
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse > Previous issues
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor for Renal Function Preservation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
- Tae Jung Oh, Ju-Young Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Hyun Ko, Hyun Jung Kim, Taehee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of the Cooperative Studies, Korean Society of Nephrology
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):489-497. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0172
- 7,803 View
- 167 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
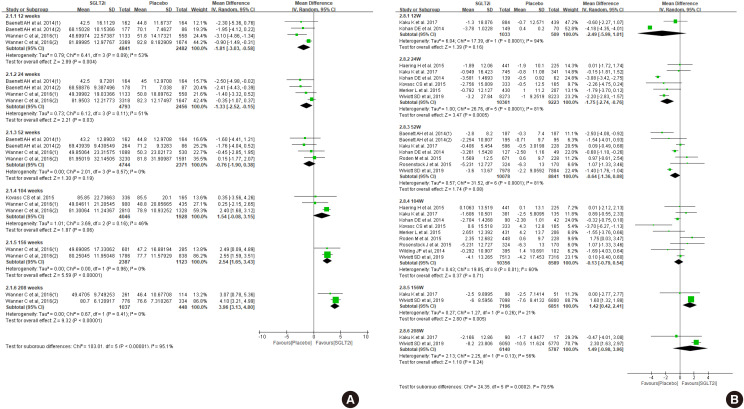
ePub Diabetes is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease. Therefore, prevention of renal dysfunction is an important treatment goal in the management of diabetes. The data of landmark cardiovascular outcome trials of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor showed profound reno-protective effects. The Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Society of Nephrology reviewed clinical trials and performed meta-analysis to assess the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on the preservation of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). We limited the data of SGLT2 inhibitors which can be prescribed in Korea. Both eGFR value and its change from the baseline were significantly more preserved in the SGLT2 inhibitor treatment group compared to the control group after 156 weeks. However, some known adverse events were increased in SGLT2 inhibitor treatment, such as genital infection, diabetic ketoacidosis, and volume depletion. We recommend the long-term use SGLT2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) for attenuation of renal function decline. However, we cannot generalize our recommendation due to lack of long-term clinical trials testing reno-protective effects of every SGLT2 inhibitor in a broad range of patients with T2DM. This recommendation can be revised and updated after publication of several large-scale renal outcome trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 701. CrossRef
- Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
- Basic Research
- Role of CRTC2 in Metabolic Homeostasis: Key Regulator of Whole-Body Energy Metabolism?
- Hye-Sook Han, Yongmin Kwon, Seung-Hoi Koo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):498-508. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0200
- 6,935 View
- 163 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
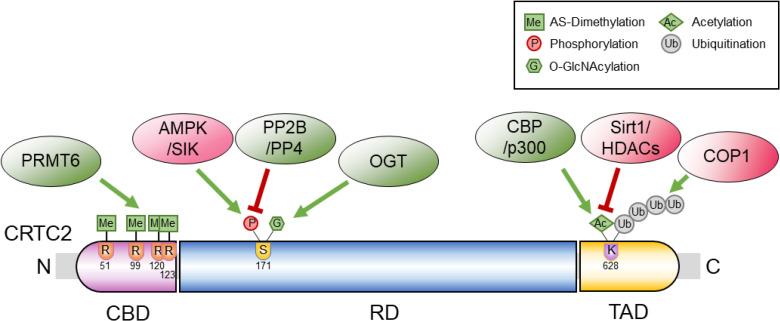
ePub Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling is critical for regulating metabolic homeostasis in mammals. In particular, transcriptional regulation by cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and its coactivator, CREB-regulated transcription coactivator (CRTC), is essential for controlling the expression of critical enzymes in the metabolic process, leading to more chronic changes in metabolic flux. Among the CRTC isoforms, CRTC2 is predominantly expressed in peripheral tissues and has been shown to be associated with various metabolic pathways in tissue-specific manners. While initial reports showed the physiological role of CRTC2 in regulating gluconeogenesis in the liver, recent studies have further delineated the role of this transcriptional coactivator in the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism in various tissues, including the liver, pancreatic islets, endocrine tissues of the small intestines, and adipose tissues. In this review, we discuss recent studies that have utilized knockout mouse models to delineate the role of CRTC2 in the regulation of metabolic homeostasis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integration of genomic and transcriptomic data of inbred mouse models for polygenic obesity and leanness revealed “obese” and “lean” candidate alleles in polyadenylation signals
Martin Šimon, Špela Mikec, Nicholas M. Morton, Santosh S. Atanur, Simon Horvat, Tanja Kunej
Gene Reports.2024; 35: 101903. CrossRef - Mylabris phalerata induces the apoptosis and cell cycle delay in HCC, and potentiates the effect of sorafenib based on the molecular and network pharmacology approach
Young Woo Kim, Seon Been Bak, Su Youn Baek, Il Kon Kim, Won-Yung Lee, Un-Jung Yun, Kwang-Il Park
Molecular & Cellular Toxicology.2023; 19(4): 731. CrossRef - Emerging Role of SMILE in Liver Metabolism
Nanthini Sadasivam, Kamalakannan Radhakrishnan, Hueng-Sik Choi, Don-Kyu Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2907. CrossRef - PIMT regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice
Bandish Kapadia, Soma Behera, Sireesh T. Kumar, Tapan Shah, Rebecca Kristina Edwin, Phanithi Prakash Babu, Partha Chakrabarti, Kishore V.L. Parsa, Parimal Misra
iScience.2023; 26(3): 106120. CrossRef - Biological functions of CRTC2 and its role in metabolism-related diseases
Hong-Yu Zheng, Yan-Xia Wang, Kun Zhou, Hai-Lin Xie, Zhong Ren, Hui-Ting Liu, Yang-Shao Ou, Zhi-Xiang Zhou, Zhi-Sheng Jiang
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling.2023; 17(3): 495. CrossRef - An insulin-regulated arrestin domain protein controls hepatic glucagon action
Sezin Dagdeviren, Megan F. Hoang, Mohsen Sarikhani, Vanessa Meier, Jake C. Benoit, Marinna C. Okawa, Veronika Y. Melnik, Elisabeth M. Ricci-Blair, Natalie Foot, Randall H. Friedline, Xiaodi Hu, Lauren A. Tauer, Arvind Srinivasan, Maxim B. Prigozhin, Sudha
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2023; 299(8): 105045. CrossRef - The Pleiotropic Face of CREB Family Transcription Factors
Md. Arifur Rahman Chowdhury, Jungeun An, Sangyun Jeong
Molecules and Cells.2023; 46(7): 399. CrossRef - It is a branched road to adipose tissue aging
N. Touitou, B. Lerrer, H. Y. Cohen
Nature Aging.2023; 3(8): 911. CrossRef - Impaired BCAA catabolism in adipose tissues promotes age-associated metabolic derangement
Hye-Sook Han, Eunyong Ahn, Eun Seo Park, Tom Huh, Seri Choi, Yongmin Kwon, Byeong Hun Choi, Jueun Lee, Yoon Ha Choi, Yujin L. Jeong, Gwang Bin Lee, Minji Kim, Je Kyung Seong, Hyun Mu Shin, Hang-Rae Kim, Myeong Hee Moon, Jong Kyoung Kim, Geum-Sook Hwang, S
Nature Aging.2023; 3(8): 982. CrossRef - Exploring the diagnostic value, prognostic value, and biological functions of NPC gene family members in hepatocellular carcinoma based on a multi-omics analysis
Keheng Chen, Xin Zhang, Huixin Peng, Fengdie Huang, Guangyu Sun, Qijiang Xu, Lusheng Liao, Zhiyong Xing, Yanping Zhong, Zhichao Fang, Meihua Liao, Shihua Luo, Wencheng Chen, Mingyou Dong
Functional & Integrative Genomics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA regulation of AMPK in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Hao Sun, Jongsook Kim Kemper
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2023; 55(9): 1974. CrossRef - Serine active site containing protein 1 depletion alters lipid metabolism and protects against high fat diet-induced obesity in mice
Miaomiao Du, Xueyun Li, Fangyi Xiao, Yinxu Fu, Yu Shi, Sihan Guo, Lifang Chen, Lu Shen, Lan Wang, Huang Cheng, Hao Li, Anran Xie, Yaping Zhou, Kaiqiang Yang, Hezhi Fang, Jianxin Lyu, Qiongya Zhao
Metabolism.2022; 134: 155244. CrossRef - cAMP Signaling in Cancer: A PKA-CREB and EPAC-Centric Approach
Muhammad Bilal Ahmed, Abdullah A. A. Alghamdi, Salman Ul Islam, Joon-Seok Lee, Young-Sup Lee
Cells.2022; 11(13): 2020. CrossRef - Hepatic Sam68 Regulates Systemic Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Sensitivity
Aijun Qiao, Wenxia Ma, Ying Jiang, Chaoshan Han, Baolong Yan, Junlan Zhou, Gangjian Qin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11469. CrossRef - The Role of Small Heterodimer Partner-Interacting Leucine Zipper
(SMILE) as a Transcriptional Corepressor in Hepatic Glucose and Lipid
Metabolism
Woo-Ram Park, Byungyoon Choi, Nanthini Sadasivam, Don-Kyu Kim
Trends in Agriculture & Life Sciences.2022; 60: 7. CrossRef - AMPK Localization: A Key to Differential Energy Regulation
Qonita Afinanisa, Min Kyung Cho, Hyun-A Seong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(20): 10921. CrossRef
- Integration of genomic and transcriptomic data of inbred mouse models for polygenic obesity and leanness revealed “obese” and “lean” candidate alleles in polyadenylation signals
- Basic Research
- Consequences of Obesity on the Sense of Taste: Taste Buds as Treatment Targets?
