
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Lifestyle
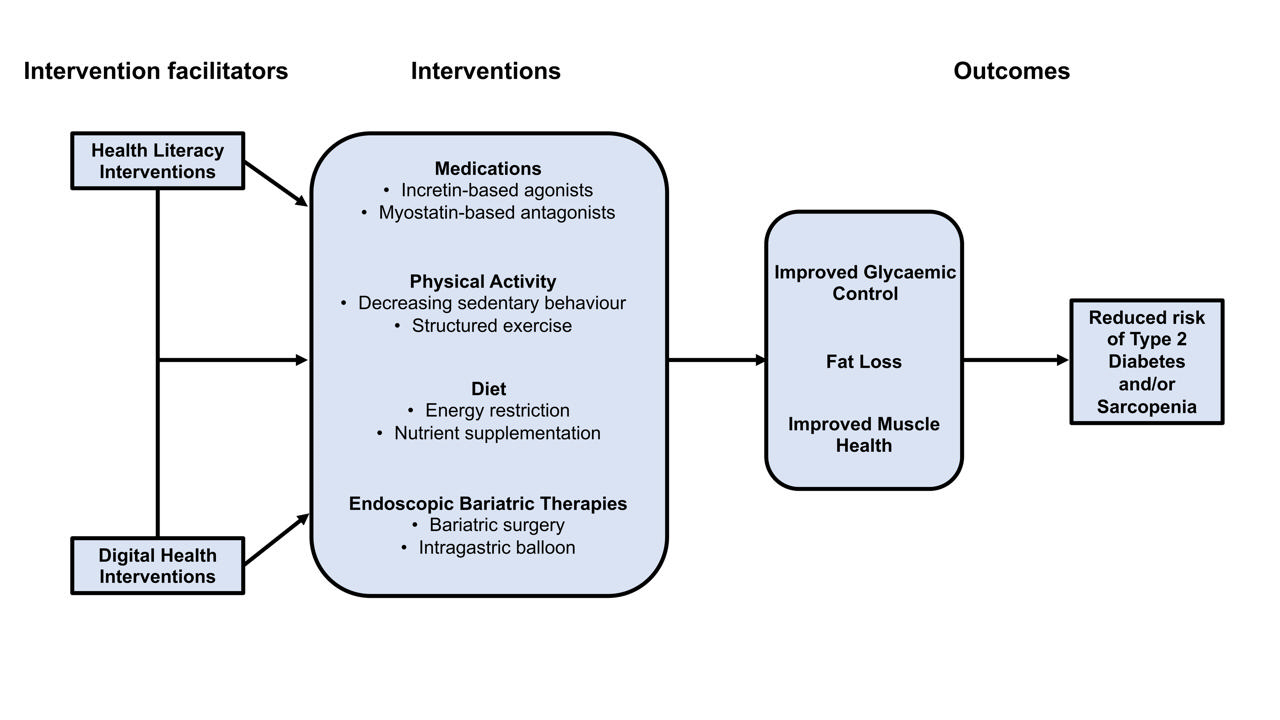
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Sarcopenia as Comorbid Chronic Diseases in Older Adults: Established and Emerging Treatments and Therapies
- Jakub Mesinovic, Jackson J. Fyfe, Jason Talevski, Michael J. Wheeler, Gloria K.W. Leung, Elena S. George, Melkamu T. Hunegnaw, Costas Glavas, Paul Jansons, Robin M. Daly, David Scott
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):719-742. Published online September 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0112
- 4,546 View
- 438 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and sarcopenia (low skeletal muscle mass and function) share a bidirectional relationship. The prevalence of these diseases increases with age and they share common risk factors. Skeletal muscle fat infiltration, commonly referred to as myosteatosis, may be a major contributor to both T2DM and sarcopenia in older adults via independent effects on insulin resistance and muscle health. Many strategies to manage T2DM result in energy restriction and subsequent weight loss, and this can lead to significant declines in muscle mass in the absence of resistance exercise, which is also a first-line treatment for sarcopenia. In this review, we highlight recent evidence on established treatments and emerging therapies targeting weight loss and muscle mass and function improvements in older adults with, or at risk of, T2DM and/or sarcopenia. This includes dietary, physical activity and exercise interventions, new generation incretin-based agonists and myostatin-based antagonists, and endoscopic bariatric therapies. We also highlight how digital health technologies and health literacy interventions can increase uptake of, and adherence to, established and emerging treatments and therapies in older adults with T2DM and/or sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fucoidan ameliorates diabetic skeletal muscle atrophy through PI3K/Akt pathway
Caixia Li, Yaping Liu, Mingzhi Yang, Haoyue Huang, Lulu Tang, Yufan Miao, Wenjie Li, Xing Li
Journal of Functional Foods.2024; 114: 106076. CrossRef
- Fucoidan ameliorates diabetic skeletal muscle atrophy through PI3K/Akt pathway
- Basic Research
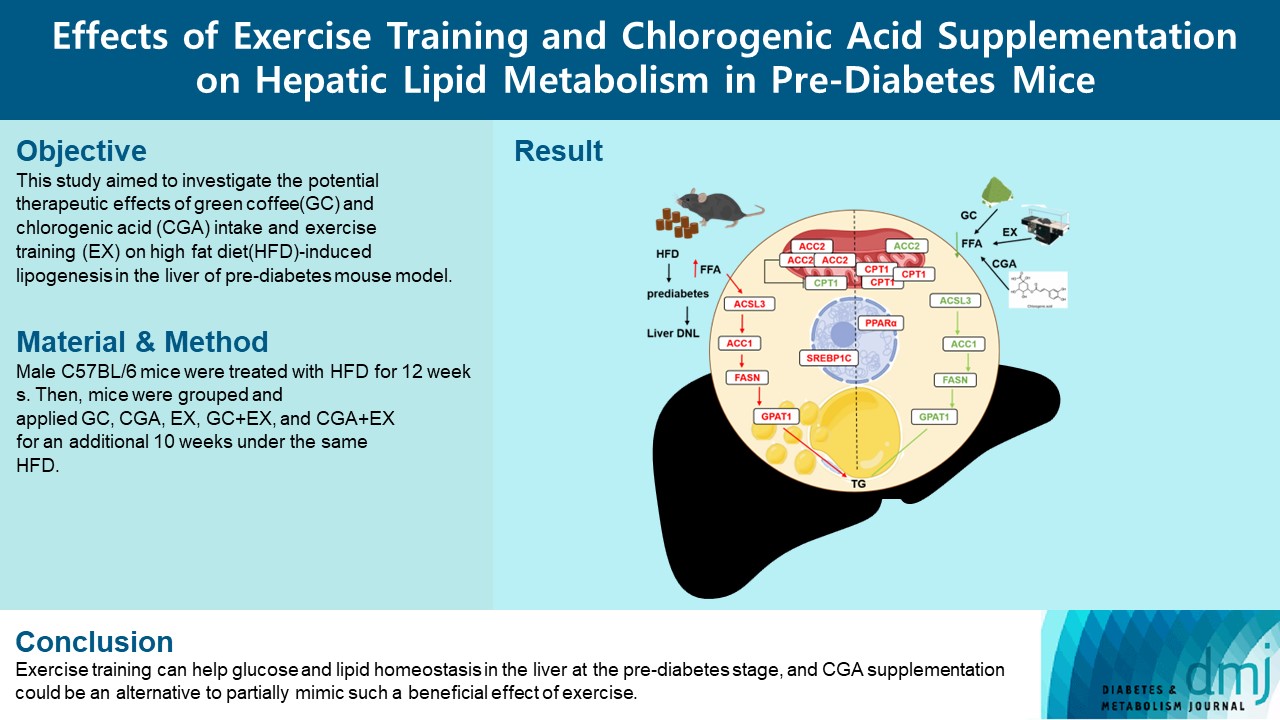
- Effects Of Exercise Training And Chlorogenic Acid Supplementation On Hepatic Lipid Metabolism In Prediabetes Mice
- Samaneh Shirkhani, Sayyed Mohammad Marandi, Mohammad Hossein Nasr-Esfahani, Seung Kyum Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):771-783. Published online September 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0265
- 2,262 View
- 167 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Since prediabetes is a risk factor for metabolic syndromes, it is important to promote a healthy lifestyle to prevent prediabetes. This study aimed to determine the effects of green coffee (GC), chlorogenic acid (CGA) intake, and exercise training (EX) on hepatic lipid metabolism in prediabetes male C57BL/6 mice.
Methods
Forty-nine mice were randomly divided into two groups feeding with a normal diet (n=7) or a high-fat diet (HFD, n=42) for 12 weeks. Then, HFD mice were further divided into six groups (n=7/group): control (pre-D), GC, CGA, EX, GC+EX, and CGA+EX. After additional 10 weeks under the same diet, plasma, and liver samples were obtained.
