent (Pinteraction=0.07), and a relationship by GRS quartiles was found in females but not in males. Moreover, the interaction effect was found to be significant on both additive and multiplicative scales. The interaction effect was evident in the variants of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1-like (CDKAL1).
Conclusion
Females with risk alleles of variants in CDKAL1 associated with T2DM had a higher risk for poor glycemic control than males. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatic Cdkal1 deletion regulates HDL catabolism and promotes reverse cholesterol transport
Dan Bi An, Soo-jin Ann, Seungmin Seok, Yura Kang, Sang-Hak Lee
Atherosclerosis.2023; 375: 21. CrossRef
- Hepatic Cdkal1 deletion regulates HDL catabolism and promotes reverse cholesterol transport
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
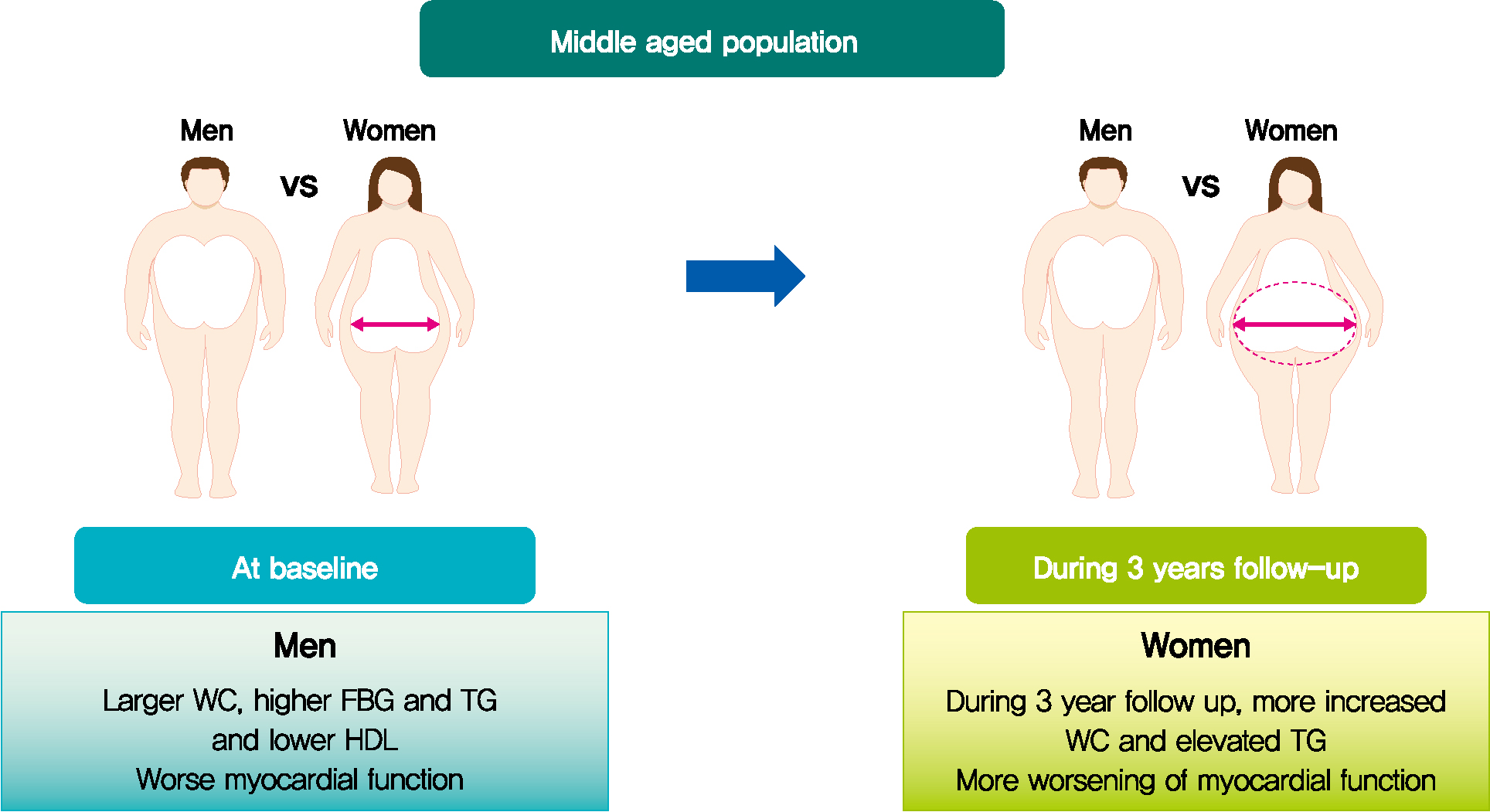
- Longitudinal Change in Myocardial Function and Clinical Parameters in Middle-Aged Subjects: A 3-Year Follow-up Study
- Dong-Hyuk Cho, Hyung Joon Joo, Mi-Na Kim, Hee-Dong Kim, Do-Sun Lim, Seong-Mi Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):719-729. Published online June 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0132
- 4,262 View
- 108 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is closely associated with the aging process. However, changes in metabolic conditions and cardiac function that occur in middle aged population remain unclear. We evaluated longitudinal changes in metabolic parameters and cardiac function during a 3-year period in subjects with suspected MetS.
Methods
We studied 191 participants with suspected MetS at baseline and after 3 years. Anthropometric parameters, including waist circumference (WC), and metabolic parameters, including fasting blood glucose and lipid profile were measured. Conventional echocardiography with two-dimensional speckle tracking was performed.
Results
Mean age was 56.2±4.4 years, and there were 97 women (50.8%). Men had increased WC and triglycerides (TG) (WC 91.2±6.8 cm vs. 84.0±8.0 cm, P<0.001; TG 184.4±116.3 mg/dL vs. 128.2±53.6 mg/dL, P<0.001), and reduced global longitudinal strain (GLS) (–15.4%±2.1% vs. –17.1%±2.0%, P<0.001) compared to women. After 3.4 years, values of WC and TG did not change in men but increased in women (all P<0.05). The absolute value of left ventricular (LV) GLS did not change in men but was reduced in women (P=0.011). Change in TG was independently associated with worsening of LV GLS only in women (standardized β, –0.309; 95% confidence interval, –0.130 to –0.009; P=0.025).
Conclusion
In middle aged population, a vulnerable period for metabolic disturbance, cardiac remodeling tended to progress, which was prominent in women. Progression of adiposity and dyslipidemia after menopause may accelerate subclinical cardiac remodeling in middle-aged women. Lifestyle modification and medical interventions may help prevent further cardiac dysfunction in these subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Positive additive interaction effects of age, sex, obesity, and metabolic syndrome on left ventricular dysfunction
Dan Zhou, Zhongwen Ye, Zhiqiang Nie, Chaolei Chen, Songyuan Luo, Mengqi Yan, Jiabin Wang, Yingqing Feng
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung-Heart Outcomes and Mortality through the 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic in a Prospective Cohort of Breast Cancer Radiotherapy Patients
Vincent Vinh-Hung, Olena Gorobets, Nele Adriaenssens, Hilde Van Parijs, Guy Storme, Dirk Verellen, Nam P. Nguyen, Nicolas Magne, Mark De Ridder
Cancers.2022; 14(24): 6241. CrossRef
- Positive additive interaction effects of age, sex, obesity, and metabolic syndrome on left ventricular dysfunction

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