- Kerstin Rohde, Imke Schamarek, Matthias Blüher
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):509-528. Published online May 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0058

- 11,388 View
- 284 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Premature obesity-related mortality is caused by cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases, type 2 diabetes mellitus, physical disabilities, osteoarthritis, and certain types of cancer. Obesity is caused by a positive energy balance due to hyper-caloric nutrition, low physical activity, and energy expenditure. Overeating is partially driven by impaired homeostatic feedback of the peripheral energy status in obesity. However, food with its different qualities is a key driver for the reward driven hedonic feeding with tremendous consequences on calorie consumption. In addition to visual and olfactory cues, taste buds of the oral cavity process the earliest signals which affect the regulation of food intake, appetite and satiety. Therefore, taste buds may play a crucial role how food related signals are transmitted to the brain, particularly in priming the body for digestion during the cephalic phase. Indeed, obesity development is associated with a significant reduction in taste buds. Impaired taste bud sensitivity may play a causal role in the pathophysiology of obesity in children and adolescents. In addition, genetic variation in taste receptors has been linked to body weight regulation. This review discusses the importance of taste buds as contributing factors in the development of obesity and how obesity may affect the sense of taste, alterations in food preferences and eating behavior.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chronic social defeat stress broadly inhibits gene expression in the peripheral taste system and alters taste responses in mice
Katelyn Tu, Mary Zhou, Jidong J. Tan, Loza Markos, Cameron Cloud, Minliang Zhou, Naoki Hayashi, Nancy E. Rawson, Robert F. Margolskee, Hong Wang
Physiology & Behavior.2024; 275: 114446. CrossRef - Commentary: Is obesity associated with taste alterations? a systematic review
Marco Alessandrini, Alessandra Vezzoli, Simona Mrakic-Sposta, Sandro Malacrida, Alessandro Micarelli
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Obese Taste Bud study: Objectives and study design
Alexander Kersten, Andrea Lorenz, Cita Nottmeier, Michael Schmidt, Anuschka Roesner, Florian Christoph Richter, Kristin Röhrborn, A. Veronica Witte, Sebastian Hahnel, Till Koehne, Matthias Blüher, Michael Stumvoll, Kerstin Rohde‐Zimmermann, Imke Schamarek
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Testing reward processing models of obesity using in-the-moment assessments of subjective enjoyment of food and non-food activities
Christina Chwyl, Erica M. LaFata, Sophie R. Abber, Adrienne S. Juarascio, Evan M. Forman
Eating Behaviors.2023; 48: 101698. CrossRef - Taste Function in Adult Humans from Lean Condition to Stage II Obesity: Interactions with Biochemical Regulators, Dietary Habits, and Clinical Aspects
Alessandro Micarelli, Alessandra Vezzoli, Sandro Malacrida, Beatrice Micarelli, Ilaria Misici, Valentina Carbini, Ilaria Iennaco, Sara Caputo, Simona Mrakic-Sposta, Marco Alessandrini
Nutrients.2023; 15(5): 1114. CrossRef - Exposure to Obesogenic Environments during Perinatal Development Modulates Offspring Energy Balance Pathways in Adipose Tissue and Liver of Rodent Models
Diana Sousa, Mariana Rocha, Andreia Amaro, Marcos Divino Ferreira-Junior, Keilah Valéria Naves Cavalcante, Tamaeh Monteiro-Alfredo, Cátia Barra, Daniela Rosendo-Silva, Lucas Paulo Jacinto Saavedra, José Magalhães, Armando Caseiro, Paulo Cezar de Freitas M
Nutrients.2023; 15(5): 1281. CrossRef - Exercise modifies fatty acid perception and metabolism
Deepankumar Shanmugamprema, Karthi Muthuswamy, Vinithra Ponnusamy, Gowtham Subramanian, Keerthana Vasanthakumar, Vasanth Krishnan, Selvakumar Subramaniam
Acta Physiologica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of the oral microbiome in obesity and metabolic disease: potential systemic implications and effects on taste perception
Imke Schamarek, Lars Anders, Rima M. Chakaroun, Peter Kovacs, Kerstin Rohde-Zimmermann
Nutrition Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smell, taste and food habits changes along body mass index increase: an observational study
Alessandro Micarelli, Sandro Malacrida, Alessandra Vezzoli, Beatrice Micarelli, Ilaria Misici, Valentina Carbini, Sara Caputo, Simona Mrakic-Sposta, Marco Alessandrini
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology.2023; 280(12): 5595. CrossRef - Sweet-inhibiting effects of gurmarin on intake during repeated acute and long-term sugar exposure: A behavioural analysis using an animal model
Raquel Rayo-Morales, Antonio Segura-Carretero, Nicolas Poirier, Loïc Briand, David Garcia-Burgos
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 108: 105743. CrossRef - Suppression of sweet taste-related responses by plant-derived bioactive compounds and eating. Part I: A systematic review in humans
Raquel Rayo-Morales, Antonio Segura-Carretero, Isabel Borras-Linares, David Garcia-Burgos
Heliyon.2023; 9(10): e19733. CrossRef - The oral microbial odyssey influencing chronic metabolic disease
Upasana Gupta, Priyankar Dey
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Taste of Fat and Obesity: Different Hypotheses and Our Point of View
Laurent Brondel, Didier Quilliot, Thomas Mouillot, Naim Akhtar Khan, Philip Bastable, Vincent Boggio, Corinne Leloup, Luc Pénicaud
Nutrients.2022; 14(3): 555. CrossRef - Effect of Obesity Surgery on Taste
Alhanouf S. Al-Alsheikh, Shahd Alabdulkader, Brett Johnson, Anthony P. Goldstone, Alexander Dimitri Miras
Nutrients.2022; 14(4): 866. CrossRef - Oral motor function in obesity
Mariana Cristina Zanin Castro, Carla Manfredi dos Santos, Raquel Eduardo Lucas, Claudia Maria de Felício, Roberto Oliveira Dantas
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2022; 49(5): 529. CrossRef - The Effect of Artificial Sweeteners Use on Sweet Taste Perception and Weight Loss Efficacy: A Review
Klara Wilk, Wiktoria Korytek, Marta Pelczyńska, Małgorzata Moszak, Paweł Bogdański
Nutrients.2022; 14(6): 1261. CrossRef - Effects of visual and aromatic stimulations on the perception of five fundamental tastes
Mayu Itoh, Aya Kitagawa, Harumi Ouchi, Mana Yamaguchi, Ran Watanabe, Hideyuki Sone, Shin Kamiyama
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry.2022; 86(5): 655. CrossRef - Taste and smell function in long-term survivors after childhood medulloblastoma/CNS-PNET
Kristine Eidal Tanem, Einar Stensvold, Petter Wilberg, Anne B. Skaare, Preet Bano Singh, Petter Brandal, Bente Brokstad Herlofson
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(7): 6155. CrossRef - Changes in Food Choice, Taste, Desire, and Enjoyment 1 Year after Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Prospective Study
Luigi Schiavo, Silvana Mirella Aliberti, Pietro Calabrese, Anna Maria Senatore, Lucia Severino, Gerardo Sarno, Antonio Iannelli, Vincenzo Pilone
Nutrients.2022; 14(10): 2060. CrossRef - Characterizing Adolescents' Dietary Intake by Taste: Results From the UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey
Areej Bawajeeh, Michael A. Zulyniak, Charlotte E. L. Evans, Janet E. Cade
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sleeve Gastrectomy-Induced Body Mass Index Reduction Increases the Intensity of Taste Perception’s and Reduces Bitter-Induced Pleasantness in Severe Obesity
Sara Rurgo, Elena Cantone, Marcella Pesce, Eleonora Efficie, Mario Musella, Barbara Polese, Barbara De Conno, Marta Pagliaro, Luisa Seguella, Bruna Guida, Giuseppe Esposito, Giovanni Sarnelli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(14): 3957. CrossRef - Genetic variation in sweet taste receptors and a mechanistic perspective on sweet and fat taste sensation in the context of obesity
Vinithra Ponnusamy, Gowtham Subramanian, Karthi Muthuswamy, Deepankumar Shanmugamprema, Vasanth Krishnan, Thirunavukkarasu Velusamy, Selvakumar Subramaniam
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Applying a systems perspective to understand the mechanisms of the European School Fruit and Vegetable Scheme
Mahshid Zolfaghari, Biljana Meshkovska, Anna Banik, Carlijn B M Kamphuis, Birgit Kopainsky, Aleksandra Luszczynska, Celine Murrin, Nanna Lien
European Journal of Public Health.2022; 32(Supplement): iv107. CrossRef - Self-Reported Sensory Decline in Older Adults Is Longitudinally Associated With Both Modality-General and Modality-Specific Factors
Alan O’ Dowd, Rebecca J Hirst, Annalisa Setti, Rose Anne Kenny, Fiona N Newell, Nancy W Glynn
Innovation in Aging.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The sweet taste receptor, glucose transporters, and the ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channel: sugar sensing for the regulation of energy homeostasis
Ryusuke Yoshida, Keiko Yasumatsu, Yuzo Ninomiya