Results
HFD-induced prediabetes conditions with increases in body weight, glucose, insulin, insulin resistance, and lipid profiles were alleviated in all treatment groups. Acsl3, a candidate gene identified through an in silico approach, was lowered in the pre-D group, while treatments partly restored it. HFD induced adverse alterations of de novo lipogenesis- and β oxidation-associated molecules in the liver. However, GC and CGA supplementation and EX reversed or ameliorated these changes. In most cases, GC or CGA supplementation combined with EX has no synergistic effect and the GC group had similar results to the CGA group.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that regular exercise is an effective non-therapeutic approach for prediabetes, and CGA supplementation could be an alternative to partially mimic the beneficial effects of exercise on prediabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research progress on the pharmacological activity and mechanism of chlorogenic acid in alleviating acute kidney injury in sepsis patients
Perioperative Precision Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research progress on the pharmacological activity and mechanism of chlorogenic acid in alleviating acute kidney injury in sepsis patients
- Basic Research
- Exercise, Mitohormesis, and Mitochondrial ORF of the 12S rRNA Type-C (MOTS-c)
- Tae Kwan Yoon, Chan Hee Lee, Obin Kwon, Min-Seon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):402-413. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0092

- 5,350 View
- 238 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Low levels of mitochondrial stress are beneficial for organismal health and survival through a process known as mitohormesis. Mitohormetic responses occur during or after exercise and may mediate some salutary effects of exercise on metabolism. Exercise-related mitohormesis involves reactive oxygen species production, mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt), and release of mitochondria-derived peptides (MDPs). MDPs are a group of small peptides encoded by mitochondrial DNA with beneficial metabolic effects. Among MDPs, mitochondrial ORF of the 12S rRNA type-c (MOTS-c) is the most associated with exercise. MOTS-c expression levels increase in skeletal muscles, systemic circulation, and the hypothalamus upon exercise. Systemic MOTS-c administration increases exercise performance by boosting skeletal muscle stress responses and by enhancing metabolic adaptation to exercise. Exogenous MOTS-c also stimulates thermogenesis in subcutaneous white adipose tissues, thereby enhancing energy expenditure and contributing to the anti-obesity effects of exercise training. This review briefly summarizes the mitohormetic mechanisms of exercise with an emphasis on MOTS-c.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
Satadeepa Kal, Sumana Mahata, Suborno Jati, Sushil K. Mahata
Peptides.2024; 172: 171147. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Low-Grade Mitochondrial Stress on Metabolic Diseases and Aging
Se Hee Min, Gil Myoung Kang, Jae Woo Park, Min-Seon Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(2): 55. CrossRef - Roles of Myokines and Muscle-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Musculoskeletal Deterioration under Disuse Conditions
Jie Zhang, Yunfang Gao, Jiangwei Yan
Metabolites.2024; 14(2): 88. CrossRef - Antifragility and antiinflammaging: Can they play a role for a healthy longevity?
Fabiola Olivieri, Francesco Prattichizzo, Fabrizia Lattanzio, Anna Rita Bonfigli, Liana Spazzafumo
Ageing Research Reviews.2023; 84: 101836. CrossRef - MOTS-c: A promising mitochondrial-derived peptide for therapeutic exploitation
Yuejun Zheng, Zilin Wei, Tianhui Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - MOTS-c: A potential anti-pulmonary fibrosis factor derived by mitochondria
Zewei Zhang, Dongmei Chen, Kaili Du, Yaping Huang, Xingzhe Li, Quwen Li, Xiaoting Lv
Mitochondrion.2023; 71: 76. CrossRef - Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c, Diabetes, and Aging-Related Diseases
Byung Soo Kong, Changhan Lee, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 315. CrossRef - MOTS-c Serum Concentration Positively Correlates with Lower-Body Muscle Strength and Is Not Related to Maximal Oxygen Uptake—A Preliminary Study
Remigiusz Domin, Michał Pytka, Mikołaj Żołyński, Jan Niziński, Marcin Rucinski, Przemysław Guzik, Jacek Zieliński, Marek Ruchała
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(19): 14951. CrossRef - Unique Properties of Apicomplexan Mitochondria
Ian M. Lamb, Ijeoma C. Okoye, Michael W. Mather, Akhil B. Vaidya
Annual Review of Microbiology.2023; 77(1): 541. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Lifestyle Interventions for Non-Obese Patients Both with, and at Risk, of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Xin-Lei Zhang, Ting-Yao Wang, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Ming-Hua Zheng
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):391-401. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0048
- 5,250 View
- 274 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease occurring in non-obese subjects (the so-called non-obese NAFLD) is a highly prevalent but neglected liver condition, which is closely associated with metabolic disorders and suboptimal lifestyles. Landmark studies have shown that lifestyle interventions are potentially beneficial in decreasing the risk of developing non-obese NAFLD and in ameliorating NAFLD in non-obese individuals with pre-existing NAFLD. Lifestyle interventions usually refer to changes in eating habits and physical activity, both of which have a powerful effect on non-obese NAFLD and on risk factors for non-obese NAFLD. However, to date, patients and health-care professionals have a poor awareness and understanding of non-obese NAFLD and the beneficial effects of lifestyle interventions in this patient population. The aim of this narrative review is to briefly discuss the evidence for the effects of lifestyle changes and what changes are needed amongst medical personnel and other stakeholders in order to raise awareness of non-obese NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglycerides Mediate the Influence of Body Mass Index on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Non-Obese Chinese Population with Normal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels
Xixi Han, Jingwen Kong, Hemin Zhang, Yuan Zhao, Yafeng Zheng, Chao Wei
Obesity Facts.2024; 17(2): 191. CrossRef - Patients with NAFLD exhibit more advanced fibrosis in liver biopsy than patients with other chronic liver diseases
Lydia Rohr, Peter Lemmer, Marie Henning, Andrea Tannapfel, Theodor Baars, Paul Manka, Ali Canbay, Jan-Peter Sowa
Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie.2023; 61(01): 29. CrossRef - Performance of Simple Fibrosis Score in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes
Seung Min Chung, Min Kyu Kang, Jun Sung Moon, Jung Gil Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 277. CrossRef - An international multidisciplinary consensus statement on MAFLD and the risk of CVD
Xiao-Dong Zhou, Giovanni Targher, Christopher D. Byrne, Virend Somers, Seung Up Kim, C. Anwar A. Chahal, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, Jingjing Cai, Michael D. Shapiro, Mohammed Eslam, Philippe Gabriel Steg, Ki-Chul Sung, Anoop Misra, Jian-Jun Li, Carlos Brotons,
Hepatology International.2023; 17(4): 773. CrossRef - Lean or Non-obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Are They Really Lean?
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 980. CrossRef - Sex-Based Differences and Risk Factors for Comorbid Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Bipolar Disorder: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study
Ying Wang, Yiyi Liu, Xun Zhang, Qing Wu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3533. CrossRef - Benefits of Physical Exercise as Approach to Prevention and Reversion of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescents with Obesity
Valeria Calcaterra, Vittoria Magenes, Matteo Vandoni, Clarissa Berardo, Luca Marin, Alice Bianchi, Erika Cordaro, Giustino Silvestro, Dario Silvestri, Vittoria Carnevale Pellino, Cristina Cereda, Gianvincenzo Zuccotti
Children.2022; 9(8): 1174. CrossRef - The effects of supplementation of probiotics, prebiotics, or synbiotics on patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wenmin Xing, Wenyan Gao, Xiaoling Lv, Zhenlei Zhao, Genxiang Mao, Xiaoyan Dong, Zuyong Zhang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Triglycerides Mediate the Influence of Body Mass Index on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Non-Obese Chinese Population with Normal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels
- Lifestyle
- Effectiveness of Resistance Exercise on Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
- Rubén Fernández-Rodríguez, Sonia Monedero-Carrasco, Bruno Bizzozero-Peroni, Miriam Garrido-Miguel, Arthur Eumann Mesas, Vicente Martínez-Vizcaíno
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):118-134. Published online April 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0007

- 9,803 View
- 310 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is related to increased inflammatory processes. The effects of resistance exercise on inflammatory biomarkers in T2DM are controversial. Our purpose was to determine the effectiveness of resistance exercise on inflammatory biomarkers in patients diagnosed with T2DM.
Methods
We searched four databases until September 2021. We included randomized clinical trials (RCTs) of the effects of resistance exercise on inflammatory biomarkers (C-reactive protein [CRP], tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, and interleukin-10) in patients with T2DM. A random effects meta-analysis was conducted to determine the standardized mean difference (SMD) and the raw mean difference (MD) for CRP.
Results
Thirteen RCTs were included in the review, and 11 in the meta-analysis for CRP. Lower CRP levels were observed when resistance exercise was compared with the control groups (SMD=–0.20; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.37 to –0.02). When conducting the MD meta-analysis, resistance exercise showed a significant decrease in CRP of –0.59 mg/dL (95% CI, –0.88 to –0.30); otherwise, in the control groups, the CRP values increased 0.19 mg/dL (95% CI, 0.17 to 0.21).
Conclusion
Evidence supports resistance exercise as an effective strategy to manage systemic inflammation by decreasing CRP levels in patients with T2DM. The evidence is still inconclusive for other inflammatory biomarkers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Körperliche Aktivität und Trainingstherapie bei Typ-2-Diabetes – ein Update
Andreas M. Nieß, Ansgar Thiel
Diabetologie und Stoffwechsel.2024; 19(01): 38. CrossRef - Genetic predisposition, lifestyle inflammation score, food-based dietary inflammatory index, and the risk for incident diabetes: Findings from the KoGES data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Bomi Park
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 642. CrossRef - Associations of meeting 24-h movement guidelines and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
S.W. Shin, Y. Choi, Y.H. Kang, J. Kim
Public Health.2024; 227: 187. CrossRef - Association of hypoglycemic events with cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Protocol for a dose-response meta-analysis
Min Ye, Ai Hong Yuan, Qi Qi Yang, Qun Wei Li, Fei Yue Li, Yan Wei, Muhammad Shahzad Aslam
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0296662. CrossRef - Exercise Interventions for the Prevention and Treatment of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review
Hongmei Li, Haiyun Liu, Boliang Wang, Xiao Jia, Jingjing Yu, Yurong Zhang, Die Sang, Yimin Zhang
Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef - Endothelial progenitor cell response to a multicomponent exercise training program in adults with cardiovascular risk factors
Suiane Cavalcante, Manuel Teixeira, Marisol Gouveia, Ana Duarte, Miriam Ferreira, Maria I. Simões, Maria Conceição, Mariana Costa, Ilda P. Ribeiro, Ana Cristina Gonçalves, José Oliveira, Fernando Ribeiro
German Journal of Exercise and Sport Research.2023; 53(2): 225. CrossRef - “Does Physical Exercise Promote Health Benefits for Diabetic Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic?”: A Systematic Review
Erivaldo de Souza, Daniela Meneses-Santos, Josué Cruz Santos, Felipe J. Aidar, Carla Roberta de Oliveira Carvalho, Jymmys Lopes dos Santos, Anderson Carlos Marçal
Sports.2023; 11(10): 192. CrossRef - Effect of exercise on inflammatory markers in postmenopausal women with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Liang Tan, Weihua Yan, Weilin Yang, Agata Kamionka, Mariusz Lipowski, Zijian Zhao, Gang Zhao
Experimental Gerontology.2023; 183: 112310. CrossRef - Resistance Training Improves Beta Cell Glucose Sensing and Survival in Diabetic Models
Gabriela Alves Bronczek, Gabriela Moreira Soares, Carine Marmentini, Antonio Carlos Boschero, José Maria Costa-Júnior
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(16): 9427. CrossRef
- Körperliche Aktivität und Trainingstherapie bei Typ-2-Diabetes – ein Update
- Lifestyle
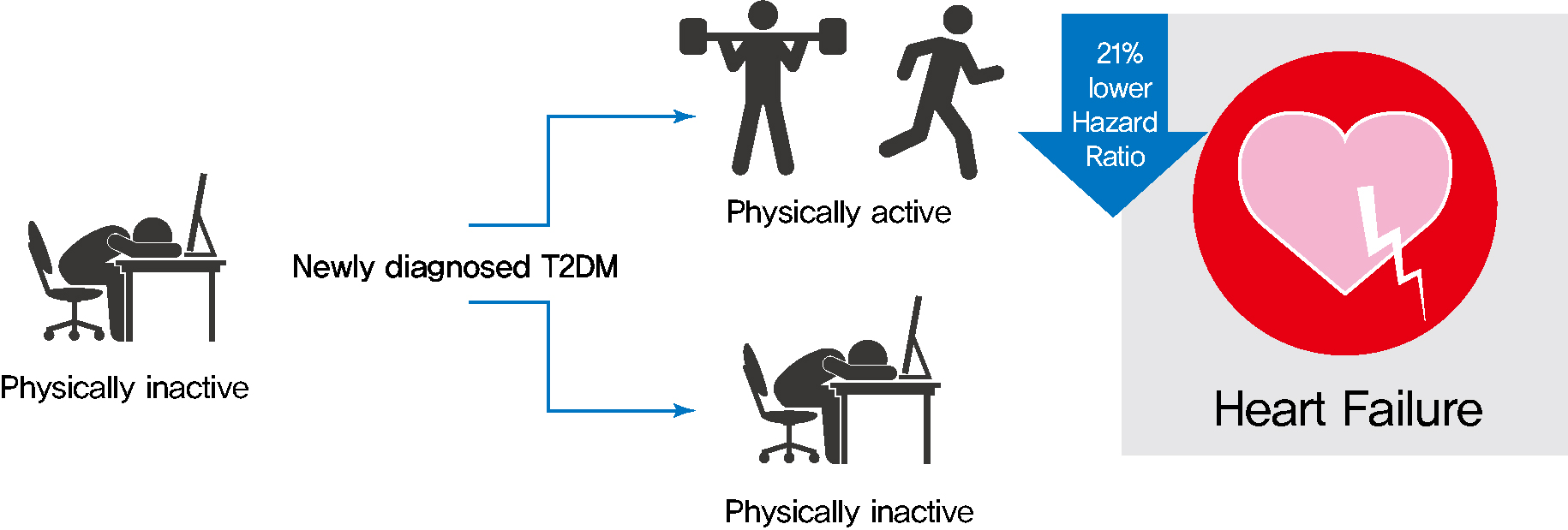
- Changes in Patterns of Physical Activity and Risk of Heart Failure in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):327-336. Published online November 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0046
- 5,379 View
- 210 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Exercise is recommended for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, the effects of physical activity (PA) for reducing the risk of heart failure (HF) has yet to be elucidated. We aimed to assess the effect of changes in patterns of PA on incident HF, especially in newly diagnosed diabetic patients.
Methods
We examined health examination data and claims records of 294,528 participants from the Korean National Health Insurance Service who underwent health examinations between 2009 and 2012 and were newly diagnosed with T2DM. Participants were classified into the four groups according to changes in PA between before and after the diagnosis of T2DM: continuously inactive, inactive to active, active to inactive, and continuously active. The development of HF was analyzed until 2017.
Results
As compared with those who were continuously inactive, those who became physically active after diagnosis showed a reduced risk for HF (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66 to 0.93). Those who were continuously active had the lowest risk for HF (aHR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62 to 0.96). As compared with those who were inactive, those who exercised regularly, either performing vigorous or moderate PA, had a lower HF risk (aHR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.91).
Conclusion
Among individuals with newly diagnosed T2DM, the risk of HF was reduced in those with higher levels of PA after diagnosis was made. Our results suggest either increasing or maintaining the frequency of PA after the diagnosis of T2DM may lower the risk of HF. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyoung Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yumie Rhee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1194. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and frailty in community-dwelling older adults
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Eyun Song, Min Jeong Park, Hye Jin Yoo, Sei Hyun Baik, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
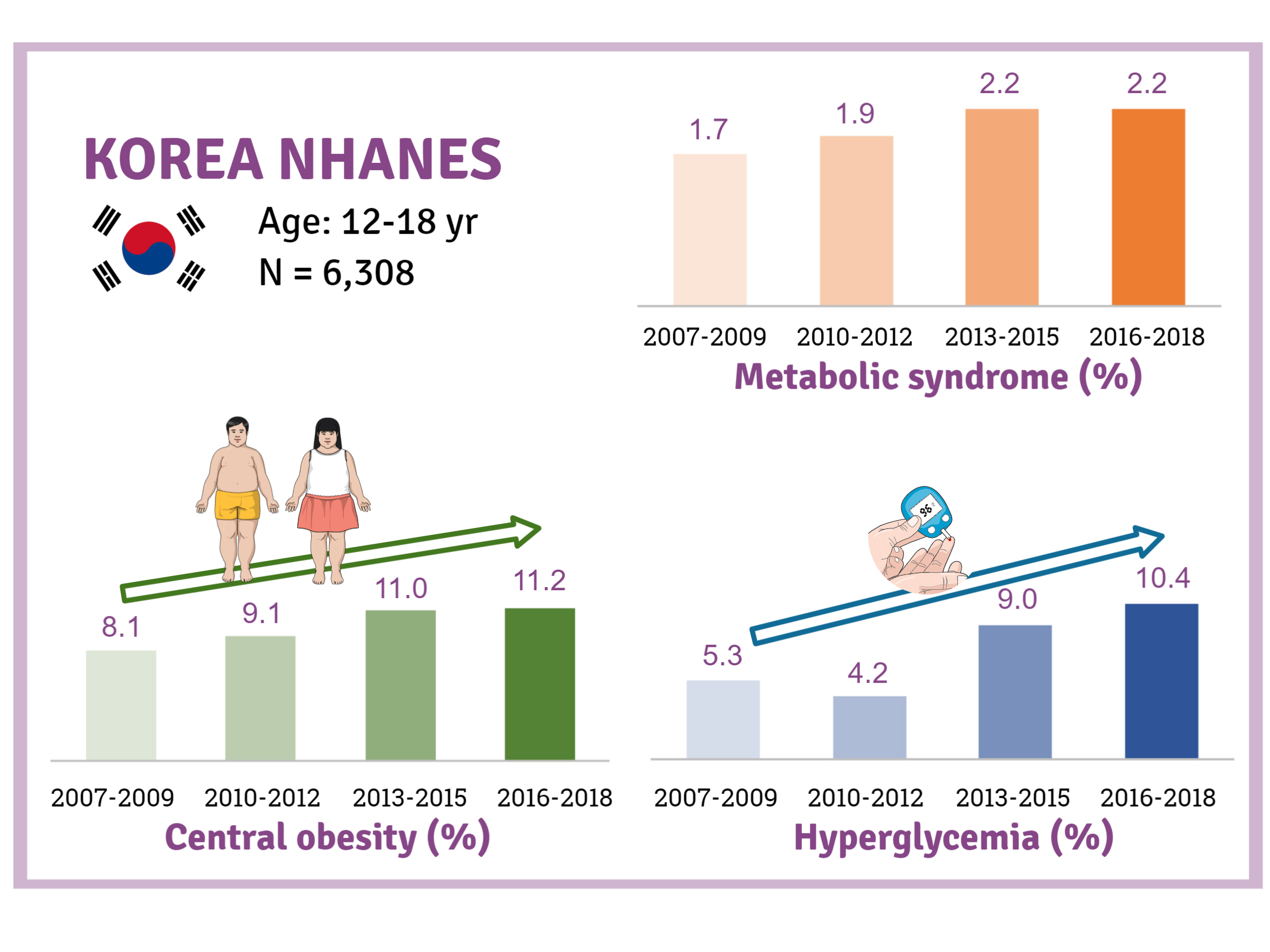
- Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018
- Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):880-889. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0185
- 5,861 View
- 239 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
There is a lack of recent research on the changes in risk factors for metabolic syndrome (MetS) in the Asian pediatric population. We aimed to determine the 12-year trends in the prevalence of MetS and relevant lifestyle factors such as smoking, exercise, and calorie intake among Korean adolescents.