Current Opinion in Physiology.2021; 20: 57. CrossRef - Gustatory Function Can Improve after Multimodal Lifestyle Intervention: A Longitudinal Observational Study in Pediatric Patients with Obesity
Laura Kalveram, Jacob Gohlisch, Jana Brauchmann, Johanna Overberg, Peter Kühnen, Susanna Wiegand
Childhood Obesity.2021; 17(2): 136. CrossRef - Single nucleotide polymorphism in CD36: Correlation to peptide YY levels in obese and non-obese adults
Muthuswamy Karthi, Shanmugamprema Deepankumar, Ponnusamy Vinithra, Subramanian Gowtham, Krishnan Vasanth, Palanivelu Praveen Raj, Rajasekaran Senthilkumar, Subramaniam Selvakumar
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(5): 2707. CrossRef - Lezzet Algısının Oluşmasında Çevresel ve Genetik Faktörlerin Etkileri
Mücahit MUSLU, Gülden Fatma GÖKÇAY
Batı Karadeniz Tıp Dergisi.2021; 5(1): 7. CrossRef - Food Preferences and Obesity
Sara Spinelli, Erminio Monteleone
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 209. CrossRef - Western Diet Induced Remodelling of the Tongue Proteome
Mriga Dutt, Yaan-Kit Ng, Jeffrey Molendijk, Hamzeh Karimkhanloo, Luoping Liao, Ronnie Blazev, Magdalene K. Montgomery, Matthew J. Watt, Benjamin L. Parker
Proteomes.2021; 9(2): 22. CrossRef - Obesity-induced taste dysfunction, and its implications for dietary intake
Fiona Harnischfeger, Robin Dando
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(8): 1644. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Understanding Peripheral Taste Decoding I: 2010 to 2020
Jea Hwa Jang, Obin Kwon, Seok Jun Moon, Yong Taek Jeong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 469. CrossRef - Smash of diabetes mellitus on smile
Farhana Akter, Mainul Haque
Advances in Human Biology.2021; 11(3): 273. CrossRef - Perception des acides gras et potentiels évoqués gustatifs : application dans l’obésité
Thomas Mouillot, Laurent Brondel, Agnès Jacquin-Piques
Cahiers de Nutrition et de Diététique.2021; 56(5): 280. CrossRef - Trastornos del gusto como indicador de enfermedad sistémica
Karla Ivohnne Pedraza Maquera, Caroll Johana Uberlinda Lévano Villanueva
Revista Odontológica Basadrina.2021; 5(2): 52. CrossRef
- Chronic social defeat stress broadly inhibits gene expression in the peripheral taste system and alters taste responses in mice
- Obesity Degree and Glycemic Status: Factors That Should Be Considered in Heart Failure
- Hye Soon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):529-531. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0166
- 4,490 View
- 125 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
- Drug/Regimen
- Switching to Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart from Basal Insulin Improves Postprandial Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyu Yong Cho, Akinobu Nakamura, Chiho Oba-Yamamoto, Kazuhisa Tsuchida, Shingo Yanagiya, Naoki Manda, Yoshio Kurihara, Shin Aoki, Tatsuya Atsumi, Hideaki Miyoshi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):532-541. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0093
- 5,552 View
- 153 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background To explore the efficacy and safety of switching from once-daily basal insulin therapy to once-daily pre-meal injection insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) with respect to the glycemic control of participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods In this multicenter, open-label, prospective, randomized, parallel-group comparison trial, participants on basal insulin therapy were switched to IDegAsp (IDegAsp group;
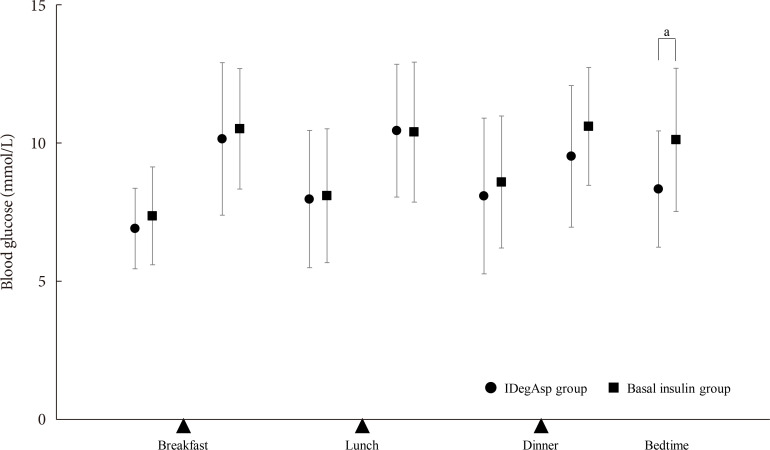
n =30) or continued basal insulin (Basal group;n =29). The primary endpoint was the superiority of IDegAsp in causing changes in the daily blood glucose profile, especially post-prandial blood glucose concentration after 12 weeks.Results Blood glucose concentrations after dinner and before bedtime were lower in the IDegAsp group, and the improvement in blood glucose before bedtime was significantly greater in the IDegAsp group than in the Basal group at 12 weeks (−1.7±3.0 mmol/L vs. 0.3±2.1 mmol/L,
P <0.05). Intriguingly, glycemic control after breakfast was not improved by IDegAsp injection before breakfast, in contrast to the favorable effect of injection before dinner on blood glucose after dinner. Glycosylated hemoglobin significantly decreased only in the IDegAsp group (58 to 55 mmol/mol,P <0.05). Changes in daily insulin dose, body mass, and recorded adverse effects, including hypoglycemia, were comparable between groups.Conclusion IDegAsp was more effective than basal insulin at reducing blood glucose after dinner and before bedtime, but did not increase the incidence of hypoglycemia. Switching from basal insulin to IDegAsp does not increase the burden on the patient and positively impacts glycemic control in patients with T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glycaemic outcomes in hospital with IDegAsp versus BIAsp30 premixed insulins
Joshua R. Walt, Julie Loughran, Spiros Fourlanos, Rahul D. Barmanray, Jasmine Zhu, Suresh Varadarajan, Mervyn Kyi
Internal Medicine Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low fasting glucose‐to‐estimated average glucose ratio was associated with superior response to insulin degludec/aspart compared with basal insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes
Han Na Jang, Ye Seul Yang, Tae Jung Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Seong Ok Lee, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Hye Seung Jung
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(1): 85. CrossRef - Comparing time to intensification between insulin degludec/insulin aspart and insulin glargine: A single-center experience from India
Rajiv Kovil
Journal of Diabetology.2022; 13(2): 171. CrossRef - Use of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus: Expert Panel Recommendations on Appropriate Practice Patterns
Tevfik Demir, Serap Turan, Kursad Unluhizarci, Oya Topaloglu, Tufan Tukek, Dilek Gogas Yavuz
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacoeconomic comparison of the second generation insulin analogs and insulins on their base
I. N. Dyakov, S. K. Zyryanov
Kachestvennaya Klinicheskaya Praktika = Good Clinical Practice.2021; 20(1): 4. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart Compared with a Conventional Premixed Insulin or Basal Insulin: A Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Hye-Soo Chung, Yoon-Jung Kim, Jae-Myung Yu, Woo-Ju Jeong, Jiwon Park, Chang-Myung Oh
Metabolites.2021; 11(9): 639. CrossRef - Insulin therapy in diabetic kidney disease
Yan Liu, Chanyue Zhao, Xiaofen Xiong, Ming Yang, Lin Sun
Diabetic Nephropathy.2021; 1(2): 67. CrossRef - Indirect comparison of efficacy and safety of insulin glargine/lixisenatide and insulin degludec/insulin aspart in type 2 diabetes patients not controlled on basal insulin
Anwar Ali Jammah
Primary Care Diabetes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Glycaemic outcomes in hospital with IDegAsp versus BIAsp30 premixed insulins
- Drug/Regimen
- γ-Linolenic Acid versus α-Lipoic Acid for Treating Painful Diabetic Neuropathy in Adults: A 12-Week, Double-Placebo, Randomized, Noninferiority Trial
- Jong Chul Won, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Seong-Su Moon, Sung Wan Chun, Chong Hwa Kim, Ie Byung Park, In Joo Kim, Jihyun Lee, Bong Yun Cha, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):542-554. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0099
- 7,954 View
- 245 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background This study was a multicenter, parallel-group, double-blind, double-dummy, randomized, noninferiority trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of γ-linolenic acid (GLA) relative to α-lipoic acid (ALA) over a 12-week treatment period in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
Methods This study included 100 T2DM patients between 20 and 75 years of age who had painful DPN and received either GLA (320 mg/day) and placebo or ALA (600 mg/day) and placebo for 12 weeks. The primary outcome measures were mean changes in pain intensities as measured by the visual analogue scale (VAS) and the total symptom scores (TSS).
Results Of the 100 subjects who initially participated in the study, 73 completed the 12-week treatment period. Per-protocol analyses revealed significant decreases in the mean VAS and TSS scores compared to baseline in both groups, but there were no significant differences between the groups. The treatment difference for the VAS (95% confidence interval [CI]) between the two groups was −0.65 (−1.526 to 0.213) and the upper bound of the 95% CI did not exceed the predefined noninferiority margin (δ1=0.51). For the TSS, the treatment difference was −0.05 (−1.211 to 1.101) but the upper bound of the 95% CI crossed the noninferiority margin (δ2=0.054). There were no serious adverse events associated with the treatments.