Methods
We investigated trends in MetS and lifestyle factors among 6,308 adolescents aged 12 to 18 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007 to 2018.
Results
The prevalence of MetS was stable from 2007 to 2018 (1.7% to 2.2%). There were significant increases in the prevalence of central obesity (from 8.1% to 11.2%, P=0.012) and hyperglycemia (from 5.3% to 10.4%, P<0.001) and decreases in hypo-high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterolemia (from 22.4% to 14.8%, P<0.001). Total calorie intake and calorie intake from fat significantly increased (P<0.001), whereas calorie intake from carbohydrates significantly decreased (P<0.001) during the study period. The proportions of tobacco smokers and regular walkers significantly decreased from 2007 to 2018. After controlling for all covariates, total calorie intake was positively correlated with waist circumference (P<0.05). HDL-cholesterol was negatively associated with carbohydrate consumption (P<0.01) and positively associated with fat consumption (P<0.001). Regular walking and regular strength training were associated with lower waist circumference (P<0.05). Smoking was associated with lower fasting glucose levels (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Although the prevalence rate of MetS is stable among Korean adolescents, the prevalence of central obesity and hyperglycemia has increased greatly in the recent decade. Public education on proper dietary intake and lifestyle modification is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
Chang In Han, Jaejun Lee
Military Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impacts of dietary sphingomyelin supplementation on metabolic parameters of healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chen-Zi Li, Li-Mei Wu, Chen-Xi Zhu, Huan-Yu Du, Guo-Xun Chen, Fang Yang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Thyroid Function and Insulin Resistance Indices in Korean Adolescents: Findings from the 2014–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunji Mun, Hye Ah Lee, Jung Eun Choi, Rosie Lee, Kyung Hee Kim, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2024; 11(3): 370. CrossRef - Ongoing increasing trends in central precocious puberty incidence among Korean boys and girls from 2008 to 2020
Sinyoung Kang, Mi Jung Park, Jung Min Kim, Jin-Sung Yuk, Shin-Hye Kim, Jun Mori
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283510. CrossRef - The association between urinary cotinine level and metabolic syndrome profiles among adolescents: findings from the Ewha Birth and growth study
Hyunjin Park, Ui-Jeong Kim, Eun Jeong Choi, Seunghee Jun, Bomi Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hyesook Park
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based Speech Analysis System for Medical Support
Eui-Sun Kim, Dong Jin Shin, Sung Tae Cho, Kyung Jin Chung
International Neurourology Journal.2023; 27(2): 99. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Increase of Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents in Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the KNHANES
Jung Eun Choi, Hye Ah Lee, Sung Won Park, Jung Won Lee, Ji Hyen Lee, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2023; 10(7): 1105. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents
Ja Hyang Cho
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 103. CrossRef - Temporal Trends of the Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents between 2007 and 2020
Jieun Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Obin Kwon, Seung-sik Hwang, Jin Soo Moon, Hyun Wook Chae, Jaehyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 170. CrossRef - Changes in the Number of Children and Adolescents with Complex Chronic Conditions and Medical Spending: Analyzing National Health Insurance Claims Data from 2011 to 2021
Jeong-Yoon Oh, Su-Jin Cho, Jin-Seon Jung, Jin-Suk Cho, Choon-Seon Park
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2023; 3(2): 155. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 351. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - Environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure in relation to metabolic syndrome in US adults
Xue Yang, Qingping Xue, Ying Wen, Yichao Huang, Yi Wang, Gaga Mahai, Tong Yan, Yanjun Liu, Tao Rong, Yixin Wang, Da Chen, Shuqin Zeng, Chun-Xia Yang, Xiong-Fei Pan
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 840: 156673. CrossRef - Commentary on "Single point insulin sensitivity estimator for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese adolescents"
Shin-Hye Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(3): 155. CrossRef
- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
- Others
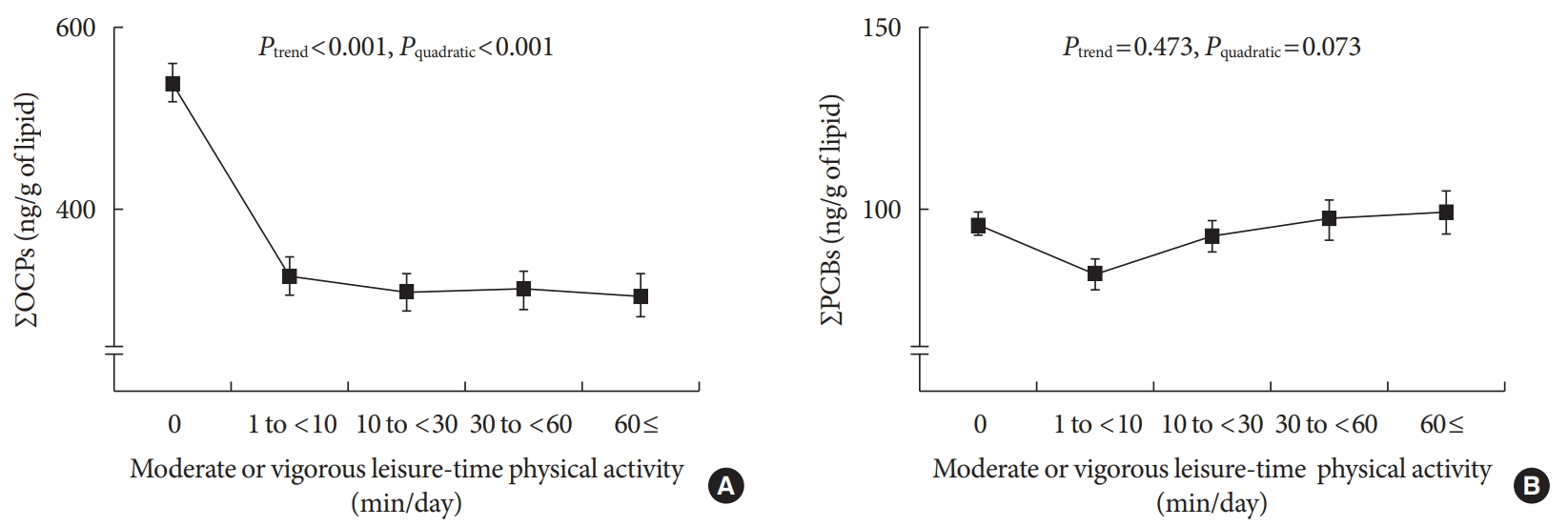
- Can Habitual Exercise Help Reduce Serum Concentrations of Lipophilic Chemical Mixtures? Association between Physical Activity and Persistent Organic Pollutants
- Yu-Mi Lee, Ji-Yeon Shin, Se-A Kim, David R. Jacobs, Duk-Hee Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):764-774. Published online May 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0158
- 5,386 View
- 87 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Low-dose persistent organic pollutants (POPs), especially organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), have emerged as a new risk factor of many chronic diseases. As serum concentrations of POPs in humans are mainly determined by both their release from adipose tissue to circulation and their elimination from circulation, management of these internal pathways may be important in controlling the serum concentrations of POPs. As habitual physical activity can increase the elimination of POPs from circulation, we evaluated whether chronic physical activity is related to low serum POP concentrations.
Methods A cross-sectional study of 1,850 healthy adults (age ≥20 years) without cardio-metabolic diseases who participated in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999 to 2004 was conducted. Information on moderate or vigorous leisure-time physical activity was obtained based on questionnaires. Serum concentrations of OCPs and polychlorinated biphenyls were investigated as typical POPs.
Results Serum concentrations of OCPs among physically active subjects were significantly lower than those among physically inactive subjects (312.8 ng/g lipid vs. 538.0 ng/g lipid,
P <0.001). This difference was maintained after adjustment for potential confounders. When analyses were restricted to physically active subjects, there were small decreases in the serum concentrations of OCPs with increasing duration of physical activity, showing a curvilinear relationship over the whole range of physical activity (P quadratic <0.001). In analyses stratified by age, sex, body mass index, and smoking status, a strong inverse association was similarly observed among all subgroups.Conclusion Physical activity may assist in decreasing serum concentrations of lipophilic chemical mixtures such as OCPs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is Physical Activity an Efficient Strategy to Control the Adverse Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Context of Obesity? A Narrative Review
Quentin A. Serrano, Sébastien Le Garf, Vincent Martin, Serge S. Colson, Nicolas Chevalier
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 883. CrossRef - Physical exercise and persistent organic pollutants
Chang Liu, Hui sheng Hou
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19661. CrossRef - Exposure to a low concentration of mixed organochlorine pesticides impairs glucose metabolism and mitochondrial function in L6 myotubes and zebrafish
Chul-Min Park, Ki-Tae Kim, Dong-Young Rhyu
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2021; 414: 125437. CrossRef - Can Environmental Pollutants Be a Factor Linking Obesity and COVID-19?
Duk-Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter to the Editor: Effect of fatty fish or nut consumption on concentrations of persistent organic pollutants in overweight or obese men and women: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Yu-Mi Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 30(5): 849. CrossRef - Can habitual exercise really increase serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants?
Yu-Mi Lee, Duk-Hee Lee
Environment International.2020; 140: 105615. CrossRef - Response to correspondence ENVINT_2020_552 “Can habitual exercise really increase serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants?”