Conclusion GLA treatment in patients with painful DPN was noninferior to ALA in terms of reducing pain intensity measured by the VAS over 12 weeks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cell metabolism pathways involved in the pathophysiological changes of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Yaowei Lv, Xiangyun Yao, Xiao Li, Yuanming Ouyang, Cunyi Fan, Yun Qian
Neural Regeneration Research.2024; 19(3): 598. CrossRef - Diyabet Tedavisinde Antioksidan Etki: Alfa Lipoik Asit
Umut DALMIŞ, Emine Merve EKİCİ
Avrasya Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2024; 7(1): 68. CrossRef - Ranking Alpha Lipoic Acid and Gamma Linolenic Acid in Terms of Efficacy and Safety in the Management of Adults With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Mario B. Prado, Karen Joy B. Adiao
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive comparison of a new technology with traditional methods for extracting Ougan (Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima) seed oils: Physicochemical properties, fatty acids, functional components, and antioxidant activities
Huaxia Yang, Yudan Lin, Xiaoxu Zhu, Haishuo Mu, Yi Li, Shuangyang Chen, Jia Li, Xuedan Cao
LWT.2024; 197: 115857. CrossRef - Genetic and Transcriptomic Background of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidative Therapies in Late Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Gašper Tonin, Vita Dolžan, Jasna Klen
Antioxidants.2024; 13(3): 277. CrossRef - Alpha-lipoic acid activates AMPK to protect against oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Tianya Zhang, Dong Zhang, Zhihong Zhang, Jiaxin Tian, Jingwen An, Wang Zhang, Ying Ben
Hormones.2023; 22(1): 95. CrossRef - Pathogenetic treatments for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Dan Ziegler
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 206: 110764. CrossRef - Omega-3 Nutrition Therapy for the Treatment of Diabetic Sensorimotor
Polyneuropathy
Deepak Menon, Evan J. H. Lewis, Bruce A. Perkins, Vera Bril
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in the Treatment of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Systematic Review
Saleh A Abubaker, Abdulaziz M Alonazy, Albasseet Abdulrahman
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into the possible mechanism(s) involved in the antinociceptive and antineuropathic activity of Descurainia sophia L. Webb ex Prantl essential oil
Donya Ziafatdoost Abed, Sajjad Jabbari, Zainul Amiruddin Zakaria, Saeed Mohammadi
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 298: 115638. CrossRef - A novel approach to alpha-lipoic acid therapy in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Alicja Sementina, Mateusz Cierzniakowski, Julia Rogalska, Izabela Piechowiak, Marek Spichalski, Aleksandra Araszkiewicz
Journal of Medical Science.2022; : e714. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Diabetic Neuropathy: a Critical, Narrative Review of Published Data from 2019
Ameet S. Nagpal, Jennifer Leet, Kaitlyn Egan, Rudy Garza
Current Pain and Headache Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic Potential of Ursolic Acid in Cancer and Diabetic Neuropathy Diseases
Manzar Alam, Sabeeha Ali, Sarfraz Ahmed, Abdelbaset Mohamed Elasbali, Mohd Adnan, Asimul Islam, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(22): 12162. CrossRef - Diagnosis and treatment of the early stages of diabetic polyneuropathy
V. N. Khramilin, A. N. Zavyalov, I. Yu. Demidova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2020; (7): 56. CrossRef
- Cell metabolism pathways involved in the pathophysiological changes of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Complications
- Differences in Clinical Outcomes between Patients with and without Hypoglycemia during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study Using Real-World Evidence
- Jeongmin Lee, Tong Min Kim, Hyunah Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):555-565. Published online May 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0064
- 6,497 View
- 101 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Some patients admitted to hospitals for glycemic control experience hypoglycemia despite regular meals and despite adhering to standard blood glucose control protocols. Different factors can have a negative impact on blood glucose control and prognosis after discharge. This study investigated risk factors for hypoglycemia and its effects on glycemic control during the hospitalization of patients in the general ward.
Methods This retrospective study included patients who were admitted between 2009 and 2018. Patients were provided regular meals at fixed times according to ideal body weights during hospitalization. We categorized the patients into two groups: those with and those without hypoglycemia during hospitalization.
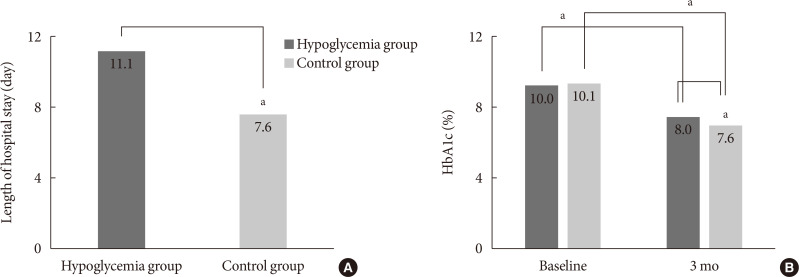
Results Of the 3,031 patients, 379 experienced at least one episode of hypoglycemia during hospitalization (HYPO group). Hypoglycemia occurred more frequently particularly in cases of premixed insulin therapy. Compared with the control group, the HYPO group was older (61.0±16.8 years vs. 59.1±16.5 years,
P =0.035), with more females (60.4% vs. 49.6%,P <0.001), lower body mass index (BMI) (23.5±4.2 kg/m2 vs. 25.1±4.4 kg/m2,P <0.001), and higher prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (6.1% vs. 2.6%,P <0.001), They had longer hospital stay (11.1±13.5 days vs. 7.6±4.6 days,P <0.001). After discharge the HYPO group had lower glycosylated hemoglobin reduction rate (−2.0%±0.2% vs. −2.5%±0.1%,P =0.003) and tended to have more frequent cases of cardiovascular disease.Conclusion Hypoglycemia occurred more frequently in older female patients with lower BMI and was associated with longer hospital stay and poorer glycemic control after discharge. Therefore, clinicians must carefully ensure that patients do not experience hypoglycemia during hospitalization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute kidney injury: a strong risk factor for hypoglycaemia in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes
Ana Carreira, Pedro Castro, Filipe Mira, Miguel Melo, Pedro Ribeiro, Lèlita Santos
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(9): 1179. CrossRef - Adherence to healthy lifestyle behaviors as a preventable risk factor for severe hypoglycemia in people with type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Yong‐Moon Park, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(9): 1533. CrossRef - Predicting hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients with diabetes: A derivation and validation study
Michal Elbaz, Jeries Nashashibi, Shiri Kushnir, Leonard Leibovici
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108611. CrossRef - Hospital care: improving outcomes in type 1 diabetes
Schafer Boeder, Kristen Kulasa
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2021; 28(1): 14. CrossRef - Data Pseudonymization in a Range That Does Not Affect Data Quality: Correlation with the Degree of Participation of Clinicians
Soo-Yong Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: Differences in Clinical Outcomes between Patients with and without Hypoglycemia during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study Using Real-World Evidence (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:555-65)
Sung-Woo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 775. CrossRef - Response: Differences in Clinical Outcomes between Patients with and without Hypoglycemia during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study Using Real-World Evidence (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:555-65)
Jeongmin Lee, Hun-Sung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 779. CrossRef - Hypoglycaemia and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Patients with Diabetes
Niki Katsiki, Kalliopi Kotsa, Anca P. Stoian, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2020; 26(43): 5637. CrossRef
- Acute kidney injury: a strong risk factor for hypoglycaemia in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes
- Complications
- Therapeutic Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 on Diabetic Nephropathy and the Possible Mechanism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Mice
- Wenya Weng, Tingwen Ge, Yi Wang, Lulu He, Tinghao Liu, Wanning Wang, Zongyu Zheng, Lechu Yu, Chi Zhang, Xuemian Lu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):566-580. Published online May 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0089

- 5,902 View
- 102 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been only reported to prevent type 1 diabetic nephropathy (DN) in the streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) mouse model. However, the FVB (Cg)-Tg (Cryaa-Tag, Ins2-CALM1) 26OVE/PneJ (OVE26) transgenic mouse is a widely recommended mouse model to recapture the most important features of T1DM nephropathy that often occurs in diabetic patients. In addition, most previous studies focused on exploring the preventive effect of FGF21 on the development of DN. However, in clinic, development of therapeutic strategy has much more realistic value compared with preventive strategy since the onset time of DN is difficult to be accurately predicted. Therefore, in the present study OVE26 mice were used to investigate the potential therapeutic effects of FGF21 on DN.
Methods Four-month-old female OVE26 mice were intraperitoneally treated with recombinant FGF21 at a dose of 100 µg/kg/day for 3 months. The diabetic and non-diabetic control mice were treated with phosphate-buffered saline at the same volume. Renal functions, pathological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, oxidative stress and fibrosis were examined in mice of all groups.
Results The results showed that severe renal dysfunction, morphological changes, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrosis were observed in OVE26 mice. However, all the renal abnormalities above in OVE26 mice were significantly attenuated by 3-month FGF21 treatment associated with improvement of renal adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) expression.
Conclusion Therefore, this study demonstrated that FGF21 might exert therapeutic effects on DN through AMPK-SIRT1 pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Wenhui Zhong, Yuheng Jiang, Huizhen Wang, Xiang Luo, Tao Zeng, Huimi Huang, Ling Xiao, Nan Jia, Aiqing Li
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119620. CrossRef - Urinary Excretion of Biomolecules Related to Cell Cycle, Proliferation, and Autophagy in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Anton I. Korbut, Vyacheslav V. Romanov, Vadim V. Klimontov
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 487. CrossRef - New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors
David M. Ornitz, Nobuyuki Itoh
WIREs Mechanisms of Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SIRT1–SIRT7 in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
Wenxiu Qi, Cheng Hu, Daqing Zhao, Xiangyan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Fibrotic Diseases
Min-Qi Jia, Cha-Xiang Guan, Jia-Hao Tao, Yong Zhou, Liang-Jun Yan
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with biopsy-confirmed diabetic nephropathy: a propensity-matched cohort study
Yutong Zou, Lijun Zhao, Junlin Zhang, Yiting Wang, Yucheng Wu, Honghong Ren, Tingli Wang, Yuancheng Zhao, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 60(2): 225. CrossRef - FGF21 and Chronic Kidney Disease
João Victor Salgado, Miguel Angelo Goes, Natalino Salgado Filho
Metabolism.2021; 118: 154738. CrossRef - The Multiple Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factor in Diabetic Nephropathy
Junyu Deng, Ye Liu, Yiqiu Liu, Wei Li, Xuqiang Nie
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 5273. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect and mechanism of combined use of FGF21 and insulin on diabetic nephropathy
Fanrui Meng, Yukai Cao, Mir Hassan Khoso, Kai Kang, Guiping Ren, Wei Xiao, Deshan Li
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2021; 713: 109063. CrossRef - FGF19 and FGF21 for the Treatment of NASH—Two Sides of the Same Coin? Differential and Overlapping Effects of FGF19 and FGF21 From Mice to Human
Emma Henriksson, Birgitte Andersen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - FGF21: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Related Metabolic Diseases
Erik J. Tillman, Tim Rolph
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fibroblast growth factor 21 alleviates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Basic Research
-
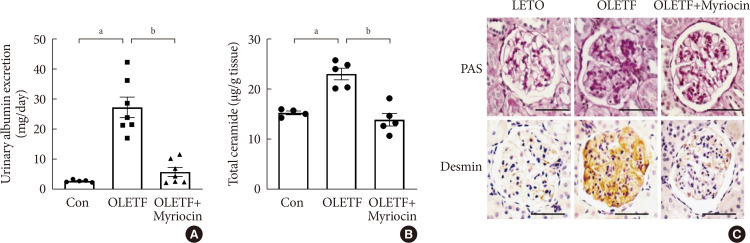
- Inhibition of Ceramide Accumulation in Podocytes by Myriocin Prevents Diabetic Nephropathy
- Chang-Yun Woo, Ji Yeon Baek, Ah-Ram Kim, Chung Hwan Hong, Ji Eun Yoon, Hyoun Sik Kim, Hyun Ju Yoo, Tae-Sik Park, Ranjan Kc, Ki-Up Lee, Eun Hee Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):581-591. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0063
- 6,158 View
- 164 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Ceramides are associated with metabolic complications including diabetic nephropathy in patients with diabetes. Recent studies have reported that podocytes play a pivotal role in the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Also, mitochondrial dysfunction is known to be an early event in podocyte injury. Thus, we tested the hypothesis that ceramide accumulation in podocytes induces mitochondrial damage through reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Methods We used Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. We fed the animals either a control- or a myriocin-containing diet to evaluate the effects of the ceramide. Also, we assessed the effects of ceramide on intracellular ROS generation and on podocyte autophagy in cultured podocytes.
Results OLETF rats and HFD-fed mice showed albuminuria, histologic features of diabetic nephropathy, and podocyte injury, whereas myriocin treatment effectively treated these abnormalities. Cultured podocytes exposed to agents predicted to be risk factors (high glucose, high free fatty acid, and angiotensin II in combination [GFA]) showed an increase in ceramide accumulation and ROS generation in podocyte mitochondria. Pretreatment with myriocin reversed GFA-induced mitochondrial ROS generation and prevented cell death. Myriocin-pretreated cells were protected from GFA-induced disruption of mitochondrial integrity.
Conclusion We showed that mitochondrial ceramide accumulation may result in podocyte damage through ROS production. Therefore, this signaling pathway could become a pharmacological target to abate the development of diabetic kidney disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury
Zilv Luo, Zhaowei Chen, Jijia Hu, Guohua Ding
Metabolism.2024; 150: 155718. CrossRef - Associations of plasma sphingolipids with measures of insulin sensitivity, β-cell function, and incident diabetes in Japanese Americans
Ji Cheol Bae, Pandora L. Wander, Rozenn N. Lemaitre, Amanda M. Fretts, Colleen M. Sitlani, Hai H. Bui, Melissa K. Thomas, Donna Leonetti, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Edward J. Boyko, Kristina M. Utzschneider
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 633. CrossRef - A review of the mechanisms of abnormal ceramide metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Alzheimer’s disease, and their co-morbidities
Yun Pan, Jieying Li, Panjie Lin, Lihua Wan, Yiqian Qu, Lingyong Cao, Lei Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ceramides and mitochondrial homeostasis
Song Ding, Guorui Li, Tinglv Fu, Tianyu Zhang, Xiao Lu, Ning Li, Qing Geng
Cellular Signalling.2024; 117: 111099. CrossRef - Reduced sphingolipid biosynthesis modulates proteostasis networks to enhance longevity
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Eric Blalock, Sangderk Lee, Kimberly M. Bretland, Jason A. MacGurn, Robert C. Dickson
Aging.2023; 15(2): 472. CrossRef - Protective effect of natural products in the metabolic-associated kidney diseases via regulating mitochondrial dysfunction
Peng Liu, Yao Chen, Jing Xiao, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Ming Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - BCAA insufficiency leads to premature ovarian insufficiency via ceramide‐induced elevation of ROS
Xiao Guo, Yuemeng Zhu, Lu Guo, Yiwen Qi, Xiaocheng Liu, Jinhui Wang, Jiangtao Zhang, Linlin Cui, Yueyang Shi, Qichu Wang, Cenxi Liu, Guangxing Lu, Yilian Liu, Tao Li, Shangyu Hong, Yingying Qin, Xuelian Xiong, Hao Wu, Lin Huang, He Huang, Chao Gu, Bin Li,
EMBO Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chinese herbal medicine and its active compounds in attenuating renal injury via regulating autophagy in diabetic kidney disease
Peng Liu, Wenhui Zhu, Yang Wang, Guijie Ma, Hailing Zhao, Ping Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated gas chromatography‐mass spectrometry and ultra‐high‐performance liquid chromatography‐mass spectrometry renal metabolomics and lipidomics deciphered the metabolic regulation mechanism of Gushudan on kidney‐yang‐deficiency‐syndrome rats
Qing Lu, Jing Zhang, Ling Xin, Yanwei Lou, Feng Qin, Longshan Zhao, Zhili Xiong
Journal of Separation Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in the pharmacological study of Chinese herbal medicine to alleviate diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial oxidative stress
Ming Chen, Yao Chen, Wenhui Zhu, Xiaoming Yan, Jing Xiao, Peiqing Zhang, Peng Liu, Ping Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115088. CrossRef - Rodent models to study type 1 and type 2 diabetes induced human diabetic nephropathy
Amit Talukdar, Mandira Basumatary
Molecular Biology Reports.2023; 50(9): 7759. CrossRef - Art2 mediates selective endocytosis of methionine transporters during adaptation to sphingolipid depletion
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Bradley Moon, Adam C. Ebert, Robert C. Dickson, Jason A. MacGurn
Journal of Cell Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2023; 19(10): 629. CrossRef - Research progress of autophagy in pathogenesis of diabetes nephropathy
Shengnan Zeng, Ying Li
Diabetic Nephropathy.2023; 3(3): 51. CrossRef - Lipidomic approaches to dissect dysregulated lipid metabolism in kidney disease
Judy Baek, Chenchen He, Farsad Afshinnia, George Michailidis, Subramaniam Pennathur
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2022; 18(1): 38. CrossRef - Podocyte Bioenergetics in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy: The Role of Mitochondria
Irena Audzeyenka, Agnieszka Bierżyńska, Abigail C Lay
Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Acylcarnitines: Can They Be Biomarkers of Diabetic Nephropathy?