Sidsel L. Domazet, Tina K. Jensen, Anders Grøntved
Environment International.2020; 140: 105616. CrossRef
- Is Physical Activity an Efficient Strategy to Control the Adverse Effects of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Context of Obesity? A Narrative Review
- Lifesytle
- Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Training Reduces Circulating Apolipoprotein J Levels and Improves Insulin Resistance in Postmenopausal Diabetic Women
- Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Hyun Jeong Kim, Hyun Jun Kim, Jang Jun Park, Yuen Suk Cho, So Hee Joung, Ji Ryang Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Sang Heon Song, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Young-Bum Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):103-112. Published online February 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0160
- 8,435 View
- 151 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Circulating apolipoprotein J (ApoJ) is closely associated with insulin resistance; however, the effect of exercise on circulating ApoJ levels and the association of ApoJ with metabolic indices remain unknown. Here, we investigated whether a combined exercise can alter the circulating ApoJ level, and whether these changes are associated with metabolic indices in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods Postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomly assigned into either an exercise (EXE,
n =30) or control (CON,n =15) group. Participants in the EXE group were enrolled in a 12-week program consisting of a combination of aerobic and resistance exercises. At baseline, 4, 8, and 12 weeks, body composition and metabolic parameters including homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and serum ApoJ levels were assessed.Results In the EXE group, ApoJ levels decreased 26.3% and 19.4%, relative to baseline, at 8 and 12 weeks, respectively. Between-group differences were significant at 8 and 12 weeks (
P <0.05 andP <0.001, respectively). In the EXE group, 12 weeks of exercise resulted in significant decreases in body weight, percent body fat, and HOMA-IR indices. Concurrently, weight-adjusted appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM/wt) was increased in the EXE group compared with the CON group. Importantly, changes in the ApoJ level were significantly correlated with changes in ASM/wt.Conclusion Exercise training resulted in a significant decrease in the circulating ApoJ level, with changes in ApoJ associated with an improvement in some insulin resistance indices. These data suggest that circulating ApoJ may be a useful metabolic marker for assessing the effects of exercise on insulin resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The function of previously unappreciated exerkines secreted by muscle in regulation of neurodegenerative diseases
Xuepeng Bian, Qian Wang, Yibing Wang, Shujie Lou
Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise modalities for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis of randomized trials
Liangying Hou, Qi Wang, Bei Pan, Rui Li, Yanfei Li, Juanjuan He, Tianzhu Qin, Liujiao Cao, Na Zhang, Changhao Cao, Long Ge, Kehu Yang
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimating the Effect of Aerobic Exercise Training on Novel Lipid Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Multivariate Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Gina Wood, Emily Taylor, Vanessa Ng, Anna Murrell, Aditya Patil, Tom van der Touw, Mitch Wolden, Nick Andronicos, Neil A. Smart
Sports Medicine.2023; 53(4): 871. CrossRef - 2023 update on Italian guidelines for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Edoardo Mannucci, Riccardo Candido, Lina delle Monache, Marco Gallo, Andrea Giaccari, Maria Luisa Masini, Angela Mazzone, Gerardo Medea, Basilio Pintaudi, Giovanni Targher, Marina Trento, Giuseppe Turchetti, Valentina Lorenzoni, Matteo Monami
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(8): 1119. CrossRef - The Effect of Eight Weeks of Concurrent Training on Serum Levels of Paraxonase-1, Irisin, Lipid Profile, and Insulin Resistance in Men With Metabolic Syndrome
Seyed Amir Hosain Diba Hosaini, Morvarid Vafaee, Bahram Abedi
Hormozgan Medical Journal.2023; 27(1): 43. CrossRef - An Overview of the TRP-Oxidative Stress Axis in Metabolic Syndrome: Insights for Novel Therapeutic Approaches
Mizael C. Araújo, Suzany H. S. Soczek, Jaqueline P. Pontes, Leonardo A. C. Marques, Gabriela S. Santos, Gisele Simão, Laryssa R. Bueno, Daniele Maria-Ferreira, Marcelo N. Muscará, Elizabeth S. Fernandes
Cells.2022; 11(8): 1292. CrossRef - Effect of Yijinjing combined with elastic band exercise on muscle mass and function in middle-aged and elderly patients with prediabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Yunda Huang, Junhua Han, Qing Gu, Yanwei Cai, Jingyuan Li, Shasha Wang, Suijun Wang, Ru Wang, Xiangyun Liu
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of combined aerobic and resistance exercise on blood pressure in postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Huihui Xi, Yayu He, Yirou Niu, Xin Sui, Jun Zhang, Ruiting Zhu, Haiyan Xu, Shuang Zhang, Yang Li, Yuan Yuan, Lirong Guo
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 155: 111560. CrossRef - Effects of Augmented-Reality-Based Exercise on Muscle Parameters, Physical Performance, and Exercise Self-Efficacy for Older Adults
Sangwan Jeon, Jiyoun Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(9): 3260. CrossRef - Apolipoprotein J is a hepatokine regulating muscle glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity
Ji A Seo, Min-Cheol Kang, Won-Mo Yang, Won Min Hwang, Sang Soo Kim, Soo Hyun Hong, Jee-In Heo, Achana Vijyakumar, Leandro Pereira de Moura, Aykut Uner, Hu Huang, Seung Hwan Lee, Inês S. Lima, Kyong Soo Park, Min Seon Kim, Yossi Dagon, Thomas E. Willnow, V
Nature Communications.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Skeletal Muscle Mass on Metabolic Health
Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 1. CrossRef - Habitual Combined Exercise Protects against Age-Associated Decline in Vascular Function and Lipid Profiles in Elderly Postmenopausal Women
Elizabeth J. Pekas, John Shin, Won-Mok Son, Ronald J. Headid, Song-Young Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(11): 3893. CrossRef
- The function of previously unappreciated exerkines secreted by muscle in regulation of neurodegenerative diseases
- Lifestyle
- Body Fat Is Related to Sedentary Behavior and Light Physical Activity but Not to Moderate-Vigorous Physical Activity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Keun Hee An, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Seo Sohn, Ie Byung Park, Hae Jin Kim, Sung Dae Moon, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):316-325. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0029
- 5,472 View
- 138 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sedentary behavior (SB) has emerged as a new risk factor for cardiovascular accidents. We investigated whether physical activity levels or SB were related to percent body fat (%BF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods In this cross sectional study, we measured the duration of SB, light physical activity (LPA), moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), total energy expenditure, and step counts using a wireless activity tracker (Fitbit HR; FB) for 7 days in free-living conditions, along with %BF using a bio impedance analyzer (Inbody; Biospace) in 120 smartphone users with T2DM. Subjects were divided into exercise (Exe,
n =68) and non-exercise (nonExe,n =52) groups based on self-reports of whether the recommended exercises (30 min/day, 3 days/week for 3 months) were performed. SBt, LPAt, MVPAt were transformed from SB, LPA, MVPA for normally distributed variables.Results Participants were: female, 59.2%; age, 59.3±8.4 years; body mass index, 25.5±3.4 kg/m2; glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), 7.6%±1.2%; %BF, 30.4%±7.1%. They performed SB for 15.7±3.7 hr/day, LPA for 4.4±1.7 hr/day, and MVPA for 0.9±0.8 hr/day. The %BF was related to SBt and LPAt, but not to MVPA after adjustments for age, gender, and HbA1c. VPA was significantly higher in the Exe group than in the nonExe group, but SB, LPA, and moderate physical activity were not different. Predicted %BF was 89.494 to 0.105 (age), −13.047 (gender), −0.507 (HbA1c), −7.655 (LPAt) (F[4, 64]=62.929,
P <0.001), with anR 2 of 0.785 in multiple linear regression analysis.Conclusion Reduced body fat in elderly diabetic patients might be associated with reduced inactivity and increased LPA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Lotte Bogaert, Iris Willems, Patrick Calders, Eveline Dirinck, Manon Kinaupenne, Marga Decraene, Bruno Lapauw, Boyd Strumane, Margot Van Daele, Vera Verbestel, Marieke De Craemer
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(4): 102995. CrossRef - Association between depression, anemia and physical activity using isotemporal substitution analysis
Hee-kyoung Nam, Jungmi Park, Sung-il Cho
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Wearable Technologies in Health Research: Scoping Review
Sophie Huhn, Miriam Axt, Hanns-Christian Gunga, Martina Anna Maggioni, Stephen Munga, David Obor, Ali Sié, Valentin Boudo, Aditi Bunker, Rainer Sauerborn, Till Bärnighausen, Sandra Barteit
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2022; 10(1): e34384. CrossRef - The Correlation of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes With Adiposity in Adults
Juan Sun, Zhen Liu, Zimu Zhang, Ziyang Zeng, Weiming Kang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Physical Activity Assessment of Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Using Accelerometer-Based Cut Points: Scoping Review
Ioana A Moldovan, Alexa Bragg, Anna S Nidhiry, Barbara A De La Cruz, Suzanne E Mitchell
Interactive Journal of Medical Research.2022; 11(2): e34433. CrossRef - Effects of 4 Weeks of a Technique-Specific Protocol with High-Intensity Intervals on General and Specific Physical Fitness in Taekwondo Athletes: An Inter-Individual Analysis
Alex Ojeda-Aravena, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, Jorge Cancino-López, José Zapata-Bastias, José Manuel García-García
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3643. CrossRef - Inter-Individual Variability of a High-Intensity Interval Training With Specific Techniques vs. Repeated Sprints Program in Sport-Related Fitness of Taekwondo Athletes
Alex Ojeda-Aravena, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, Jorge Cancino-López, José Zapata-Bastias, José Manuel García-García
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - EFFECT OF SPORTS MEDICINE ON REDUCING BODY FAT PERCENTAGE AND LEAN BODY MASS
Chunyan Fan
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2021; 27(7): 714. CrossRef - Validation of the effectiveness of a digital integrated healthcare platform utilizing an AI-based dietary management solution and a real-time continuous glucose monitoring system for diabetes management: a randomized controlled trial
Sung Woon Park, Gyuri Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Woo Je Lee, Hyunjin Park, Jae Hyeon Kim
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Brain activity during a working memory task in different postures: an EEG study
Ju-Yeon Jung, Hwi-Young Cho, Chang-Ki Kang
Ergonomics.2020; 63(11): 1359. CrossRef
- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Three Months Monitored Metabolic Fitness Modulates Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Diabetic Patients
- Ilenia Cirilli, Sonia Silvestri, Fabio Marcheggiani, Fabiola Olivieri, Roberta Galeazzi, Roberto Antonicelli, Rina Recchioni, Fiorella Marcheselli, Tiziana Bacchetti, Luca Tiano, Patrick Orlando
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):893-897. Published online June 27, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0254
- 3,898 View