Xiaodie Mu, Min Yang, Peiyao Ling, Aihua Wu, Hua Zhou, Jingting Jiang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 247. CrossRef - Research Progress on Natural Products’ Therapeutic Effects on Atrial Fibrillation by Regulating Ion Channels
Jinshan He, Sicong Li, Yumeng Ding, Yujia Tong, Xuebin Li, Simona Saponara
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Mechanisms of podocyte injury and implications for diabetic nephropathy
Federica Barutta, Stefania Bellini, Gabriella Gruden
Clinical Science.2022; 136(7): 493. CrossRef - A Rheostat of Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as a Determinant of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Kidney Injury
Norishi Ueda
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 4010. CrossRef - Implications of Sphingolipid Metabolites in Kidney Diseases
Shamroop kumar Mallela, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4244. CrossRef - Role of ceramides in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications
Nawajes Mandal, Richard Grambergs, Koushik Mondal, Sandip K. Basu, Faiza Tahia, Sam Dagogo-Jack
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(2): 107734. CrossRef - Rotten to the Cortex: Ceramide-Mediated Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Rebekah J. Nicholson, Marcus G. Pezzolesi, Scott A. Summers
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing lifespan of budding yeast by pharmacological lowering of amino acid pools
Nathaniel L. Hepowit, Jessica K. A. Macedo, Lyndsay E. A. Young, Ke Liu, Ramon C. Sun, Jason A. MacGurn, Robert C. Dickson
Aging.2021; 13(6): 7846. CrossRef - New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease
Alla Mitrofanova, George Burke, Sandra Merscher, Alessia Fornoni
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(5): 524. CrossRef - Excessively Enlarged Mitochondria in the Kidneys of Diabetic Nephropathy
Kiyoung Kim, Eun-Young Lee
Antioxidants.2021; 10(5): 741. CrossRef - Mechanistic insights into the role of serum-glucocorticoid kinase 1 in diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review
Saba Noor, Taj Mohammad, Gulam M. Ashraf, Joviana Farhat, Anwar L. Bilgrami, Mathew Suji Eapen, Sukhwinder Singh Sohal, Dharmendra Kumar Yadav, Md Imtaiyaz Hassan
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2021; 193: 562. CrossRef - The Updates of Podocyte Lipid Metabolism in Proteinuric Kidney Disease
Yu Sun, Sijia Cui, Yunfeng Hou, Fan Yi
Kidney Diseases.2021; 7(6): 438. CrossRef - Saturated fatty acids induce insulin resistance in podocytes through inhibition of IRS1 via activation of both IKKβ and mTORC1
Benoit Denhez, Marina Rousseau, Crysta Spino, David-Alexandre Dancosst, Marie-Ève Dumas, Andréanne Guay, Farah Lizotte, Pedro Geraldes
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Interplay of lipid metabolism and inflammation in podocyte injury
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
-
- Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):592-601. Published online April 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0104
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2020;44(5):783

- 6,635 View
- 142 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Recent studies suggest an association between diabetes and increased risk of heart failure (HF). However, the associations among obesity status, glycemic status, and risk of HF are not known. In this study, we analyzed whether the risk of HF increases in participants according to baseline glycemic status and whether this increased risk is associated with obesity status.
Methods We analyzed the risk of HF according to baseline glycemic status (normoglycemia, impaired fasting glucose [IFG], and diabetes) in 9,720,220 Koreans who underwent Korean National Health Screening in 2009 without HF at baseline with a median follow-up period of 6.3 years. The participants were divided into five and six groups according to baseline body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference, respectively.
Results Participants with IFG and those with diabetes showed a 1.08- and 1.86-fold increased risk of HF, respectively, compared to normoglycemic participants. Compared to the normal weight group (BMI, 18.5 to 22.9 kg/m2), the underweight group (BMI <18.5 kg/m2) showed a 1.7-fold increased risk of HF, and those with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 showed a 1.1-fold increased risk of HF, suggesting a J-shaped association with BMI. When similar analyses were performed for different glycemic statuses, the J-shaped association between BMI and HF risk was consistently observed in both groups with and without diabetes.
Conclusion Participants with IFG and diabetes showed a significantly increased HF risk compared to normoglycemic participants. This increased risk of HF was mostly prominent in underweight and class II obese participants than in participants with normal weight.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Research on obesity using the National Health Information Database: recent trends
Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 35. CrossRef - Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential Impact of Obesity on the Risk of Diabetes Development in Two Age Groups: Analysis from the National Health Screening Program
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ga Eun Nam, Sang Hyun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 846. CrossRef - Characterization of the oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in metabolically healthy obese individuals
Hazhmat Ali
Al-Kufa University Journal for Biology.2023; 15(3): 28. CrossRef - The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Changes in Patterns of Physical Activity and Risk of Heart Failure in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 327. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - Impact of hypoglycemia at the time of hospitalization for heart failure from emergency department on major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with and without type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Gee-Hee Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin resistance and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Pathogenetic and therapeutic crossroads
O. V. Tsygankova, N. E. Evdokimova, V. V. Veretyuk, L. D. Latyntseva, A. S. Ametov
Diabetes mellitus.2022; 25(6): 535. CrossRef - The association between metabolic syndrome and heart failure in middle-aged male and female: Korean population-based study of 2 million individuals
Tae-Eun Kim, Hyeongsu Kim, JiDong Sung, Duk-Kyung Kim, Myoung-Soon Lee, Seong Woo Han, Hyun-Joong Kim, Sung Hea Kim, Kyu-Hyung Ryu
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022078. CrossRef - Diabetes and Heart Failure
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(1): 12. CrossRef - Prediabetes and the risk of heart failure: A meta‐analysis
Xiaoyan Cai, Xiong Liu, Lichang Sun, Yiting He, Sulin Zheng, Yang Zhang, Yuli Huang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(8): 1746. CrossRef - Diabetes and Heart Failure
Eun-Jung Rhee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(2): 21. CrossRef - Effects of Lipid Overload on Heart in Metabolic
Diseases
An Yan, Guinan Xie, Xinya Ding, Yi Wang, Liping Guo
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2021; 53(12): 771. CrossRef - Obesity Degree and Glycemic Status: Factors That Should Be Considered in Heart Failure
Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 529. CrossRef - Letter: Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:592-601)
Darae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 777. CrossRef - Response: Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:592-601)
Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 781. CrossRef
- Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
- Covid-19
-
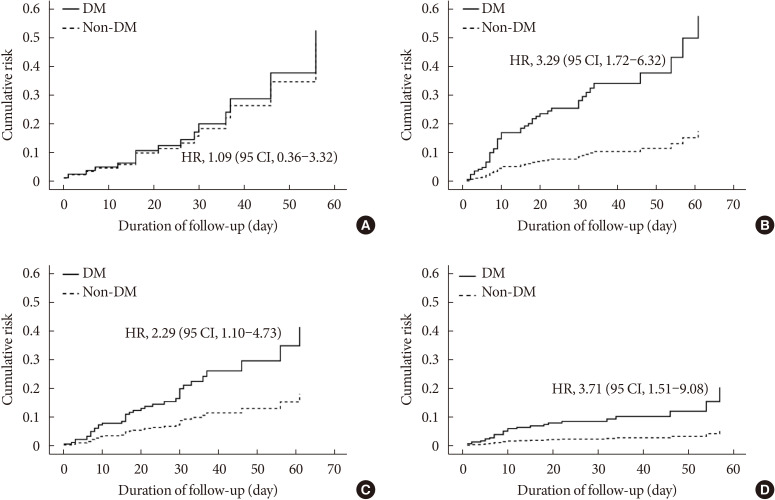
- The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea
- Mi Kyung Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung-Woo Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Nan Hee Cho, Eugene Han, Ji Hong You, Ji Yeon Lee, Miri Hyun, Jae Seok Park, Yong Shik Kwon, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Ki Tae Kwon, Shin Yup Lee, Eon Ju Jeon, Jin-Woo Kim, Hyo-Lim Hong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Chi Young Jung, Yin Young Lee, Eunyeoung Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jian Hur, June Hong Ahn, Na-young Kim, Shin-Woo Kim, Hyun Ha Chang, Yong Hoon Lee, Jaehee Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Hyun Ah Kim, Ji-Hyun Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):602-613. Published online August 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
- 13,299 View
- 206 Download
- 67 Web of Science
- 74 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global pandemic that had affected more than eight million people worldwide by June 2020. Given the importance of the presence of diabetes mellitus (DM) for host immunity, we retrospectively evaluated the clinical characteristics and outcomes of moderate-to-severe COVID-19 in patients with diabetes.
Methods We conducted a multi-center observational study of 1,082 adult inpatients (aged ≥18 years) who were admitted to one of five university hospitals in Daegu because of the severity of their COVID-19-related disease. The demographic, laboratory, and radiologic findings, and the mortality, prevalence of severe disease, and duration of quarantine were compared between patients with and without DM. In addition, 1:1 propensity score (PS)-matching was conducted with the DM group.
Results Compared with the non-DM group (
n =847), patients with DM (n =235) were older, exhibited higher mortality, and required more intensive care. Even after PS-matching, patients with DM exhibited more severe disease, and DM remained a prognostic factor for higher mortality (hazard ratio, 2.40; 95% confidence interval, 1.38 to 4.15). Subgroup analysis revealed that the presence of DM was associated with higher mortality, especially in older people (≥70 years old). Prior use of a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor or a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor did not affect mortality or the clinical severity of the disease.Conclusion DM is a significant risk factor for COVID-19 severity and mortality. Our findings imply that COVID-19 patients with DM, especially if elderly, require special attention and prompt intensive care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Potential use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors during acute illness: a systematic review based on COVID-19
Carmen Tisch, Eleni Xourgia, Aristomenis Exadaktylos, Mairi Ziaka
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin and Metformin Administration: Unravelling the Multifaceted Association with Mortality across Various Clinical Settings Considering Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
Łukasz Lewandowski, Agnieszka Bronowicka-Szydełko, Maciej Rabczyński, Dorota Bednarska-Chabowska, Joanna Adamiec-Mroczek, Adrian Doroszko, Małgorzata Trocha, Krzysztof Kujawa, Agnieszka Matera-Witkiewicz, Edwin Kuźnik, Paweł Lubieniecki, Marcin Madziarski
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 605. CrossRef - Pre-admission use of sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT-2i) may significantly improves Covid-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Hikmat Permana, Theo Audi Yanto, Timotius Ivan Hariyanto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 195: 110205. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study
A. V. Alieva, A. A. Djalilov, F. A. Khaydarova, A. V. Alimov, D. Z. Khalilova, V. A. Talenova, N. U. Alimova, M. D. Aripova, A. S. Sadikova
Obesity and metabolism.2023; 20(2): 92. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Epidemiological features and consequences of COVID‐19 in patients with and without gastrointestinal symptoms in southwestern Iran. A retrospective observational study
Habibollah Azarbakhsh, Leila Moftakhar, Aliasghar Valipour, Alireza Mirahmadizadeh, Hekmat Allah Moradi, Elahe Piraee
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Long-Term Conditions and Comorbidity Patterns on COVID-19 Infection and Hospitalisation: A Cohort Study
Yun-Ting Huang, Andrew Steptoe, Riyaz S. Patel, Esme Fuller Thomson, Dorina Cadar
Gerontology.2023; 69(10): 1200. CrossRef - Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tiantian Han, Shaodi Ma, Chenyu Sun, Huimei Zhang, Guangbo Qu, Yue Chen, Ce Cheng, Eric L. Chen, Mubashir Ayaz Ahmed, Keun Young Kim, Raveena Manem, Mengshi Chen, Zhichun Guo, Hongru Yang, Yue Yan, Qin Zhou
Archives of Medical Research.2022; 53(2): 186. CrossRef - Use of DPP4i reduced odds of clinical deterioration and hyperinflammatory syndrome in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: Propensity score analysis of a territory-wide cohort in Hong Kong
Carlos K.H. Wong, David T.W. Lui, Angel Y.C. Lui, Ashley C.Y. Kwok, Marshall C.H. Low, Kristy T.K. Lau, Ivan C.H. Au, Xi Xiong, Matthew S.H. Chung, Eric H.Y. Lau, Benjamin J. Cowling
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(1): 101307. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-IV) inhibitor was associated with mortality reduction in COVID-19 — A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ahmad Fariz Malvi Zamzam Zein, Wilson Matthew Raffaello
Primary Care Diabetes.2022; 16(1): 162. CrossRef - Prevalence and impact of diabetes in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sian A. Bradley, Maciej Banach, Negman Alvarado, Ivica Smokovski, Sonu M. M. Bhaskar
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(2): 144. CrossRef - Interplay between Inflammaging, Frailty and Nutrition in Covid-19: Preventive and Adjuvant Treatment Perspectives
A. Padilha de Lima, M. Macedo Rogero, T. Araujo Viel, H.M. Garay-Malpartida, I. Aprahamian, Sandra Maria Lima Ribeiro
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2022; 26(1): 67. CrossRef - Increase in blood glucose level and incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus in the Daegu-Gyeongbuk area during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Mi Seon Lee, Rosie Lee, Cheol Woo Ko, Jung Eun Moon
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2022; 39(1): 46. CrossRef - Interrelationship between 2019-nCov receptor DPP4 and diabetes mellitus targets based on protein interaction network
Qian Gao, Wenjun Zhang, Tingting Li, Guojun Yang, Wei Zhu, Naijun Chen, Huawei Jin
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Can sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor reduce the risk of adverse complications due to COVID-19? – Targeting hyperinflammation
Afnan Alshnbari, Iskandar Idris
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2022; 38(3): 357. CrossRef - Commentary: Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Li-Min Zhao, Xie-Hui Chen, Mei Qiu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetes
Awadhesh Kumar Singh, Kamlesh Khunti
Annual Review of Medicine.2022; 73(1): 129. CrossRef - The enzymes in COVID-19: A review
Maria Helena Menezes Estevam Alves, Layla Carvalho Mahnke, Tifany Cerqueira Macedo, Thais Ketinly dos Santos Silva, Luiz Bezerra Carvalho Junior
Biochimie.2022; 197: 38. CrossRef - IMPACT OF ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS ON RISK AND OUTCOME OF COVID-19 INFECTION: A REVIEW
Adnan A. Zainal, Marwan M. Merkhan
Military Medical Science Letters.2022; 91(2): 140. CrossRef - Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Adithan Ganesh, Michael D. Randall
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 88(6): 2642. CrossRef - Diabetes, Metformin and the Clinical Course of Covid-19: Outcomes, Mechanisms and Suggestions on the Therapeutic Use of Metformin
Clifford J. Bailey, Mike Gwilt
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia on COVID-19 Infection Course—A Narrative Review
Evangelia Tzeravini, Eleftherios Stratigakos, Chris Siafarikas, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
Nam Nhat Nguyen, Dung Si Ho, Hung Song Nguyen, Dang Khanh Ngan Ho, Hung-Yuan Li, Chia-Yuan Lin, Hsiao-Yean Chiu, Yang-Ching Chen
Metabolism.2022; 131: 155196. CrossRef - Glucose-Lowering Agents and COVID-19
Ah Reum Khang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes on COVID‐19 mortality and hospital outcomes from a global perspective: An umbrella systematic review and meta‐analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Yidan Chen, Xingfei Lv, Sang Lin, Mohammad Arshad, Mengjun Dai
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis Revealing Critical Bias Across a Body of Observational Research
Jordan Loader, Frances C. Taylor, Erik Lampa, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2–Is There a Mutual Connection?
Anna P. Jedrzejak, Edyta K. Urbaniak, Jadwiga A. Wasko, Natalia Ziojla, Malgorzata Borowiak
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of age, sex and prothrombin time related to the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta analysis
Audrey Fabianisa Mirza, Ceria Halim, Mutiara Indah Sari
F1000Research.2022; 11: 729. CrossRef - Are lipid ratios and triglyceride-glucose index associated with critical care outcomes in COVID-19 patients?
Marzieh Rohani-Rasaf, Kosar Mirjalili, Akram Vatannejad, Maryam Teimouri, Xiao-Feng Yang
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0272000. CrossRef - Early glycaemic variability increases 28-day mortality and prolongs intensive care unit stay in critically ill patients with pneumonia
Seong Ho Kim, Ji Young Kim, Eun Song Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Annals of Medicine.2022; 54(1): 2724. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in COVID-19: Beyond glycemic control
Niya Narayanan, Dukhabandhu Naik, Jayaprakash Sahoo, Sadishkumar Kamalanathan
World Journal of Virology.2022; 11(6): 399. CrossRef - Prevalencia de secuelas en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 sobrevivientes al COVID-19
Gianela M. Cancino-Castillo, Miguel A. Tresierra-Ayala, Jorge L. Campos-Reyna, Jaime Rosales-Rimache
REVISTA MÉDICA VALLEJIANA/ Vallejian Medical Journal.2022; 11(2): 48. CrossRef - Predictors of adverse in-hospital outcome and recovery in patients with diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 pneumonia in Iraq
Hussein Nafakhi, Mohammed Alareedh, Karrar Al-Buthabhak, Foaad Shaghee, Ahmed Nafakhi, Samet Kasim
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(1): 33. CrossRef - Non-insulin anti-diabetic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A Critical Appraisal of Literature
Awadhesh Kumar Singh, Ritu Singh, Banshi Saboo, Anoop Misra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(1): 159. CrossRef - COVID-19 associated with diabetes and other noncommunicable diseases led to a global health crisis
Mark Thomaz Ugliara Barone, Belinda Ngongo, Simone Bega Harnik, Lucas Xavier de Oliveira, Dániel Végh, Patrícia Vieira de Luca, Hermelinda Cordeiro Pedrosa, Franco Giraudo, Roque Cardona-Hernandez, Nayanjeet Chaudhury, Luiz Menna-Barreto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108587. CrossRef - A meta-analysis on the preadmission use of DPP-4 inhibitors and risk of a fatal or severe course of illness in patients with COVID-19
Chia Siang Kow, Syed Shahzad Hasan
Therapies.2021; 76(4): 361. CrossRef - Disentangling conflicting evidence on DPP-4 inhibitors and outcomes of COVID-19: narrative review and meta-analysis
B. M. Bonora, A. Avogaro, G. P. Fadini
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(7): 1379. CrossRef - Prognostic bioindicators in severe COVID-19 patients
L. Bergantini, E. Bargagli, M. d'Alessandro, R.M. Refini, P. Cameli, L. Galasso, C. Scapellato, F. Montagnani, S. Scolletta, F. Franchi, S. Valente, D. Bennett, G. Sebastiani, B. Frediani, F. Dotta
Cytokine.2021; 141: 155455. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in diabetic versus non-diabetic patients
Leila Moftakhar, Parisa Moftakhar, Elahe Piraee, Haleh Ghaem, Aliasghar Valipour, Habibollah Azarbakhsh
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(3): 383. CrossRef - DPP-4 inhibition and COVID-19: From initial concerns to recent expectations
André J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(2): 101213. CrossRef - Use of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors and prognosis of COVID‐19 in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: A propensity score analysis from the CORONADO study
Ronan Roussel, Patrice Darmon, Matthieu Pichelin, Thomas Goronflot, Yawa Abouleka, Leila Ait Bachir, Ingrid Allix, Deborah Ancelle, Sara Barraud, Lyse Bordier, Aurélie Carlier, Nicolas Chevalier, Christine Coffin‐Boutreux, Emmanuel Cosson, Anne Dorange, O
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(5): 1162. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Rimesh Pal, Mainak Banerjee, Soham Mukherjee, Ranjitpal Singh Bhogal, Amanpreet Kaur, Sanjay K. Bhadada
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882199648. CrossRef - Renin–angiotensin-system inhibitors and all-cause mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Chirag Bavishi, Paul K. Whelton, Giuseppe Mancia, Giovanni Corrao, Franz H. Messerli
Journal of Hypertension.2021; 39(4): 784. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Current Therapeutic Approaches for COVID-19: A Systematic Review and a Meta-analysis
Zeinab Abdelrahman, Qian Liu, Shanmei Jiang, Mengyuan Li, Qingrong Sun, Yue Zhang, Xiaosheng Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor and outcome from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in diabetic patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Timotius Ivan Hariyanto, Andree Kurniawan
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(1): 543. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes mellitus on in-hospital mortality in adult patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Halla Kaminska, Lukasz Szarpak, Dariusz Kosior, Wojciech Wieczorek, Agnieszka Szarpak, Mahdi Al-Jeabory, Wladyslaw Gawel, Aleksandra Gasecka, Milosz J. Jaguszewski, Przemyslawa Jarosz-Chobot
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(8): 1101. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) – A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Iis Inayati Rakhmat, Yudith Yunia Kusmala, Dewi Ratih Handayani, Henny Juliastuti, Eka Noneng Nawangsih, Arief Wibowo, Michael Anthonius Lim, Raymond Pranata
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(3): 777. CrossRef - Post-infection depressive, anxiety and post-traumatic stress symptoms: A prospective cohort study in patients with mild COVID-19
Flavia Ismael, João C.S. Bizario, Tatiane Battagin, Beatriz Zaramella, Fabio E. Leal, Julio Torales, Antonio Ventriglio, Megan E. Marziali, Silvia S. Martins, João M. Castaldelli-Maia
Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry.2021; 111: 110341. CrossRef - Managing diabetes in diabetic patients with COVID: where do we start from?