- 46 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Cardiovascular diseases represent the leading cause of death and moderate physical exercise is associated with a reduction in cardiovascular risk. The aim of the study was to evaluate the correlation between the amount of exercise recorded daily by a wearable gravitometer for 3 months and selected biochemical and clinical parameters. Nineteen sedentary type 2 diabetics were recruited and distributed into three homogenous groups, low, medium, and high exercise, according to the level of physical exercise monitored and expressed as MOVEs. Data showed an inverse correlation between MOVEs and oxidative stress indexes and a significant improvement in paraoxonase-1 activities and endothelial functionality. Decrease of visceral/total adipose tissue ratio, systolic blood pressure and a down-regulation of the inflammatory microRNA-146a in high exercise group were observed. Finally, a decrease of glycosylated hemoglobin and an up-regulation of the angiogenic microRNA-130a in medium exercise one was obtained. In this study, precise daily monitoring permitted to underline the importance of the amount of physical activity to counteract some cardiovascular risk factors persisting in diabetes. Finally, it identifies new microRNA biomarkers for future investigation on the same topic.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emerging roles of microRNAs as diagnostics and potential therapeutic interest in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dharmsheel Shrivastav, Desh Deepak Singh
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2024; 12(3): 525. CrossRef - Effects of Seven Weeks of Combined Physical Training on High-Density Lipoprotein Functionality in Overweight/Obese Subjects
Tiziana Bacchetti, Camilla Morresi, Gianna Ferretti, Anders Larsson, Torbjörn Åkerfeldt, Michael Svensson
Metabolites.2023; 13(10): 1068. CrossRef - Physical Exercise Protects Against Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases
Juan Gao, Xue Pan, Guoping Li, Emeli Chatterjee, Junjie Xiao
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research.2022; 15(3): 604. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Training on the Paracrine Function of Circulating Angiogenic Cells
William S. Evans, Ryan M. Sapp, Katherine I. Kim, James M. Heilman, James Hagberg, Steven J. Prior
International Journal of Sports Medicine.2021; 42(12): 1047. CrossRef - Chronic and Transient Hyperglycemia Induces Changes in the Expression Patterns of IL6 and ADIPOQ Genes and Their Associated Epigenetic Modifications in Differentiating Human Visceral Adipocytes
Adam Wróblewski, Justyna Strycharz, Ewa Świderska, Aneta Balcerczyk, Janusz Szemraj, Józef Drzewoski, Agnieszka Śliwińska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(13): 6964. CrossRef - The Potential Role of MicroRNA in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 54. CrossRef
- Emerging roles of microRNAs as diagnostics and potential therapeutic interest in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Effectiveness of Exercise Intervention in Reducing Body Weight and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ji-Eun Jang, Yongin Cho, Byung Wan Lee, Ein-Soon Shin, Sun Hee Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):302-318. Published online November 19, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0062
- 5,291 View
- 97 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of exercise intervention in reducing body weight and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Korea.
Methods Cochrane, PubMed, Embase, KoreaMed, KMbase, NDSL, KCI, RISS, and DBpia databases were used to search randomized controlled trials and controlled clinical trials that compared exercise with non-exercise intervention among patients with non-insulin-treated T2DM in Korea. The effectiveness of exercise intervention was estimated by the mean difference in body weight changes and HbA1c level. Weighted mean difference (WMD) with its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) was used as the effect size. The pooled mean differences of outcomes were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results We identified 7,692 studies through literature search and selected 23 articles (723 participants). Compared with the control group, exercise intervention (17 studies) was associated with a significant decline in HbA1c level (WMD, −0.58%; 95% CI, −0.89 to −0.27;
I 2=73%). Although no significant effectiveness on body weight was observed, eight aerobic training studies showed a significant reduction in body weight (WMD, −2.25 kg; 95% CI, −4.36 to −0.13;I 2=17%) in the subgroup analysis.Conclusion Exercise significantly improves glycemic control; however, it does not significantly reduce body weight. Aerobic training can be beneficial for patients with non-insulin-treated T2DM in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The anti-inflammatory effects of aerobic exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Georgia Papagianni, Chrystalla Panayiotou, Michail Vardas, Nikolaos Balaskas, Constantinos Antonopoulos, Dimitrios Tachmatzidis, Triantafyllos Didangelos, Vaia Lambadiari, Nikolaos P.E. Kadoglou
Cytokine.2023; 164: 156157. CrossRef - Glucose Control in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus according to Body Mass Index
Ye-lim Shin, Heesoh Yoo, Joo Young Hong, Jooeun Kim, Kyung-do Han, Kyu-Na Lee, Yang-Hyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(1): 55. CrossRef - Exercise therapy for diabetes mellitus
Chaiho Jeong, Tae-Seo Sohn
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 427. CrossRef - Effects of an evidence‐based nursing intervention on prevention of anxiety and depression in the postpartum period
Jun Meng, Junying Du, Xiaoli Diao, Yingxia Zou
Stress and Health.2022; 38(3): 435. CrossRef - Effect of exercise intervention dosage on reducing visceral adipose tissue: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yu-Hsuan Chang, Hui-Ying Yang, Shiow-Ching Shun
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(5): 982. CrossRef - Development and validation of the type 2 diabetes mellitus 10-year risk score prediction models from survey data
Gregor Stiglic, Fei Wang, Aziz Sheikh, Leona Cilar
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(4): 699. CrossRef - Pioglitazone for NAFLD Patients With Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
Jingxuan Lian, Jianfang Fu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise Training: The Holistic Approach in Cardiovascular Prevention
Francesco Giallauria, Teresa Strisciuglio, Gianluigi Cuomo, Anna Di Lorenzo, Andrea D’Angelo, Mario Volpicelli, Raffaele Izzo, Maria Virginia Manzi, Emanuele Barbato, Carmine Morisco
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention.2021; 28(6): 561. CrossRef - Effect of chronic High Intensity Interval Training on glycosylated haemoglobin in people with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis
María Cristina Arrieta-Leandro, Jessenia Hernández-Elizondo, Judith Jiménez-Díaz
Human Movement.2021; 24(1): 32. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
Byung-Wan Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Nan-Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Bong-Soo Cha, Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 382. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Glycemic Control among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: The Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Mee Ock Gu
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 235. CrossRef
- The anti-inflammatory effects of aerobic exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Beneficial Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training Combined with Rosiglitazone on Glucose Metabolism in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats
- Shan-Ji Piao, So Hun Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seong-Bin Hong, Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hae Seo, In-Sun Park, Moonsuk Nam
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):474-485. Published online November 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.474
- 3,830 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Regular aerobic exercise is essential for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and may be particularly beneficial for those treated with thiazolidinediones, since it may prevent associated weight gain. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of combined exercise and rosiglitazone treatment on body composition and glucose metabolism in obese diabetes-prone animals.
Methods We analyzed metabolic parameters, body composition, and islet profiles in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty rats after 28 weeks of aerobic exercise, rosiglitazone treatment, and combined exercise and rosiglitazone treatment.
Results Combined exercise with rosiglitazone showed significantly less increase in weight and epididymal fat compared to rosiglitazone treatment. Aerobic exercise alone and combined rosiglitazone and exercise treatment led to similar retention of lean body mass. All experimental groups showed a decrease in fasting glucose. However, the combined exercise and rosiglitazone therapy group showed prominent improvement in glucose tolerance compared to the other groups. Rescue of islet destruction was observed in all experimental groups, but was most prominent in the combined therapy group.
Conclusion Regular aerobic exercise combined with rosiglitazone treatment can compensate for the adverse effect of rosiglitazone treatment and has benefit for islet preservation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impacts of an Exercise Intervention on the Health of Pancreatic Beta-Cells: A Review
Shuang Zhang, Yaru Wei, Chunxiao Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(12): 7229. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms by which aerobic exercise induces insulin sensitivity
Habib Yaribeygi, Stephen L. Atkin, Luis E. Simental‐Mendía, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(8): 12385. CrossRef
- Impacts of an Exercise Intervention on the Health of Pancreatic Beta-Cells: A Review
- Others
- The Effect of 12 Weeks Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises on Omentin-1 Levels and Insulin Resistance among Type 2 Diabetic Middle-Aged Women
- Zeinab AminiLari, Mohammad Fararouei, Sasan Amanat, Ehsan Sinaei, Safa Dianatinasab, Mahmood AminiLari, Nima Daneshi, Mostafa Dianatinasab
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(3):205-212. Published online May 18, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.205
- 5,245 View
- 104 Download
- 51 Web of Science
- 50 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Recent studies have shown that omentin-1 derived from adipokines can affect physiological regulations and some metabolic dis-eases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods The purpose of this study was to examine the impact of 12 weeks of aerobic (cycle ergometer), resistance, and combined exercises on omentin-1 level, glucose and insulin resistance indices in overweight middle age women with T2DM. In this study, 60 overweight middle age diabetic women were selected using simple random sampling and they were assigned to three groups of aerobic exercise (
n =12), resistant exercise (n =12) and combined exercise (n =13), and one control group (n =15). Exercises were done in a three times per week sessions for a total of 12 weeks. Blood samples were collected before each exercise session and 24 hours after of the last session.Results Present study showed that fasting blood sugar decreased significantly in all intervention groups, while homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) decreased only in the aerobic and combined exercises groups. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the omentin-1 level only in the combined exercise group.