Angelo Avogaro, Benedetta Bonora, Gian Paolo Fadini
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(11): 1441. CrossRef - Is diabetes mellitus a wrongdoer to COVID-19 severity?
Sanjib Sarkar, Dibyendu Das, Sawlang Borsingh Wann, Jatin Kalita, Prasenjit Manna
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108936. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor, an Update
Ju Hee Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(2): 91. CrossRef - Correlation Analysis Between Serum Uric Acid, Prealbumin Level, Lactate Dehydrogenase, and Severity of COVID-19
Zhenmu Jin, Mo Zheng, Jichan Shi, Xinchun Ye, Fang Cheng, Que-Lu Chen, Jianping Huang, Xian-Gao Jiang
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Use and COVID-19 Outcomes
Anna R. Kahkoska, Trine Julie Abrahamsen, G. Caleb Alexander, Tellen D. Bennett, Christopher G. Chute, Melissa A. Haendel, Klara R. Klein, Hemalkumar Mehta, Joshua D. Miller, Richard A. Moffitt, Til Stürmer, Kajsa Kvist, John B. Buse, Tim Q. Duong
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(7): 1564. CrossRef - The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus
Wenxing Yang, Xuehong Sun, Jun Zhang, Kui Zhang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108977. CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Primary Prevention and COVID‐19
Jordan Loader, Erik Lampa, Stefan Gustafsson, Thomas Cars, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing on development of COVID-19 pneumonia and association with oral anti-diabetic drugs in hospitalized patients with diabetes mellitus
Ayça Elibol, Didem Eren, Macide Deniz Erdoğan, Merve Elmaağaç, Oguzhan Sıtkı Dizdar, İlhami Çelik, Ali İhsan Günal
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(5): 806. CrossRef - Aging & COVID-19 susceptibility, disease severity, and clinical outcomes: The role of entangled risk factors
Melina Farshbafnadi, Sara Kamali Zonouzi, Mohammadmahdi Sabahi, Mahsa Dolatshahi, Mohammad Hadi Aarabi
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 154: 111507. CrossRef - Classical and Counter-Regulatory Renin–Angiotensin System: Potential Key Roles in COVID-19 Pathophysiology
Moudhi Almutlaq, Abir Abdullah Alamro, Fayhan Alroqi, Tlili Barhoumi
CJC Open.2021; 3(8): 1060. CrossRef - Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yin Li, Xue Yang, Peijing Yan, Tong Sun, Zhi Zeng, Sheyu Li
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pre-existing health conditions and severe COVID-19 outcomes: an umbrella review approach and meta-analysis of global evidence
Marina Treskova-Schwarzbach, Laura Haas, Sarah Reda, Antonia Pilic, Anna Borodova, Kasra Karimi, Judith Koch, Teresa Nygren, Stefan Scholz, Viktoria Schönfeld, Sabine Vygen-Bonnet, Ole Wichmann, Thomas Harder
BMC Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - High Fibrosis-4 Index Is Related with Worse Clinical Outcome in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes Mellitus: A Multicenter Observational Study
Sung-Woo Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Jun Sung Moon, Mi Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 800. CrossRef - Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Chengxia Kan, Yang Zhang, Fang Han, Qian Xu, Tongtong Ye, Ningning Hou, Xiaodong Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of influence of background therapy for comorbidities in the period before infection on the risk of the lethal COVID outcome. Data from the international ACTIV SARS-CoV-2 registry («Analysis of chronic non-infectious diseases dynamics after COVID-
E. I. Tarlovskaya, A. G. Arutyunov, A. O. Konradi, Yu. M. Lopatin, A. P. Rebrov, S. N. Tereshchenko, A. I. Chesnikova, H. G. Hayrapetyan, A. P. Babin, I. G. Bakulin, N. V. Bakulina, L. A. Balykova, A. S. Blagonravova, M. V. Boldina, A. R. Vaisberg, A. S.
Kardiologiia.2021; 61(9): 20. CrossRef - Association of clinical characteristics, antidiabetic and cardiovascular agents with diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: a 7-month follow-up cohort study
Marzieh Pazoki, Fatemeh Chichagi, Azar Hadadi, Samira Kafan, Mahnaz Montazeri, Sina Kazemian, Arya Aminorroaya, Mehdi Ebrahimi, Haleh Ashraf, Mojgan Mirabdolhagh Hazaveh, Mohammad Reza Khajavi, Reza Shariat Moharari, Seyed Hamidreza Sharifnia, Shahrokh Ka
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1545. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetes: A Comprehensive Review of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2, Mutual Effects and Pharmacotherapy
Lingli Xie, Ziying Zhang, Qian Wang, Yangwen Chen, Dexue Lu, Weihua Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Diabetes on COVID-19 Mortality and Hospital Outcomes, a Global Perspective: An ONTOP Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Decision Trees: Predictions of Global Vulnerability to Coronavirus Outbreaks
Moacir José da Silva
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The potential association between common comorbidities and severity and mortality of coronavirus disease 2019: A pooled analysis
Liman Luo, Menglu Fu, Yuanyuan Li, Shuiqing Hu, Jinlan Luo, Zhihui Chen, Jing Yu, Wenhua Li, Ruolan Dong, Yan Yang, Ling Tu, Xizhen Xu
Clinical Cardiology.2020; 43(12): 1478. CrossRef - The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Antonia Anna Lukito, Raymond Pranata, Joshua Henrina, Michael Anthonius Lim, Sherly Lawrensia, Ketut Suastika
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(6): 2177. CrossRef - Risk Factors on the Progression to Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients in South Korea: Using National Data
Seon-Rye Kim, Seoul-Hee Nam, Yu-Rin Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 8847. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 901. CrossRef
- Potential use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors during acute illness: a systematic review based on COVID-19
- Complications
- Short-Term Walking Outcomes in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Unilateral Transtibial Amputees
- Dong Gyu Kwak, Jeong-Yong Hur, Jun Sung Moon, Min Cheol Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):614-618. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0080
- 4,156 View
- 85 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub This study compared short-term walking outcomes in diabetic amputees after prosthesis fitting compared to that in non-diabetic amputees. We retrospectively investigated walking outcomes at 3 months after starting gait training with a prosthesis. Forty-four unilateral transtibial amputees with (
n =18) and without diabetes (n =26) were included. At 3 months after gait training with a prosthesis, only 2/18 (11.1%) and 3/18 (16.7%) diabetic amputees were capable of independent outdoor and indoor walking without cane, respectively. However, 21/26 (80.8%) and 24/26 (92.3%) non-diabetic amputees were capable of independent outdoor and indoor walking without cane, respectively. With assistance of cane, most of non-diabetic amputees (n =24, 92.3%) were capable of walking in both outdoor and indoor but only seven (38.9%) and nine (50.0%) diabetic amputees were capable, respectively. Thus, short-term walking outcome were poor in transtibial amputee with diabetes compare to those without diabetes, and these results suggest intensive rehabilitation would be needed to them.
- Letter: Association between Cigarette Smoking and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in 78,212 Koreans Using Self-Reported Questionnaire and Urine Cotinine (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:426–35) - Bo-Yeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):619-620. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0147
- 3,886 View
- 47 Download
- Letter: The Risk of Diabetes on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Cohort Study (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:405–13) - So-Yeon Kim, Kyung-Soo Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):621-622. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0151
- 4,914 View
- 55 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evolution of a Cohort of COVID-19 Infection Suspects Followed-Up from Primary Health Care
Valle Coronado-Vázquez, Maria del Valle Ramírez-Durán, Juan Gómez-Salgado, María Silvia Dorado-Rabaneda, Elena Benito-Alonso, Marina Holgado-Juan, Cristina Bronchalo-González
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(6): 459. CrossRef
- Evolution of a Cohort of COVID-19 Infection Suspects Followed-Up from Primary Health Care
- Response: Association between Cigarette Smoking and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in 78,212 Koreans Using Self-Reported Questionnaire and Urine Cotinine (
Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:426–35) - Ji Hye Kim, Byung Jin Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):623-624. Published online August 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0169
- [Original]
- 4,191 View
- 67 Download

 KDA
KDA


 First
First Prev
Prev