Conclusion Compared to aerobic and resistance exercises, 12 weeks of combined exercise was more efficient in improving HOMA-IR and increasing serum omentin-1 among women with T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Exercise Training on Some Anti-Inflammatory Adipokines, High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, and Clinical Outcomes in Sedentary Adults With Metabolic Syndrome
Kelian Gao, Zhanguo Su, Junyan Meng, Yuzhong Yao, LiGuang Li, Yiping Su, Gholam Rasul Mohammad Rahimi
Biological Research For Nursing.2024; 26(1): 125. CrossRef - Enhancing cardiometabolic health: unveiling the synergistic effects of high-intensity interval training with spirulina supplementation on selected adipokines, insulin resistance, and anthropometric indices in obese males
Maryam Delfan, Ayoub Saeidi, Rashmi Supriya, Kurt A Escobar, Ismail Laher, Katie M. Heinrich, Katja Weiss, Beat Knechtle, Hassane Zouhal
Nutrition & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mitochondria‐associated membranes contribution to exercise‐mediated alleviation of hepatic insulin resistance: Contrasting high‐intensity interval training with moderate‐intensity continuous training in a high‐fat diet mouse model
Xi Li, Jun Yang Yang, Wen Zhi Hu, YuXin Ruan, Hong Ying Chen, Qiang Zhang, Zhe Zhang, Zhe Shu Ding
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Resistance Exercise Training on Glycemic Control Among Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Yuwen Wan, Zhanguo Su
Biological Research For Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise training-induced changes in exerkine concentrations may be relevant to the metabolic control of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Antonio García-Hermoso, Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Javier Díez, Arantxa González, Mikel Izquierdo
Journal of Sport and Health Science.2023; 12(2): 147. CrossRef - Physical Activity Types, Physical Activity Levels and Risk of Diabetes in General Adults: The NHANES 2007–2018
Chunnan Li, Shaomei Shang, Wannian Liang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(2): 1398. CrossRef - Intensity Differences of Resistance Training for Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tenglong Fan, Man-Hsu Lin, Kijin Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(3): 440. CrossRef - Chronic Resistance Training Effects on Serum Adipokines in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Pablo Jiménez-Martínez, Rodrigo Ramirez-Campillo, Carlos Alix-Fages, Javier Gene-Morales, Amador García-Ramos, Juan C. Colado
Healthcare.2023; 11(4): 594. CrossRef - The impact of high intensity interval training on serum omentin-1 levels, lipid profile, and insulin resistance in obese men with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ahmed S. Ahmed, Marwan S. Ahmed
Isokinetics and Exercise Science.2023; 31(3): 221. CrossRef - Long‐term effects of different exercise training modes on cytokines and adipokines in individuals with overweight/obesity and cardiometabolic diseases: A systematic review, meta‐analysis, and meta‐regression of randomized controlled trials
Sebastian Del Rosso, María Lucía Baraquet, Adrián Barale, María Daniela Defagó, Fernando Tortosa, Nilda Raquel Perovic, Maria Pilar Aoki
Obesity Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Eight Weeks of Circuit Resistance Training on Serum METRNL Levels and Insulin Resistance in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Seyed Morteza Tayebi, Milad Golmohammadi, Rasoul Eslami, Nadia Shakiba, Pablo B. Costa
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(2): 1151. CrossRef - The Effect of Eight Weeks of Concurrent Training on Serum Levels of Paraxonase-1, Irisin, Lipid Profile, and Insulin Resistance in Men With Metabolic Syndrome
Seyed Amir Hosain Diba Hosaini, Morvarid Vafaee, Bahram Abedi
Hormozgan Medical Journal.2023; 27(1): 43. CrossRef - Omentin-1 and diabetes: more evidence but far from enough
Jing Xu, Min Li, Xinli Jiang, Yuling Wang, Huijie Ma, Yaru Zhou, Meimei Tian, Yan Liu
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; : 1. CrossRef - The effect of exercise training on serum Omentin-1 levels, glycemic control and body composition in adults population: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Ali Asgari, Arghavan Niyazi, Ali Nejatian Hoseinpour, Shayan Setayesh, Rokhsare Fazolahzade Mousavi, Gholam Rasul Mohammad Rahimi
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Astaxanthin Supplementation Augments the Benefits of CrossFit Workouts on Semaphorin 3C and Other Adipokines in Males with Obesity
Rashmi Supriya, Sevda Rahbari Shishvan, Movahed Kefayati, Hossein Abednatanzi, Omid Razi, Reza Bagheri, Kurt A. Escobar, Zhaleh Pashaei, Ayoub Saeidi, Shahnaz Shahrbanian, Sovan Bagchi, Pallav Sengupta, Maisa Hamed Al Kiyumi, Katie M. Heinrich, Hassane Zo
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4803. CrossRef - Joint Association of Relative Grip Strength and Resting Heart Rate with the Risk of Developing Diabetes in Middle-Aged Adults
DooYong Park, YeonSoo Kim, Eunkyung Kim
The Korean Journal of Sports Medicine.2023; 41(4): 216. CrossRef - High-intensity Interval Training Improves Lipocalin-2 and Omentin-1 Levels in Men with Obesity
Sirvan Atashak, Stephen R. Stannard, Ali Daraei, Mohammad Soltani, Ayoub Saeidi, Fatah Moradi, Ismail Laher, Anthony C. Hackney, Hassane Zouhal
International Journal of Sports Medicine.2022; 43(04): 328. CrossRef - Effect of resistance training on HbA1c in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the moderating effect of changes in muscular strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Anna K Jansson, Li X Chan, David R Lubans, Mitch J Duncan, Ronald C Plotnikoff
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(2): e002595. CrossRef - Exercise and Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Brief Guide for Exercise Professionals
Alexios Batrakoulis, Athanasios Z. Jamurtas, Ioannis G. Fatouros
Strength & Conditioning Journal.2022; 44(6): 64. CrossRef - Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training on Selected Adipokines and Cardiometabolic Risk Markers in Normal-Weight and Overweight/Obese Young Males—A Pre-Post Test Trial
Nejmeddine Ouerghi, Mohamed Kacem Ben Fradj, Martine Duclos, Anissa Bouassida, Moncef Feki, Katja Weiss, Beat Knechtle
Biology.2022; 11(6): 853. CrossRef - Comparison of the Effect of Endurance, Strength and Endurance-Strength Training on Glucose and Insulin Homeostasis and the Lipid Profile of Overweight and Obese Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Małgorzata Jamka, Aleksandra Makarewicz-Bukowska, Kamila Bokayeva, Angelika Śmidowicz, Jakub Geltz, Marta Kokot, Nina Kaczmarek, Agnieszka Żok, Victoria Kononets, Judyta Cielecka-Piontek, Edyta Mądry, Jarosław Walkowiak
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 14928. CrossRef - The effects of physical activity on adipokines in individuals with overweight/obesity across the lifespan: A narrative review
Ayoub Saeidi, Marjan Mosalman Haghighi, Sarkawt Kolahdouzi, Ali Daraei, Abderraouf Ben Abderrahmane, M. Faadiel Essop, Ismail Laher, Anthony C. Hackney, Hassane Zouhal
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of combined resistance aerobic exercise training on concentrations of asprosin and complement C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein-1 in men with type 2 diabetes
Mehdi Zarei, Javad Nakhzari Khodakheyr, Amin Rashidlamir, Amir Montazeri
Sport Sciences for Health.2021; 17(4): 863. CrossRef - Relationships between serum omentin-1 concentration, body composition and physical activity levels in older women
Shuo Li, Jingjing Xue, Ping Hong
Medicine.2021; 100(10): e25020. CrossRef - Markers of branched-chain amino acid catabolism are not affected by exercise training in pregnant women with obesity
Brittany R. Allman, Beverly J. Spray, Kelly E. Mercer, Aline Andres, Elisabet Børsheim
Journal of Applied Physiology.2021; 130(3): 651. CrossRef - Physical activity and adipokine levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A literature review and practical applications
Hassane Zouhal, Navabeh Zare-kookandeh, Marjan Mosalman Haghighi, Ali Daraei, Maysa de Sousa, Mohammad Soltani, Abderraouf Ben Abderrahman, Jed M. Tijani, Anthony C. Hackney, Ismail Laher, Ayoub Saeidi
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2021; 22(4): 987. CrossRef - Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Fasting Blood Glucose and Blood Pressure Levels of Diabetic-Hypertensive Clients at a Diabetes Clinicin Accra, Ghana
Edmund Lotsu, Samuel Kwakye, Tawagidu Mohammed, Bridgette Opoku, Jonathan Quartey, Henry Lawson
Journal of Preventive and Rehabilitative Medicine.2021; 3(2): 75. CrossRef - The Effects of Different Exercise Modalities in the Treatment of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Obese Adolescents with Sedentary Behavior—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Daxin Li, Ping Chen
Children.2021; 8(11): 1062. CrossRef - Effectiveness of combined exercise in people with type 2 diabetes and concurrent overweight/obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaoyan Zhao, Qianyu He, Yongmei Zeng, Li Cheng
BMJ Open.2021; 11(10): e046252. CrossRef - The effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercises on the plasma irisin levels, HOMA-IR, and lipid profiles in women with metabolic syndrome: A randomized controlled trial
Aria Dianatinasab, Roghayeh Koroni, Mehrdad Bahramian, Zahra Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Mojtaba Vaismoradi, Mohammad Fararouei, Sasan Amanat
Journal of Exercise Science & Fitness.2020; 18(3): 168. CrossRef - The association between serum omentin level and bodyweight: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Arman Arab, Seyedeh Parisa Moosavian, Amir Hadi, Elham Karimi, Maryam Nasirian
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2020; 39: 22. CrossRef Antidiabetic Effects of Physical Activity: How It Helps to Control Type 2 Diabetes
Addisu Dabi Wake
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 2909. CrossRef- Role of swimming on muscle PGC-1α, FNDC5 mRNA, and assessment of serum omentin, adropin, and irisin in high carbohydrate high fat (HCHF) diet induced obesity in rats
Ehsan Badawy, Nabila A. El-laithy, Safaa M. Morsy, Magdi N. Ashour, Tahany R. Elias, Mahmoud M. Masoud, Omnia Aly
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of 12 Weeks of Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises Training on the Serum Levels of Nesfatin-1, Irisin-1 and HOMA-IR
Sasan Amanat, Ehsan Sinaei, Mohammad Panji, Reza MohammadporHodki, Zahra Bagheri-Hosseinabadi, Hadis Asadimehr, Mohammad Fararouei, Aria Dianatinasab
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Aging on Adipose Function and Adipokine Synthesis
Peter Mancuso, Benjamin Bouchard
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Omentin-1 in diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiongfeng Pan, Atipatsa C. Kaminga, Shi Wu Wen, Kwabena Acheampong, Aizhong Liu, Omid Beiki
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(12): e0226292. CrossRef - Physical Exercise and Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder
Zuleide M. Ignácio, Renato S. da Silva, Marcos E. Plissari, João Quevedo, Gislaine Z. Réus
Molecular Neurobiology.2019; 56(12): 8323. CrossRef - Effects of Eight Weeks of High Intensity Functional Training on Glucose Control and Body Composition among Overweight and Obese Adults
Yuri Feito, Pratik Patel, Andrea Sal Redondo, Katie Heinrich
Sports.2019; 7(2): 51. CrossRef - Exercise and Omentin: Their Role in the Crosstalk Between Muscle and Adipose Tissues in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rat Models
Cynthia Aparecida de Castro, Karina Ana da Silva, Marina Campos Rocha, Marcela Sene-Fiorese, Keico Okino Nonaka, Iran Malavazi, Fernanda de Freitas Anibal, Ana Cláudia Garcia de Oliveira Duarte
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yubo Liu, Weibing Ye, Qian Chen, Yong Zhang, Chia-Hua Kuo, Mallikarjuna Korivi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(1): 140. CrossRef - Mechanisms Involved in Glycemic Control Promoted by Exercise in Diabetics
Eric Francelino Andrade, Víviam de Oliveira Silva, Débora Ribeiro Orlando, Luciano José Pereira
Current Diabetes Reviews.2019; 15(2): 105. CrossRef - Effects of 12 weeks of high intensity circuit training on abdominal fat, physical fitness, blood lipids, and insulin resistance in middle-aged obese women
Won-Beom Park, Hyun-Seok Cho, Man-Gyoon Lee
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2019; 30(2): 236. CrossRef - The effect of a 12-week combinational exercise program on CD4 count and mental health among HIV infected women: A randomized control trial
Mostafa Dianatinasab, Mohammad Fararouei, Valiollah Padehban, Aria Dianatinasab, Yousef Alimohamadi, Shohreh Beheshti, Zeinab AminiLari, Mahmood AminiLari
Journal of Exercise Science & Fitness.2018; 16(1): 21. CrossRef - Green tea consumption reduces apelin and orexin-A in overweight and obese women with different training modalities
Rahman Soori, Azadeh Safei, Parisa Pournemati, Amine Ghram
Sport Sciences for Health.2018; 14(2): 421. CrossRef - Lifestyle interventions for improving health and health behaviours in women with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of the literature 2011–2017
Charrlotte Seib, Joy Parkinson, Nicole McDonald, Haruka Fujihira, Stephanie Zietek, Debra Anderson
Maturitas.2018; 111: 1. CrossRef - Association of Self-Care Behaviors and Quality of Life among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Chaldoran County, Iran
Towhid Babazadeh, Mostafa Dianatinasab, Amin Daemi, Hossein Ali Nikbakht, Fatemeh Moradi, Saber Ghaffari-fam
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 449. CrossRef - Response: The Effect of 12 Weeks Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises on Omentin-1 Levels and Insulin Resistance among Type 2 Diabetic Middle-Aged Women (Diabetes Metab J2017;41:205-12)
Sasan Amanat, Mohammad Fararouei, Mostafa Dianatinasab
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(4): 324. CrossRef - Effects of Resistance Training on Serum Inflammatory Markers and CatSper 1-4 Protein Expression in Testis of OLETF Rats
Min-Ki Lee, Se-Hwan Park, Jin-Hwan Yoon
Exercise Science.2017; 26(3): 204. CrossRef - Letter: The Effect of 12 Weeks Aerobic, Resistance, and Combined Exercises on Omentin-1 Levels and Insulin Resistance among Type 2 Diabetic Middle-Aged Women (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:205-12)
Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(4): 322. CrossRef - Role of Omentin, Vaspin, Cardiotrophin-1, TWEAK and NOV/CCN3 in Obesity and Diabetes Development
Xavier Escoté, Saioa Gómez-Zorita, Miguel López-Yoldi, Iñaki Milton-Laskibar, Alfredo Fernández-Quintela, J. Martínez, María Moreno-Aliaga, María Portillo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(8): 1770. CrossRef
- Effect of Exercise Training on Some Anti-Inflammatory Adipokines, High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, and Clinical Outcomes in Sedentary Adults With Metabolic Syndrome
- Maximal Fat Oxidation Rate during Exercise in Korean Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Min Hwa Suk, Yeo-Jin Moon, Sung Woo Park, Cheol-Young Park, Yun A Shin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(4):328-334. Published online July 8, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.328
- 4,068 View
- 38 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to determine the appropriate exercise intensity associated with maximum fat oxidation, improvement of body composition, and metabolic status in Korean women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods The study included a T2DM group (12 women) and a control group (12 women). The groups were matched in age and body mass index. The subjects performed a graded exercise test on a cycle ergometer to measure their maximal fat oxidation (Fatmax). We also measured their body composition, metabolic profiles, and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
Results The exercise intensity for Fatmax was significantly lower in the T2DM group (34.19% maximal oxygen uptake [VO2 max]) than the control group (51.80% VO2 max). Additionally, the rate of fat oxidation during exercise (
P <0.05) and mtDNA (P <0.05) were significantly lower in the T2DM group than the control group. The VO2 max level (P <0.001) and the insulin level (P <0.05) were positively correlated with the rate of fat oxidation.Conclusion The results of this study suggest lower exercise intensity that achieves Fatmax is recommended for improving fat oxidation and enhancing fitness levels in Korean women with T2DM. Our data could be useful when considering an exercise regimen to improve health and fitness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Toward Exercise Guidelines for Optimizing Fat Oxidation During Exercise in Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression
Isaac A. Chávez-Guevara, Francisco J. Amaro-Gahete, Arnulfo Ramos-Jiménez, Jean Frederic Brun
Sports Medicine.2023; 53(12): 2399. CrossRef - Cardiorespiratory fitness in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Aline Chagastelles Pinto de Macedo, Camila Wohlgemuth Schaan, Patricia Martins Bock, Mariana Brutto de Pinto, Cintia Ehlers Botton, Daniel Umpierre, Beatriz D. Schaan
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inclusion of sprints during moderate-intensity continuous exercise enhances post-exercise fat oxidation in young males
Bruno Nicanor Mello-Silva, Gabriel Völz Protzen, Fabrício Boscolo Del Vecchio
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2022; 47(2): 165. CrossRef - Resting and exercise metabolic characteristics in obese children with insulin resistance
Cao Youxiang, Zhu Lin, Chen Zekai, Xie Weijun
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Acute Eccentric versus Concentric Running on Exercise-Induced Fat Oxidation and Postexercise Physical Activity in Untrained Men
Shaea Alkahtani, Osama Aljuhani, Nasser Alkhalidi, Naif Almasuod, Omar Hezam, Ibrahim Aljaloud, Haitham Abdel Hamid Dawoud, Ahmed Abdusalam
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Diurnal influences of fasted and non-fasted brisk walking on gastric emptying rate, metabolic responses, and appetite in healthy males
Victoria J. McIver, Lewis R. Mattin, Gethin H. Evans, Adora M.W. Yau
Appetite.2019; 143: 104411. CrossRef - Myokine/Adipokine Response to “Aerobic” Exercise: Is It Just a Matter of Exercise Load?
Zihong He, Ye Tian, Pedro L. Valenzuela, Chuanye Huang, Jiexiu Zhao, Ping Hong, Zilin He, Shuhui Yin, Alejandro Lucia
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise as ‘precision medicine’ for insulin resistance and its progression to type 2 diabetes: a research review
Fred J. DiMenna, Avigdor D. Arad
BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - High-intensity aerobic interval training improves aerobic fitness and HbA1c among persons diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
Eva Maria Støa, Sondre Meling, Lill-Katrin Nyhus, Glenn Strømstad, Karl Magnus Mangerud, Jan Helgerud, Solfrid Bratland-Sanda, Øyvind Støren
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2017; 117(3): 455. CrossRef
- Toward Exercise Guidelines for Optimizing Fat Oxidation During Exercise in Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





